Abstract
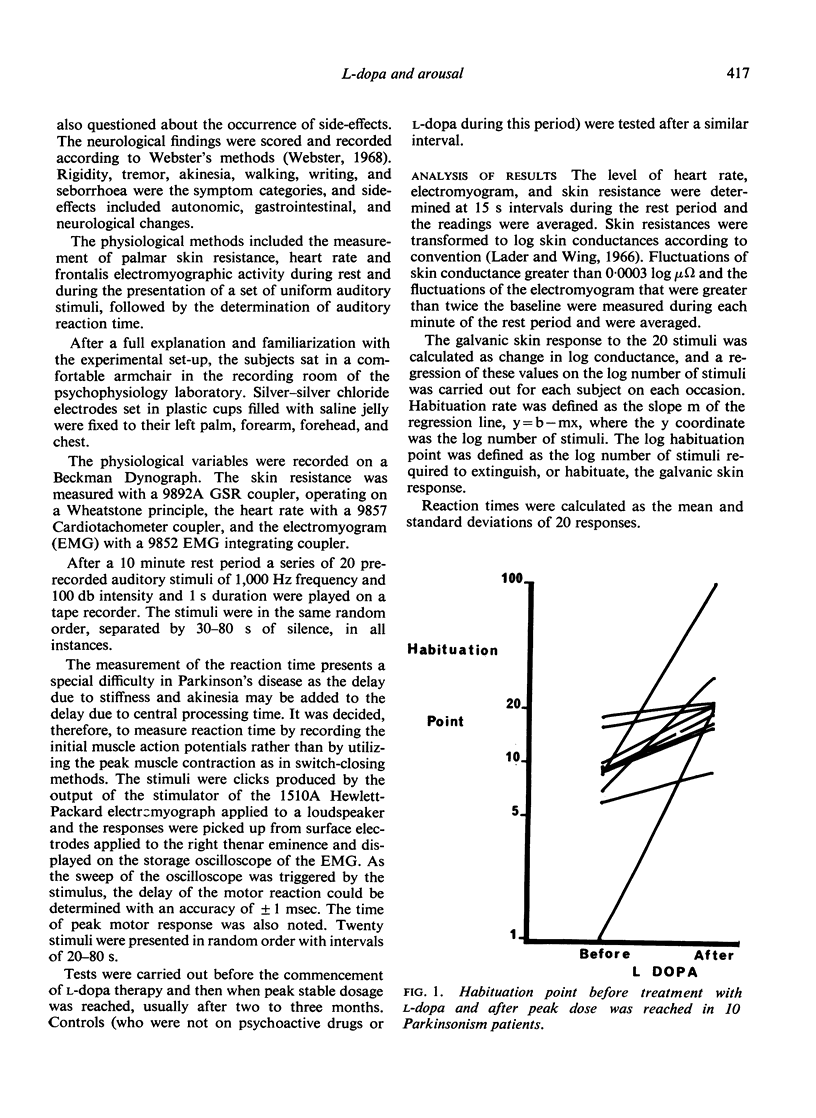
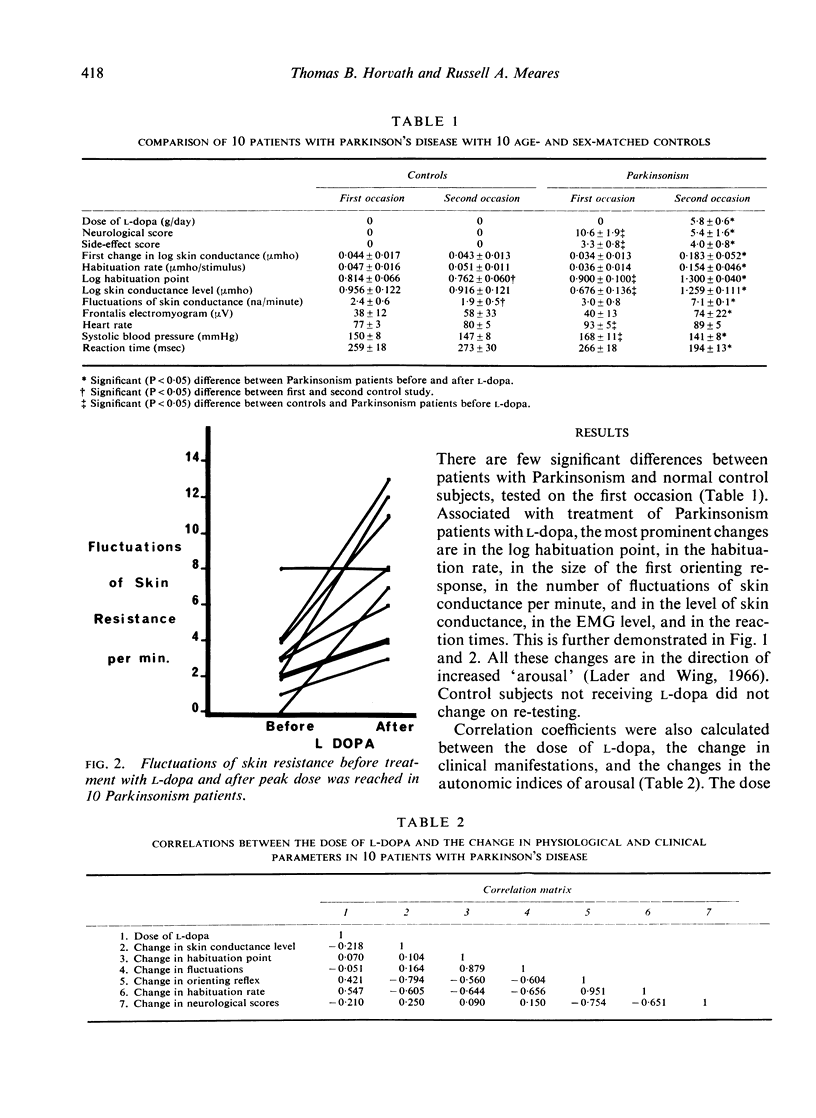
In 10 patients with Parkinsonism, treatment with L-dopa was associated with a rise in the skin conductance level and its fluctuations, an increased electromyographic activity in the frontalis muscle, and with faster reaction times. The change of skin conductance in response to a loud noise also increased and its habituation to the repetition of the stimulus was delayed. One patient developed a schizophreniform psychosis and showed high arousal and absent habituation. It is possible that dopamine is the transmitter associated with the arousal reaction and that it plays a part in the pathogenesis of schizophrenia.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andén N. E., Butcher S. G., Corrodi H., Fuxe K., Ungerstedt U. Receptor activity and turnover of dopamine and noradrenaline after neuroleptics. Eur J Pharmacol. 1970;11(3):303–314. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(70)90006-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERTLER A., ROSENGREN E. Occurrence and distribution of catechol amines in brain. Acta Physiol Scand. 1959 Dec 12;47:350–361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbeau A. Long-term side-effects of levodopa. Lancet. 1971 Feb 20;1(7695):395–395. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)92226-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom F. E., Giarman N. J. Physiologic and pharmacologic considerations of biogenic amines in the nervous system. Annu Rev Pharmacol. 1968;8:229–258. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.08.040168.001305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunney W. E., Janowsky D. S., Goodwin F. K., Davis J. M., Brodie H. K., Murphy D. L., Chase T. N. Effect of L-DOPA on depression. Lancet. 1969 Apr 26;1(7600):885–886. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)91921-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunney W. E., Jr, Brodie H. K., Murphy D. L., Goodwin F. K. Studies of alpha-methyl-para-tyrosine, L-dopa, and L-tryptophan in depression and mania. Am J Psychiatry. 1971 Jan;127(7):872–881. doi: 10.1176/ajp.127.7.872. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butcher L. L., Engel J. Behavioral and biochemical effects of L-dopa after peripheral decarboxylase inhibition. Brain Res. 1969 Sep;15(1):233–242. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(69)90322-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHAPMAN J., McGHIE A. A comparative study of disordered attention in schizophrenia. J Ment Sci. 1962 Jul;108:487–500. doi: 10.1192/bjp.108.455.487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celesia G. G., Barr A. N. Psychosis and other psychiatric manifestations of levodopa therapy. Arch Neurol. 1970 Sep;23(3):193–200. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1970.00480270003001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotzias G. C., Papavasiliou P. S., Gellene R. Modification of Parkinsonism--chronic treatment with L-dopa. N Engl J Med. 1969 Feb 13;280(7):337–345. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196902132800701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett G. M., Borcherding J. W. L-dopa: effect on concentrations of dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin in brains of mice. Science. 1970 May 15;168(3933):849–850. doi: 10.1126/science.168.3933.849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FELDBERG W., SHERWOOD S. L. Injections of drugs into the lateral ventricle of the cat. J Physiol. 1954 Jan;123(1):148–167. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godwin-Austen R. B., Tomlinson E. B., Frears C. C., Kok H. W. Effects of L-dopa in Parkinson's disease. Lancet. 1969 Jul 26;2(7613):165–168. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)91417-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEBB D. O. Drives and the C.N.S. (conceptual nervous system). Psychol Rev. 1955 Jul;62(4):243–254. doi: 10.1037/h0041823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinterberger H. The biochemistry of catecholamines in relation to Parkinson's disease. Aust N Z J Med. 1971 May;1(Suppl):14–18. doi: 10.1111/j.1445-5994.1971.tb02560.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hornykiewicz O. Dopamine (3-hydroxytyramine) and brain function. Pharmacol Rev. 1966 Jun;18(2):925–964. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jouvet M. Neurophysiology of the states of sleep. Physiol Rev. 1967 Apr;47(2):117–177. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1967.47.2.117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knopp W. Psychiatric changes in patients treated with levodopa. I. The clinical experiment. Neurology. 1970 Dec;20(12 Suppl):23–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANSING R. W., SCHWARTZ E., LINDSLEY D. B. Reaction time and EEG activation under alerted and nonalerted conditions. J Exp Psychol. 1959 Jul;58(1):1–7. doi: 10.1037/h0041016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LINDSLEY D. B. Psychological phenomena and the electroencephalogram. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1952 Nov;4(4):443–456. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(52)90075-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lader M. H., Wing L. Physiological measures in agitated and retarded depressed patients. J Psychiatr Res. 1969 Dec;7(2):89–100. doi: 10.1016/0022-3956(69)90014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lammers A. J., van Rossum J. M. Bizarre social behaviour in rats induced by a combination of a peripheral decarboxylase inhibitor and DOPA. Eur J Pharmacol. 1968 Dec;5(1):103–106. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(68)90163-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh G. G., Markham C. M., Ansel R. Levodopa's awakening effect on patients with Parkinsonism. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1971 Jun;34(3):209–218. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.34.3.209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meares R., Horvath T. A physiological difference between hallucinosis and schizophrenia. Br J Psychiatry. 1973 Jun;122(571):687–688. doi: 10.1192/bjp.122.6.687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien C. P., DiGiacomo J. N., Fahn S., Schwarz G. A. Mental effects of high-dosage levodopa. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1971 Jan;24(1):61–64. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1971.01750070063008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROTHBALLER A. B. The effects of catecholamines on the central nervous system. Pharmacol Rev. 1959 Jun;11(2 Pt 2):494–547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheckel C. L., Boff E., Pazery L. M. Hyperactive states related to the metabolism of norepinephrine and similar biochemicals. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1969 Jul 30;159(3):939–958. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1969.tb12990.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schildkraut J. J., Kety S. S. Biogenic amines and emotion. Science. 1967 Apr 7;156(3771):21–37. doi: 10.1126/science.156.3771.21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schildkraut J. J. The catecholamine hypothesis of affective disorders: a review of supporting evidence. Am J Psychiatry. 1965 Nov;122(5):509–522. doi: 10.1176/ajp.122.5.509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder S. H. Catecholamines in the brain as mediators of amphetamine psychosis. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1972 Aug;27(2):169–179. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1972.01750260021004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ungerstedt U. Stereotaxic mapping of the monoamine pathways in the rat brain. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1971;367:1–48. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-201x.1971.tb10998.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warburton J. W. Memory disturbance and the Parkinson syndrome. Br J Med Psychol. 1967 Jun;40(2):169–171. doi: 10.1111/j.2044-8341.1967.tb00566.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster D. D. Critical analysis of the disability in Parkinson's disease. Mod Treat. 1968 Mar;5(2):257–282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yahr M. D., Duvoisin R. C., Schear M. J., Barrett R. E., Hoehn M. M. Treatment of parkinsonism with levodopa. Arch Neurol. 1969 Oct;21(4):343–354. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1969.00480160015001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



