Abstract
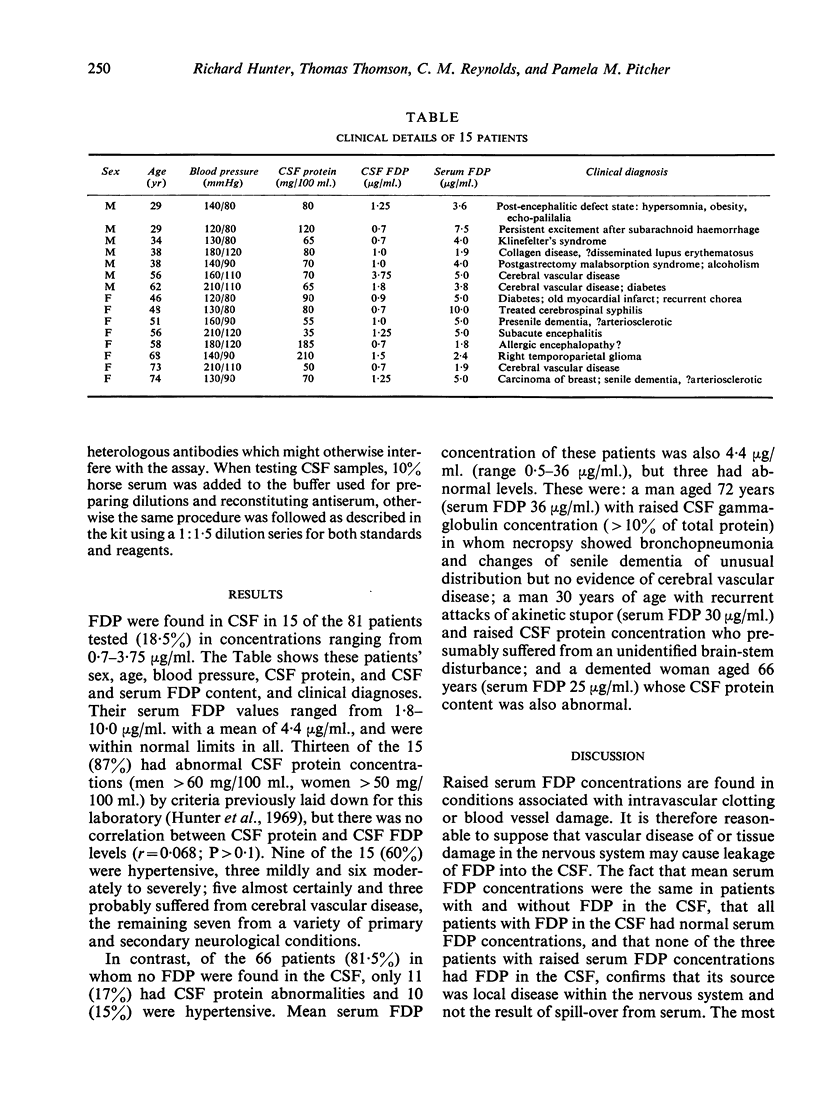
Paired cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and serum samples collected from 81 of 241 patients admitted to a district psychiatric hospital during a six month period were assayed for fibrin/fibrinogen degradation products (FDP) using a haemagglutination inhibition technique. FDP were found in all serum samples. Fifteen patients (18·5%) had FDP in the CSF (range 0·7-3·75 μg/ml.) and of these 13 (87%) had associated CSF protein abnormalities and 9 (60%) were hypertensive. Mean serum FDP values were the same (4·4 μg/ml.) in patients with and without FDP in the CSF. Three patients had raised serum FDP concentrations but no FDP in the CSF. The evidence suggests that the presence of FDP in CSF indicates recent central nervous system damage. In this series the most common cause was vascular disease.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Clarkson A. R., MacDonald M. K., Petrie J. J., Cash J. D., Robson J. S. Serum and urinary fibrin-fibrinogen degradation products in glomerulonephritis. Br Med J. 1971 Aug;3(5772):447–451. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5772.447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarkson A. R., Morton J. B., Cash J. D. Urinary fibrin-fibrinogen degradation poducts after renal homotransplantation. Lancet. 1970 Dec 12;2(7685):1220–1223. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)92181-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das P. C., Allan A. G., Woodfield D. G., Cash J. D. Fibrin degradation products in sera of normal subjects. Br Med J. 1967 Dec 23;4(5581):718–720. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5581.718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLETCHER A. P., ALKJAERSIG N., SHERRY S. Pathogenesis of the coagulation defect developing during pathological plasma proteolytic ("fibrinolytic") states. I. The significance of fibrinogen proteolysis and circulating fibrinogen breakdown products. J Clin Invest. 1962 Apr;41:896–916. doi: 10.1172/JCI104546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter R., Jones M., Malleson A. Abnormal cerebrospinal fluid total protein and gamma-blobulin levels in 256 patients admitted to a psychiatric unit. J Neurol Sci. 1969 Jul-Aug;9(1):11–38. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(69)90056-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merskey C., Kleiner G. J., Johnson A. J. Quantitative estimation of split products of fibrinogen in human serum, relation to diagnosis and treatment. Blood. 1966 Jul;28(1):1–18. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NUSSENZWEIG V., SELIGMANN M. [Analysis, by immuno-chemical methods, of the degradation by plasmin of human fibrinogen and fibrin, at different stages]. Nouv Rev Fr Hematol. 1960 Nov-Dec;15:451–466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruckley C. V., Das P. C., Leitch A. G., Donaldson A. A., Copland W. A., Redpath A. T., Scott P., Cash J. D. Serum fibrin-fibrinogen degradation products associated with postoperative pulmonary embolus and venous thrombosis. Br Med J. 1970 Nov 14;4(5732):395–398. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5732.395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson J. E., 3rd, Frenkel E. P., Pierce A. K., Johnson R. L., Jr, Winga E. R., Curry G. C., Mierzwiak D. S. Spontaneous fibrinolysis in pulmonary embolism. J Clin Invest. 1971 Mar;50(3):474–480. doi: 10.1172/JCI106515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


