Abstract
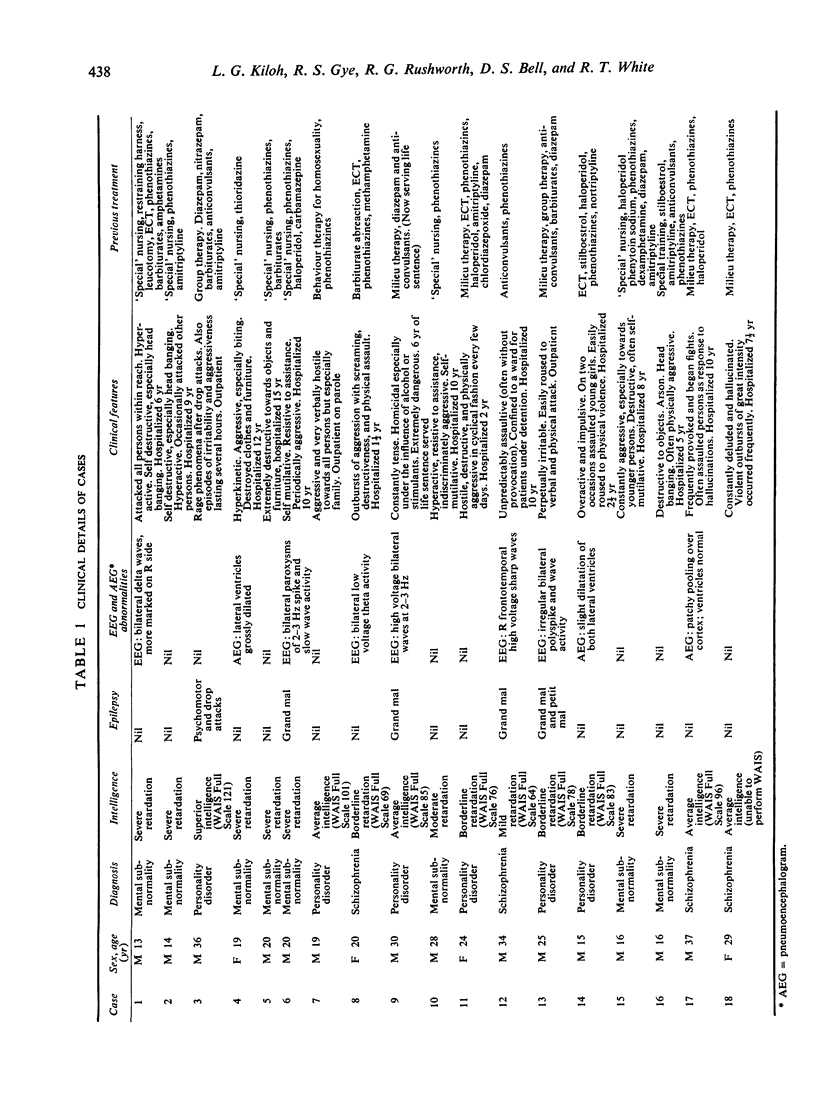
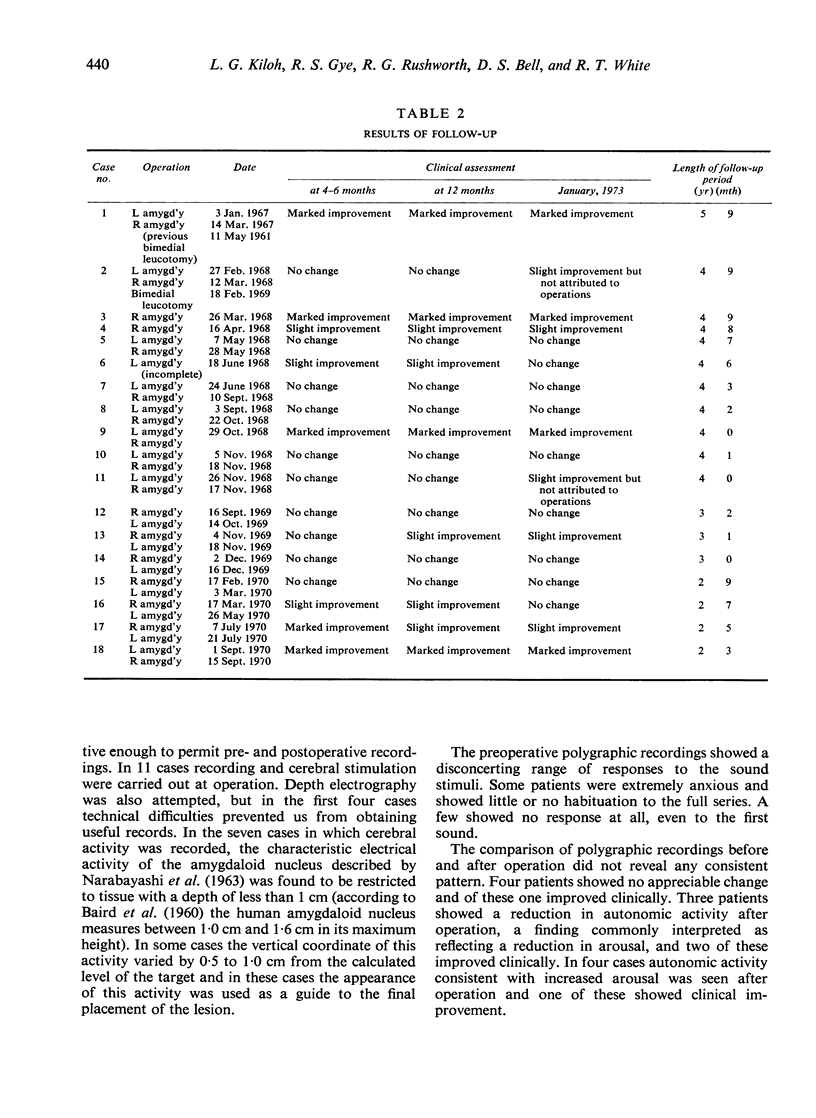
Amygdaloidotomy was performed bilaterally on 15 and unilaterally on three patients exhibiting severe aggressive or self-mutilating behaviour. Nine subjects (50%) were improved a year after operation; improvement was maintained in seven (39%) for periods ranging from 27 months to nearly six years. Four non-epileptic cases had convulsions during the period of review; one of them has a persistent mild hemiparesis dating from the postoperative period. There was a tendency for epileptics to respond better than non-epileptics and for mentally retarded patients to respond poorly, but none of the differences was statistically significant.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BAIRD H. W., 3rd, SPIEGEL E. A., WYCIS H. T. Studies in stereoencephalotomy. IX. The variability in the extent and position of the amygdala. Confin Neurol. 1960;20:26–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balasubramaniam V., Ramamurthi B. Stereotaxic amygdalotomy in behavior disorders. Confin Neurol. 1970;32(2):367–373. doi: 10.1159/000103439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balasubramaniam V., Ramamurthi B. Stereotaxic amygdalotomy. Proc Aust Assoc Neurol. 1968;5(2):277–278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEATH R. G., MONROE R. R., MICKLE W. A. Stimulation of the amygdaloid nucleus in a schizophrenic patient. Am J Psychiatry. 1955 May;111(11):862–863. doi: 10.1176/ajp.111.11.862. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heimburger R. F., Whitlock C. C., Kalsbeck J. E. Stereotaxic amygdalotomy for epilepsy with aggressive behavior. JAMA. 1966 Nov 14;198(7):741–745. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaada B. Brain mechanisms related to aggressive behavior. UCLA Forum Med Sci. 1967;7:95–133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NARABAYASHI H., NAGAO T., SAITO Y., YOSHIDA M., NAGAHATA M. Stereotaxic amygdalotomy for behavior disorders. Arch Neurol. 1963 Jul;9:1–16. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1963.00460070011001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narabayashi H., Mizutani T. Epileptic seizures and the stereotaxic amygdalotomy. Confin Neurol. 1970;32(2):289–297. doi: 10.1159/000103429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narabayashi H., Uno M. Long range results of stereotaxic amygdalotomy for behavior disorders. Confin Neurol. 1966;27(1):168–171. doi: 10.1159/000103950. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAWA M., UEKI Y., ARITA M., HARADA T. Preliminary report on the amygdaloidectomy on the psychotic patients, with interpretation of oral-emotional manifestation in schizophrenics. Folia Psychiatr Neurol Jpn. 1954 Mar;7(4):309–329. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1819.1954.tb01278.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwab R. S., Sweet W. H., Mark V. H., Kjellberg R. N., Ervin F. R. Treatment of intractable temporal lobe epilepsy by stereotactic amygdala lesions. Trans Am Neurol Assoc. 1965;90:12–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnbull F. Neurosurgery in the control of unmanageable affective reactions: a critical review. Clin Neurosurg. 1969;16:218–233. doi: 10.1093/neurosurgery/16.cn_suppl_1.218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaernet K., Madsen A. Stereotaxic amygdalotomy and basofrontal tractotomy in psychotics with aggressive behaviour. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1970 Dec;33(6):858–863. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.33.6.858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


