Abstract
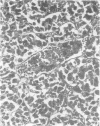
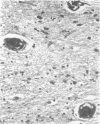
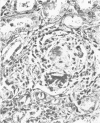
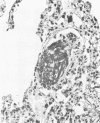
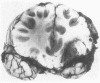
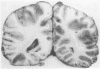
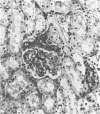
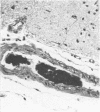
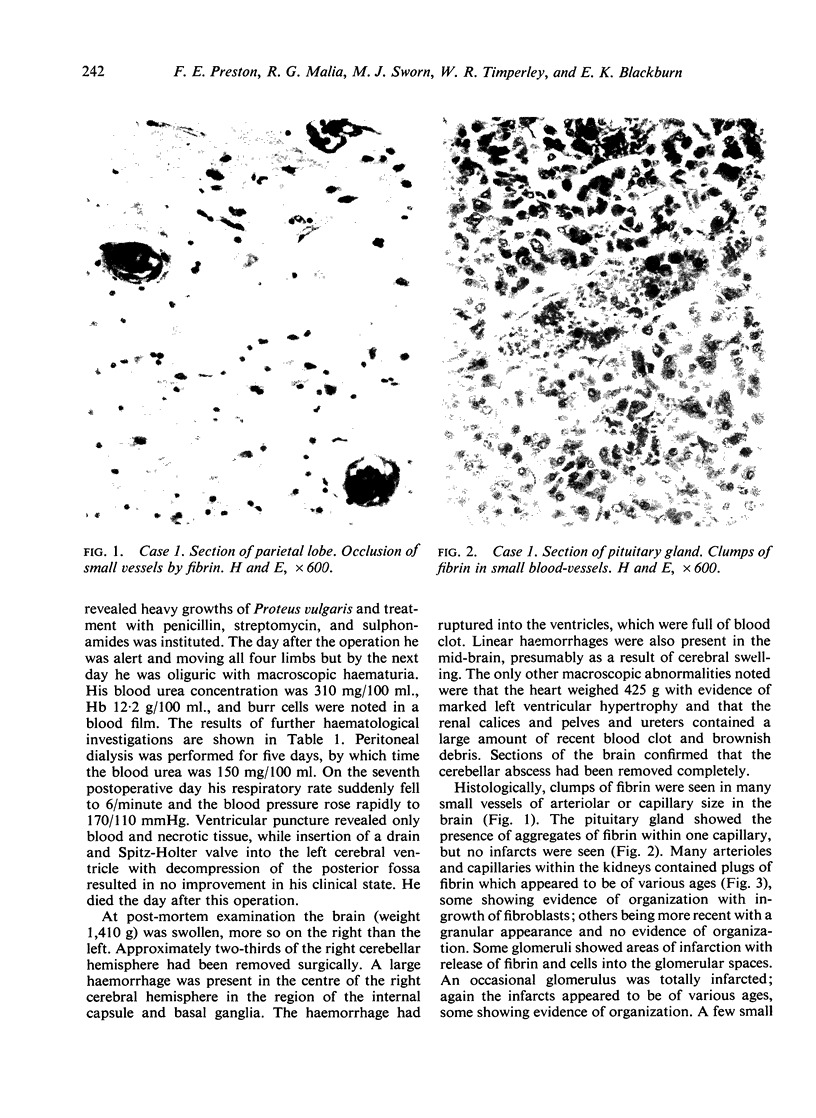
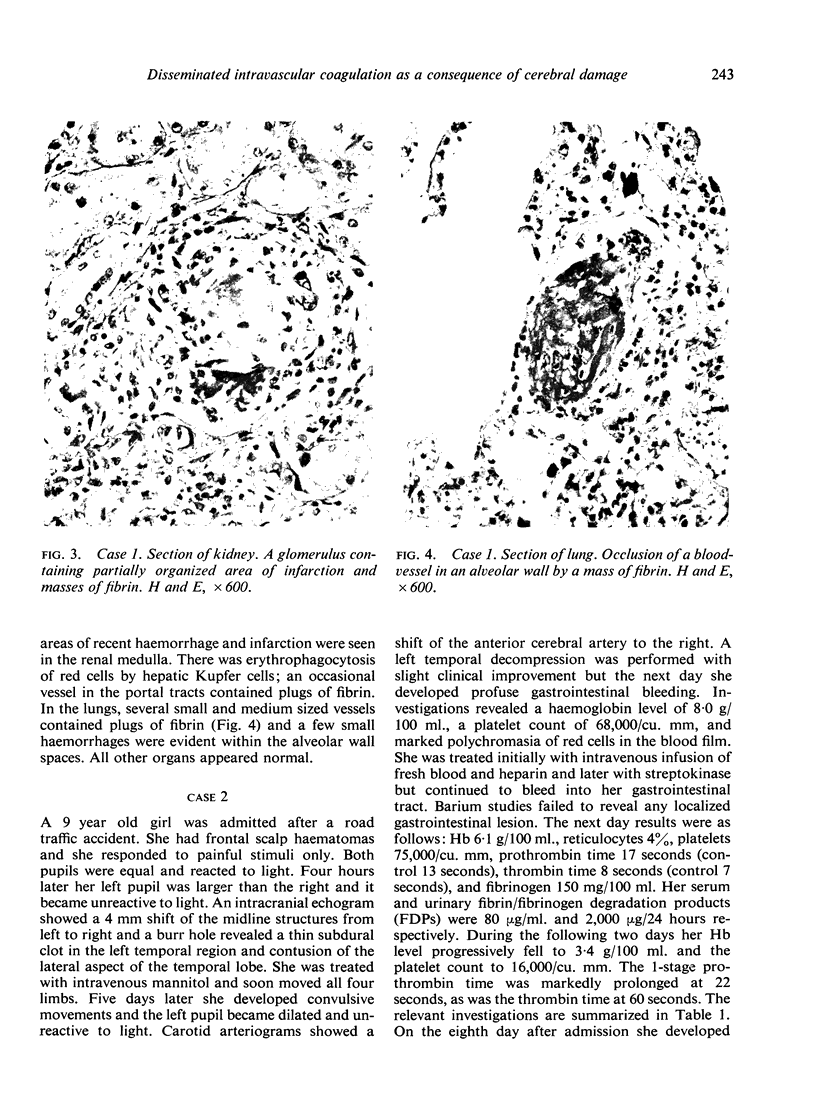
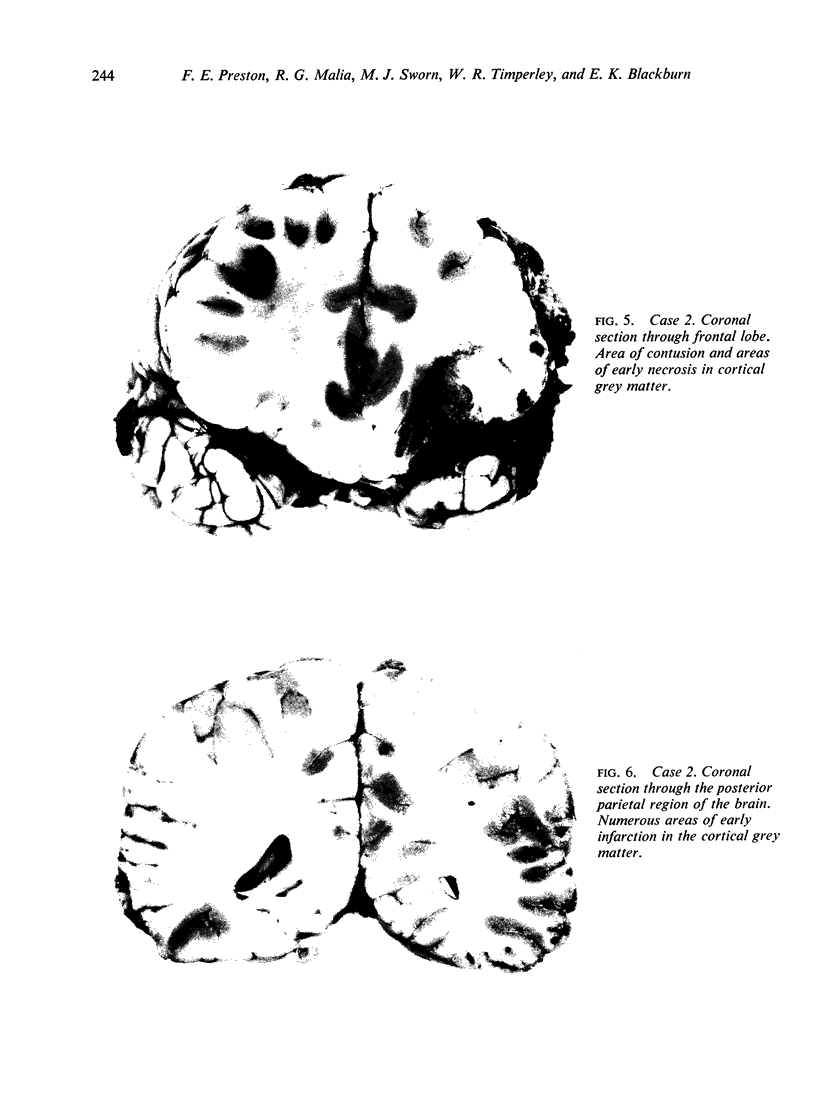
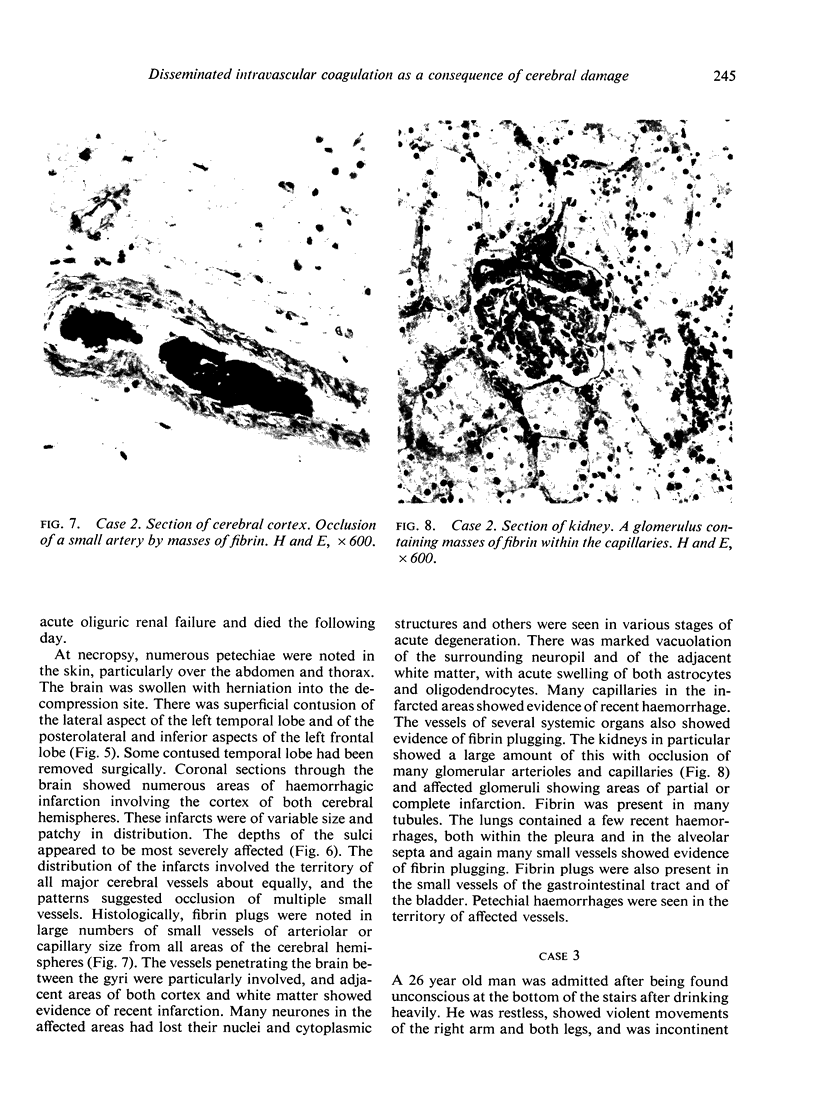
Three cases with intracranial lesions developed evidence of disseminated intravascular coagulation which was confirmed at necropsy. The factors engendering this state, including release of potent thromboplastin from neural tissue are discussed and the danger of this intermediary mechanism of disease increasing the mortality of intracranial disease is demonstrated. Careful haematological investigation of all patients with intracranial disease is therefore advised, especially if they manifest evidence of a bleeding tendency.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Clarkson A. R., MacDonald M. K., Fuster V., Cash J. D., Robson J. S. Glomerular coagulation in acute ischaemic renal failure. Q J Med. 1970 Oct;39(156):585–599. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldenfarb P. B., Zucker S., Corrigan J. J., Jr, Cathey M. H. The coagulation mechanism in acute bacterial infection. Br J Haematol. 1970 Jun;18(6):643–652. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1970.tb01589.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham D. I., Adams J. H. Ischaemic brain damage in fatal head injuries. Lancet. 1971 Feb 6;1(7693):265–266. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)91003-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larrieu M. J., Rigollot C., Marder V. J. Comparative effects of fibrinogen degradation fragments D and E on coagulation. Br J Haematol. 1972 Jun;22(6):719–733. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1972.tb05717.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marder V. J., Shulman N. R. High molecular weight derivatives of human fibrinogen produced by plasmin. II. Mechanism of their anticoagulant activity. J Biol Chem. 1969 Apr 25;244(8):2120–2124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nalbandain R. M., Henry R. L., Kessler K. L., Camp F. R., Jr, Wolf P. L. Consumption coagulopathy: practical principles of diagnosis and management. Hum Pathol. 1971 Sep;2(3):377–388. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(71)80005-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston F. E., Malia R. G., Sworn M. J., Blackburn E. K. Intravascular coagulation and E. coli septicaemia. J Clin Pathol. 1973 Feb;26(2):120–125. doi: 10.1136/jcp.26.2.120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston F. E., Malia R. G., Sworn M. J., Blackburn E. K. Intravascular coagulation and renal failure in E. coli septicaemia. J Clin Pathol. 1972 Nov;25(11):1006–1007. doi: 10.1136/jcp.25.11.1006-c. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regoeczi E., Brain M. C. Organ distribution of fibrin in disseminated intravascular coagulation. Br J Haematol. 1969 Jul;17(1):73–81. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1969.tb05665.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]