Abstract
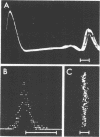
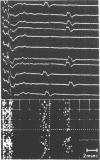
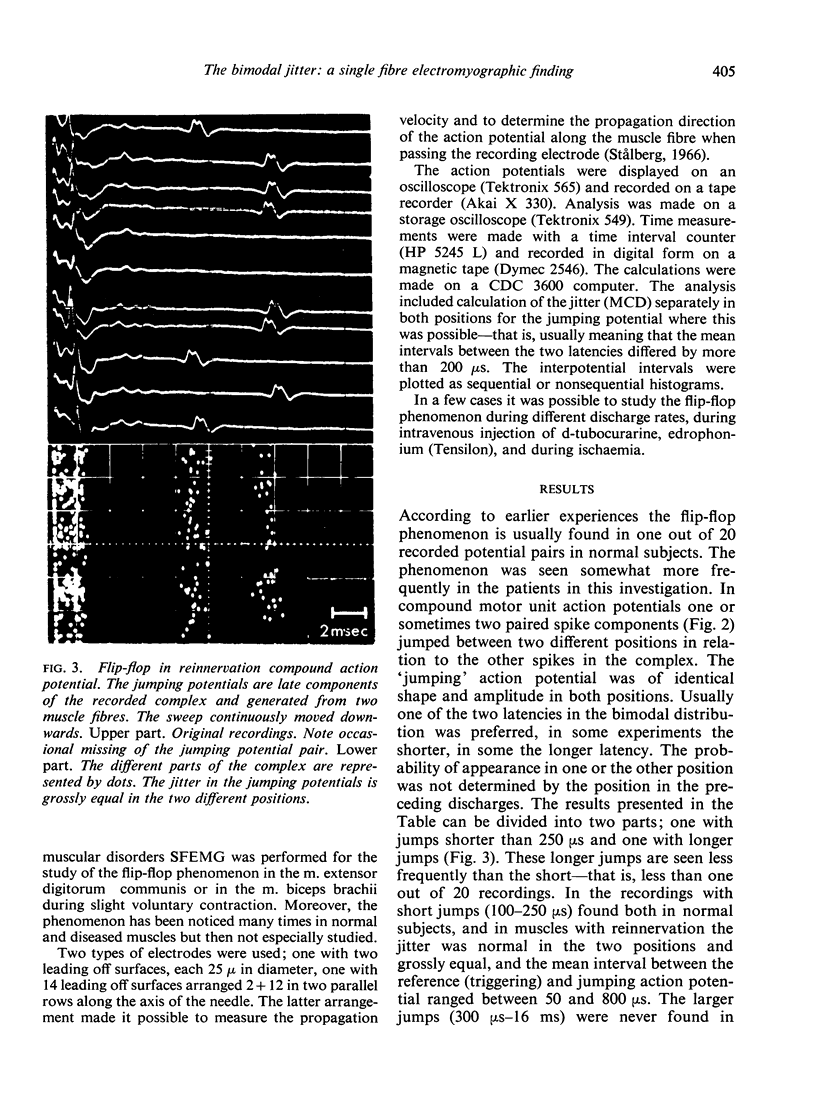
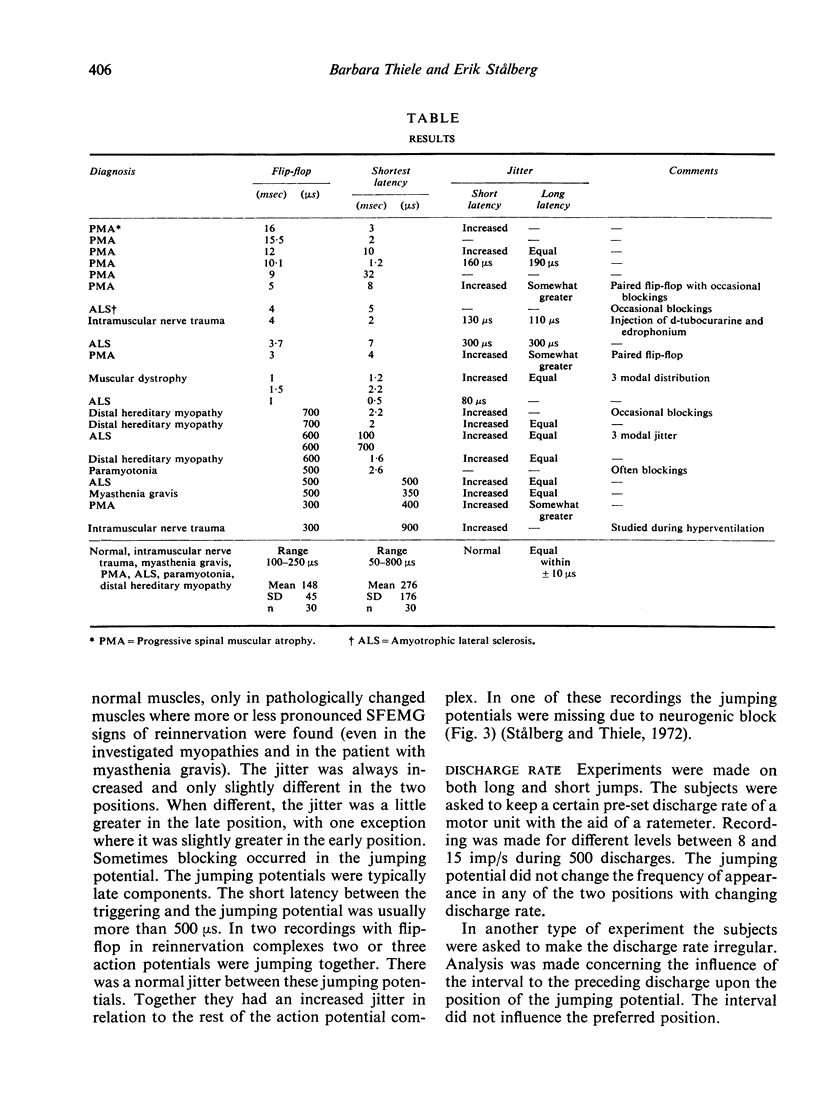
The jitter, obtained by SFEMG recordings, mainly reflects the neuromuscular transmission time variability and is usually Gaussian distributed. Here is reported the bimodal distribution of the interpotential intervals, the flip-flop phenomenon. Long flip-flop in cases of reinnervation may indicate alternatively continuous and saltatory nerve conduction. Short flip-flop in normal subjects may be due to muscle fibre interaction or nerve conduction irregularities.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dahlbäck L. O., Ekstedt J., Stålberg E. Ischemic effects on impulse transmission to muscle fibers in man. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1970 Dec;29(6):579–591. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(70)90100-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EKSTEDT J. HUMAN SINGLE MUSCLE FIBER ACTION POTENTIALS. EXTRACELLULAR RECORDING DURING VOLUNTARY AND CHEMICAL ACTIVATION. WITH SOME COMMENTS ON END-PLATE PHYSIOLOGY AND ON THE FIBER ARRANGEMENT OF THE MOTOR UNIT. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1964:SUPPL 226–226:1+. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edström L., Kugelberg E. Histochemical composition, distribution of fibres and fatiguability of single motor units. Anterior tibial muscle of the rat. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1968 Oct;31(5):424–433. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.31.5.424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekstedt J., Stålberg E. Abnormal connections between skeletal muscle fibers. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1969 Dec;27(6):607–609. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(69)90074-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekstedt J., Stålberg E. The effect of non-paralytic doses of D-tubocurarine on individual motor end-plates in man, studied with a new electrophysiological method. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1969 Dec;27(6):557–562. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(69)90066-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GILLIATT R. W., WILLISON R. G. The refractory and supernormal periods of the human median nerve. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1963 Apr;26:136–147. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.26.2.136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallin R. G., Torebjörk H. E. Afferent and efferent C units recorded from human skin nerves in situ. A preliminary report. Acta Soc Med Ups. 1970;75(5-6):277–281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Schmitt O. H. Electric interaction between two adjacent nerve fibres. J Physiol. 1940 Feb 14;97(4):471–488. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1940.sp003823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto M., Riker W. F., Jr Subacute denervation: a means of disclosing mammalian motor nerve terminals as critical sites of acetylcholine and facilitatory drug actions. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1969 Apr;166(2):217–224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STANDAERT F. G. THE ACTION OF D-TUBOCURARINE ON THE MOTOR NERVE TERMINAL. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1964 Feb;143:181–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stålberg E., Thiele B. Transmission block in terminal nerve twigs: a single fibre electromyographic finding in man. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1972 Feb;35(1):52–59. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.35.1.52. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vizoso A. D., Young J. Z. Internode length and fibre diameter in developing and regenerating nerves. J Anat. 1948 Apr;82(Pt 1-2):110–134.1. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOHLFART G. Collateral regeneration from residual motor nerve fibers in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurology. 1957 Feb;7(2):124–134. doi: 10.1212/wnl.7.2.124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright E. A., McQuillen M. P. Hypoexcitability of ulnar nerve in patients with normal motor nerve conduction velocities. Neurology. 1973 Jan;23(1):78–83. doi: 10.1212/wnl.23.1.78. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]