Abstract
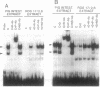
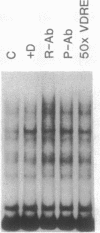
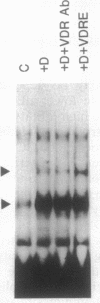
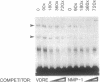
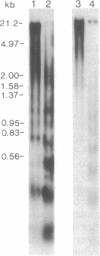
The observation that vitamin D-mediated enhancement of osteocalcin (OC) gene expression is dependent on and reciprocally related to the level of basal gene expression suggests that an interaction of the vitamin D responsive element (VDRE) with basal regulatory elements of the OC gene promoter contributes to both basal and vitamin D-enhanced transcription. Protein-DNA interactions at the VDRE of the rat OC gene (nucleotides -466 to -437) are reflected by direct sequence-specific and antibody-sensitive binding of the endogenous vitamin D receptor present in ROS 17/2.8 osteosarcoma nuclear protein extracts. In addition, a vitamin D-responsive increase in OC gene transcription is accompanied by enhanced non-vitamin D receptor-mediated protein-DNA interactions in the "TATA" box region (nucleotides -44 to +23), which also contains a potential glucocorticoid responsive element. Evidence for proximity of the VDRE with the basal regulatory elements is provided by two features of nuclear architecture. (i) Nuclear matrix attachment elements in the rat OC gene promoter that bind nuclear matrix proteins with sequence specificity may impose structural constraints on promoter conformation. (ii) Limited micrococcal nuclease digestion and Southern blot analysis indicate that three nucleosomes can be accommodated in the sequence spanning the OC gene VDRE, the OC/CCAAT box (nucleotides -99 to -76), and the TATA/glucocorticoid responsive element, and thereby the potential distance between the VDRE and the basal regulatory elements can be reduced. A model is presented for the contribution of both the VDRE and proximal promoter elements to the enhancement of OC gene transcription in response to vitamin D. The vitamin D receptor plus accessory proteins may function cooperatively with basal regulatory factors to modulate the extent to which the OC gene is transcribed.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aronow M. A., Gerstenfeld L. C., Owen T. A., Tassinari M. S., Stein G. S., Lian J. B. Factors that promote progressive development of the osteoblast phenotype in cultured fetal rat calvaria cells. J Cell Physiol. 1990 May;143(2):213–221. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041430203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown T. A., DeLuca H. F. Phosphorylation of the 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 receptor. A primary event in 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 action. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 15;265(17):10025–10029. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dame M. C., Pierce E. A., Prahl J. M., Hayes C. E., DeLuca H. F. Monoclonal antibodies to the porcine intestinal receptor for 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3: interaction with distinct receptor domains. Biochemistry. 1986 Aug 12;25(16):4523–4534. doi: 10.1021/bi00364a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demay M. B., Gerardi J. M., DeLuca H. F., Kronenberg H. M. DNA sequences in the rat osteocalcin gene that bind the 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 receptor and confer responsiveness to 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(1):369–373. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.1.369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dworetzky S. I., Fey E. G., Penman S., Lian J. B., Stein J. L., Stein G. S. Progressive changes in the protein composition of the nuclear matrix during rat osteoblast differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4605–4609. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dworetzky S. I., Wright K. L., Fey E. G., Penman S., Lian J. B., Stein J. L., Stein G. S. Sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins are components of a nuclear matrix-attachment site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 1;89(9):4178–4182. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.9.4178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauschka P. V., Lian J. B., Cole D. E., Gundberg C. M. Osteocalcin and matrix Gla protein: vitamin K-dependent proteins in bone. Physiol Rev. 1989 Jul;69(3):990–1047. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1989.69.3.990. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh J. C., Jurutka P. W., Galligan M. A., Terpening C. M., Haussler C. A., Samuels D. S., Shimizu Y., Shimizu N., Haussler M. R. Human vitamin D receptor is selectively phosphorylated by protein kinase C on serine 51, a residue crucial to its trans-activation function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):9315–9319. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.9315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerner S. A., Scott R. A., Pike J. W. Sequence elements in the human osteocalcin gene confer basal activation and inducible response to hormonal vitamin D3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(12):4455–4459. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.12.4455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lian J., Stewart C., Puchacz E., Mackowiak S., Shalhoub V., Collart D., Zambetti G., Stein G. Structure of the rat osteocalcin gene and regulation of vitamin D-dependent expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(4):1143–1147. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.4.1143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao J., Ozono K., Sone T., McDonnell D. P., Pike J. W. Vitamin D receptor interaction with specific DNA requires a nuclear protein and 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9751–9755. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald P. N., Haussler C. A., Terpening C. M., Galligan M. A., Reeder M. C., Whitfield G. K., Haussler M. R. Baculovirus-mediated expression of the human vitamin D receptor. Functional characterization, vitamin D response element interactions, and evidence for a receptor auxiliary factor. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 5;266(28):18808–18813. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majeska R. J., Rodan S. B., Rodan G. A. Parathyroid hormone-responsive clonal cell lines from rat osteosarcoma. Endocrinology. 1980 Nov;107(5):1494–1503. doi: 10.1210/endo-107-5-1494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markose E. R., Stein J. L., Stein G. S., Lian J. B. Vitamin D-mediated modifications in protein-DNA interactions at two promoter elements of the osteocalcin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(5):1701–1705. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.5.1701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirkovitch J., Mirault M. E., Laemmli U. K. Organization of the higher-order chromatin loop: specific DNA attachment sites on nuclear scaffold. Cell. 1984 Nov;39(1):223–232. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90208-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno M. L., Chrysogelos S. A., Stein G. S., Stein J. L. Reversible changes in the nucleosomal organization of a human H4 histone gene during the cell cycle. Biochemistry. 1986 Sep 23;25(19):5364–5370. doi: 10.1021/bi00367a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison N. A., Shine J., Fragonas J. C., Verkest V., McMenemy M. L., Eisman J. A. 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D-responsive element and glucocorticoid repression in the osteocalcin gene. Science. 1989 Dec 1;246(4934):1158–1161. doi: 10.1126/science.2588000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Vogel R. L., Craig A. M., Prahl J., DeLuca H. F., Denhardt D. T. Identification of a DNA sequence responsible for binding of the 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 receptor and 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 enhancement of mouse secreted phosphoprotein 1 (SPP-1 or osteopontin) gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9995–9999. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen T. A., Aronow M. S., Barone L. M., Bettencourt B., Stein G. S., Lian J. B. Pleiotropic effects of vitamin D on osteoblast gene expression are related to the proliferative and differentiated state of the bone cell phenotype: dependency upon basal levels of gene expression, duration of exposure, and bone matrix competency in normal rat osteoblast cultures. Endocrinology. 1991 Mar;128(3):1496–1504. doi: 10.1210/endo-128-3-1496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen T. A., Aronow M., Shalhoub V., Barone L. M., Wilming L., Tassinari M. S., Kennedy M. B., Pockwinse S., Lian J. B., Stein G. S. Progressive development of the rat osteoblast phenotype in vitro: reciprocal relationships in expression of genes associated with osteoblast proliferation and differentiation during formation of the bone extracellular matrix. J Cell Physiol. 1990 Jun;143(3):420–430. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041430304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen T. A., Bortell R., Yocum S. A., Smock S. L., Zhang M., Abate C., Shalhoub V., Aronin N., Wright K. L., van Wijnen A. J. Coordinate occupancy of AP-1 sites in the vitamin D-responsive and CCAAT box elements by Fos-Jun in the osteocalcin gene: model for phenotype suppression of transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9990–9994. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozono K., Liao J., Kerner S. A., Scott R. A., Pike J. W. The vitamin D-responsive element in the human osteocalcin gene. Association with a nuclear proto-oncogene enhancer. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 15;265(35):21881–21888. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pienta K. J., Getzenberg R. H., Coffey D. S. Cell structure and DNA organization. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 1991;1(4):355–385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross T. K., Moss V. E., Prahl J. M., DeLuca H. F. A nuclear protein essential for binding of rat 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 receptor to its response elements. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 1;89(1):256–260. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.1.256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saltzman A. G., Weinmann R. Promoter specificity and modulation of RNA polymerase II transcription. FASEB J. 1989 Apr;3(6):1723–1733. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.3.6.2649403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schepmoes G., Breen E., Owen T. A., Aronow M. A., Stein G. S., Lian J. B. Influence of dexamethasone on the vitamin D-mediated regulation of osteocalcin gene expression. J Cell Biochem. 1991 Oct;47(2):184–196. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240470212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small D., Nelkin B., Vogelstein B. The association of transcribed genes with the nuclear matrix of Drosophila cells during heat shock. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Apr 11;13(7):2413–2431. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.7.2413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sone T., McDonnell D. P., O'Malley B. W., Pike J. W. Expression of human vitamin D receptor in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Purification, properties, and generation of polyclonal antibodies. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 15;265(35):21997–22003. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strömstedt P. E., Poellinger L., Gustafsson J. A., Carlstedt-Duke J. The glucocorticoid receptor binds to a sequence overlapping the TATA box of the human osteocalcin promoter: a potential mechanism for negative regulation. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;11(6):3379–3383. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.6.3379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terpening C. M., Haussler C. A., Jurutka P. W., Galligan M. A., Komm B. S., Haussler M. R. The vitamin D-responsive element in the rat bone Gla protein gene is an imperfect direct repeat that cooperates with other cis-elements in 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3- mediated transcriptional activation. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Mar;5(3):373–385. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-3-373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong M. M., Rao L. G., Ly H., Hamilton L., Tong J., Sturtridge W., McBroom R., Aubin J. E., Murray T. M. Long-term effects of physiologic concentrations of dexamethasone on human bone-derived cells. J Bone Miner Res. 1990 Aug;5(8):803–813. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.5650050803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]