Abstract
AIMS--To evaluate the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) demonstration of clonal immunoglobulin heavy chain gene rearrangements using routinely prepared, unstained, and stained formalin fixed, paraffin wax embedded tissue samples. METHODS--Extracts from (a) fresh frozen tissue samples, (b) unstained, and (c) haematoxylin and eosin stained formalin fixed, paraffin wax embedded 5 microns tissue sections from 42 cases of low grade B cell lymphoma, all shown to be monoclonal by Southern blot analysis, were analysed using PCR. Two regions of the variable segment of the immunoglobulin heavy chain gene were amplified (framework 2 to joining region [Fr2/JH] and framework 3 to joining region [Fr3/JH]). Twelve samples of reactive lymphoid tissue were studied as controls. Products from each case were directly compared on polyacrylamide gels. RESULTS--Using both primer combinations, monoclonality was detected in 38 of 42 (90%) cases using fresh material, 37 of 42 (88%) using unstained paraffin wax embedded samples, and in 35 of 42 (83%) cases using haematoxylin and eosin stained sections. No false positive results attributable to fixation, processing, or staining were identified, although the efficiency of amplification using the Fr2/JH primers was significantly reduced. CONCLUSIONS--PCR determination of B cell clonality using paraffin wax embedded material is sufficiently sensitive and reliable for use as a routine diagnostic adjunct to conventional morphological and immunocytochemical assessment of lymphoproliferative disease.
Full text
PDF
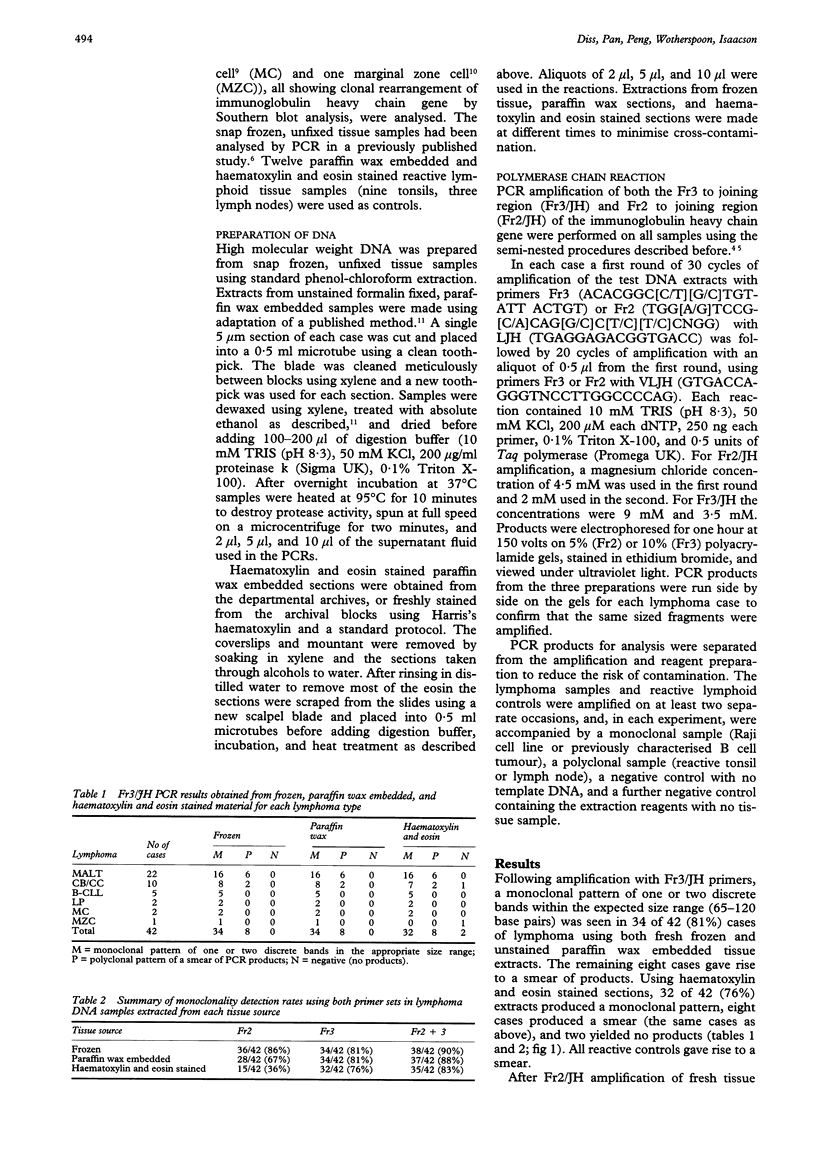

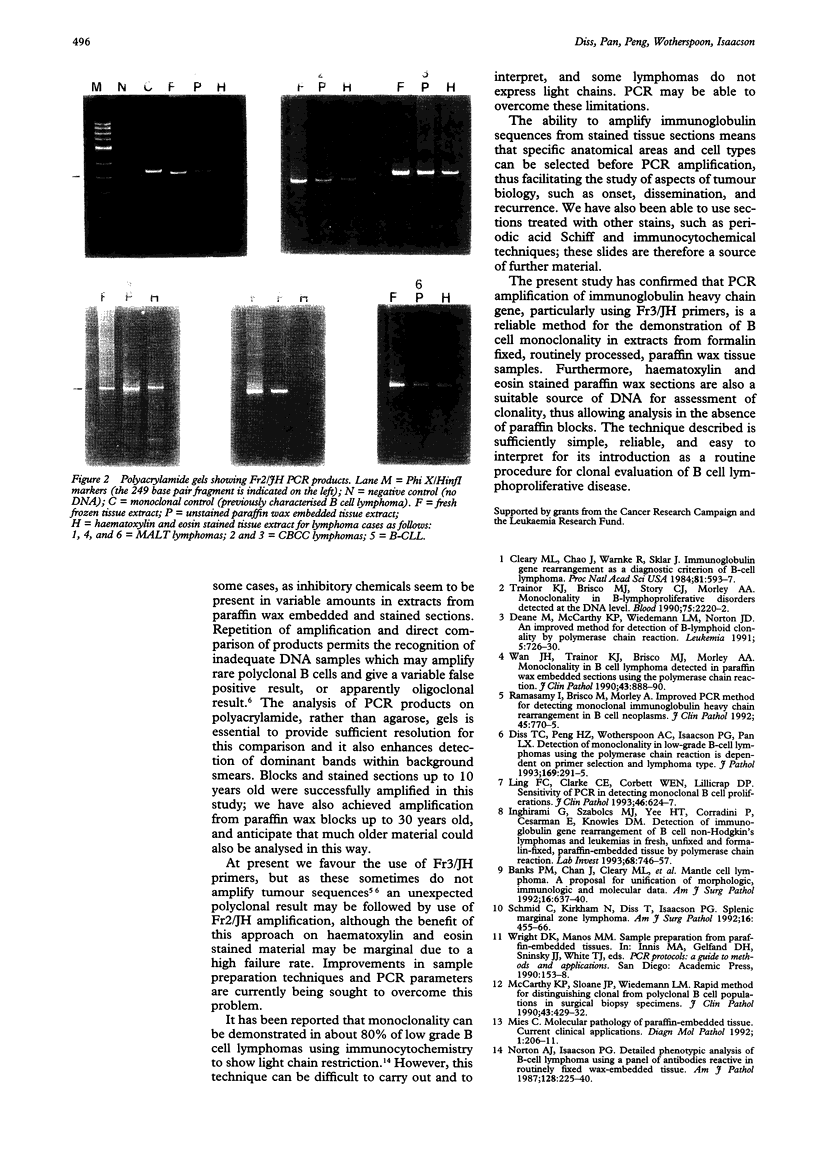
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banks P. M., Chan J., Cleary M. L., Delsol G., De Wolf-Peeters C., Gatter K., Grogan T. M., Harris N. L., Isaacson P. G., Jaffe E. S. Mantle cell lymphoma. A proposal for unification of morphologic, immunologic, and molecular data. Am J Surg Pathol. 1992 Jul;16(7):637–640. doi: 10.1097/00000478-199207000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleary M. L., Chao J., Warnke R., Sklar J. Immunoglobulin gene rearrangement as a diagnostic criterion of B-cell lymphoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):593–597. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deane M., McCarthy K. P., Wiedemann L. M., Norton J. D. An improved method for detection of B-lymphoid clonality by polymerase chain reaction. Leukemia. 1991 Aug;5(8):726–730. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diss T. C., Peng H., Wotherspoon A. C., Isaacson P. G., Pan L. Detection of monoclonality in low-grade B-cell lymphomas using the polymerase chain reaction is dependent on primer selection and lymphoma type. J Pathol. 1993 Mar;169(3):291–295. doi: 10.1002/path.1711690303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inghirami G., Szabolcs M. J., Yee H. T., Corradini P., Cesarman E., Knowles D. M. Detection of immunoglobulin gene rearrangement of B cell non-Hodgkin's lymphomas and leukemias in fresh, unfixed and formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue by polymerase chain reaction. Lab Invest. 1993 Jun;68(6):746–757. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling F. C., Clarke C. E., Corbett W. E., Lillicrap D. P. Sensitivity of PCR in detecting monoclonal B cell proliferations. J Clin Pathol. 1993 Jul;46(7):624–627. doi: 10.1136/jcp.46.7.624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy K. P., Sloane J. P., Wiedemann L. M. Rapid method for distinguishing clonal from polyclonal B cell populations in surgical biopsy specimens. J Clin Pathol. 1990 May;43(5):429–432. doi: 10.1136/jcp.43.5.429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mies C. Molecular pathology of paraffin-embedded tissue. Current clinical applications. Diagn Mol Pathol. 1992 Sep;1(3):206–211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norton A. J., Isaacson P. G. Detailed phenotypic analysis of B-cell lymphoma using a panel of antibodies reactive in routinely fixed wax-embedded tissue. Am J Pathol. 1987 Aug;128(2):225–240. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramasamy I., Brisco M., Morley A. Improved PCR method for detecting monoclonal immunoglobulin heavy chain rearrangement in B cell neoplasms. J Clin Pathol. 1992 Sep;45(9):770–775. doi: 10.1136/jcp.45.9.770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid C., Kirkham N., Diss T., Isaacson P. G. Splenic marginal zone cell lymphoma. Am J Surg Pathol. 1992 May;16(5):455–466. doi: 10.1097/00000478-199205000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trainor K. J., Brisco M. J., Story C. J., Morley A. A. Monoclonality in B-lymphoproliferative disorders detected at the DNA level. Blood. 1990 Jun 1;75(11):2220–2222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wan J. H., Trainor K. J., Brisco M. J., Morley A. A. Monoclonality in B cell lymphoma detected in paraffin wax embedded sections using the polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Pathol. 1990 Nov;43(11):888–890. doi: 10.1136/jcp.43.11.888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]