Abstract
A new commercial test for the diagnosis of rotavirus gastroenteritis was assessed. With some modifications it compared favourably with electron microscopy and immunofluorescence.
Full text
PDF

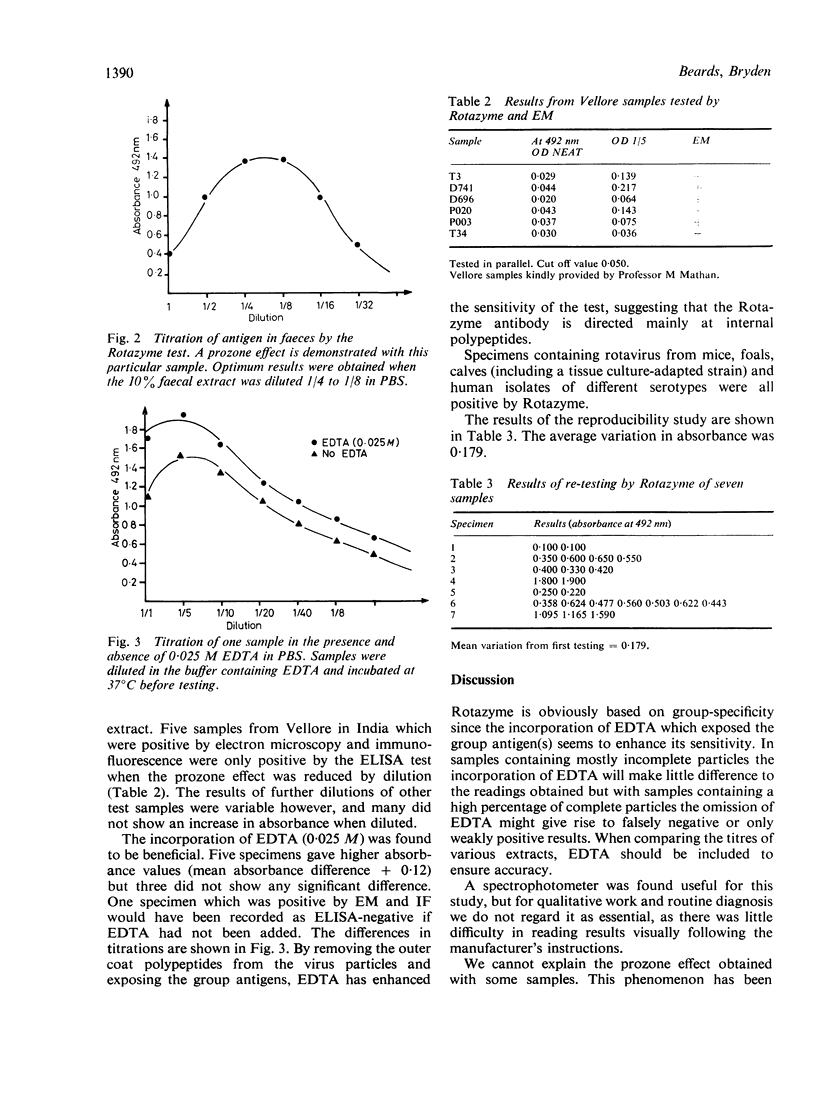

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beards G. M., Pilfold J. N., Thouless M. E., Flewett T. H. Rotavirus serotypes by serum neutralisation. J Med Virol. 1980;5(3):231–237. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890050307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bridger J. C. Location of type-specific antigens in calf rotaviruses. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Dec;8(6):625–628. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.6.625-628.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryden A. S., Davies H. A., Thouless M. E., Flewitt T. H. Diagnosis of rotavirus infection by cell culture. J Med Microbiol. 1977 Feb;10(1):121–125. doi: 10.1099/00222615-10-1-121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. Ribonucleic acid polymerase activity associated with purified calf rotavirus. J Gen Virol. 1977 Sep;36(3):395–402. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-36-3-395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flewett T. H., Bryden A. S., Davies H. Diagnostic electron microscopy of faeces. I. The viral flora of the faeces as seen by electron microscopy. J Clin Pathol. 1974 Aug;27(8):603–608. doi: 10.1136/jcp.27.8.603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- House J. A. Economic impact of rotavirus and other neonatal disease agents of animals. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1978 Sep 1;173(5 Pt 2):573–576. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalica A. R., Purcell R. H., Sereno M. M., Wyatt R. G., Kim H. W., Chanock R. M., Kapikian A. Z. A microtiter solid phase radioimmunoassay for detection of the human reovirus-like agent in stools. J Immunol. 1977 Apr;118(4):1275–1279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherrer R., Bernard S. Application d'une technique immunoenzymologique (ELISA) a la détection du rotavirus bovin et des anticorps dirigés contre lui. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1977 May-Jun;128A(4):499–510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirley J. A., Beards G. M., Thouless M. E., Flewett T. H. The influence of divalent cations on the stability of human rotavirus. Arch Virol. 1981;67(1):1–9. doi: 10.1007/BF01314596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spence L., Fauvel M., Bouchard S., Babiuk L., Saunders Letter: Test for reovirus-like agent. Lancet. 1975 Aug 16;2(7929):322–322. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)92752-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thouless M. E., Bryden A. S., Flewett T. H. Serotypes of human rotavirus. Lancet. 1978 Jan 7;1(8054):39–39. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)90381-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yolken R. H., Kim H. W., Clem T., Wyatt R. G., Kalica A. R., Chanock R. M., Kapikian A. Z. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for detection of human reovirus-like agent of infantile gastroenteritis. Lancet. 1977 Aug 6;2(8032):263–267. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)90951-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yolken R. H., Wyatt R. G., Zissis G., Brandt C. D., Rodriguez W. J., Kim H. W., Parrott R. H., Urrutia J. J., Mata L., Greenberg H. B. Epidemiology of human rotavirus Types 1 and 2 as studied by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. N Engl J Med. 1978 Nov 23;299(21):1156–1161. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197811232992103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zissis G., Lambert J. P. Different serotypes of human rotaviruses. Lancet. 1978 Jan 7;1(8054):38–39. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)90380-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]