Abstract
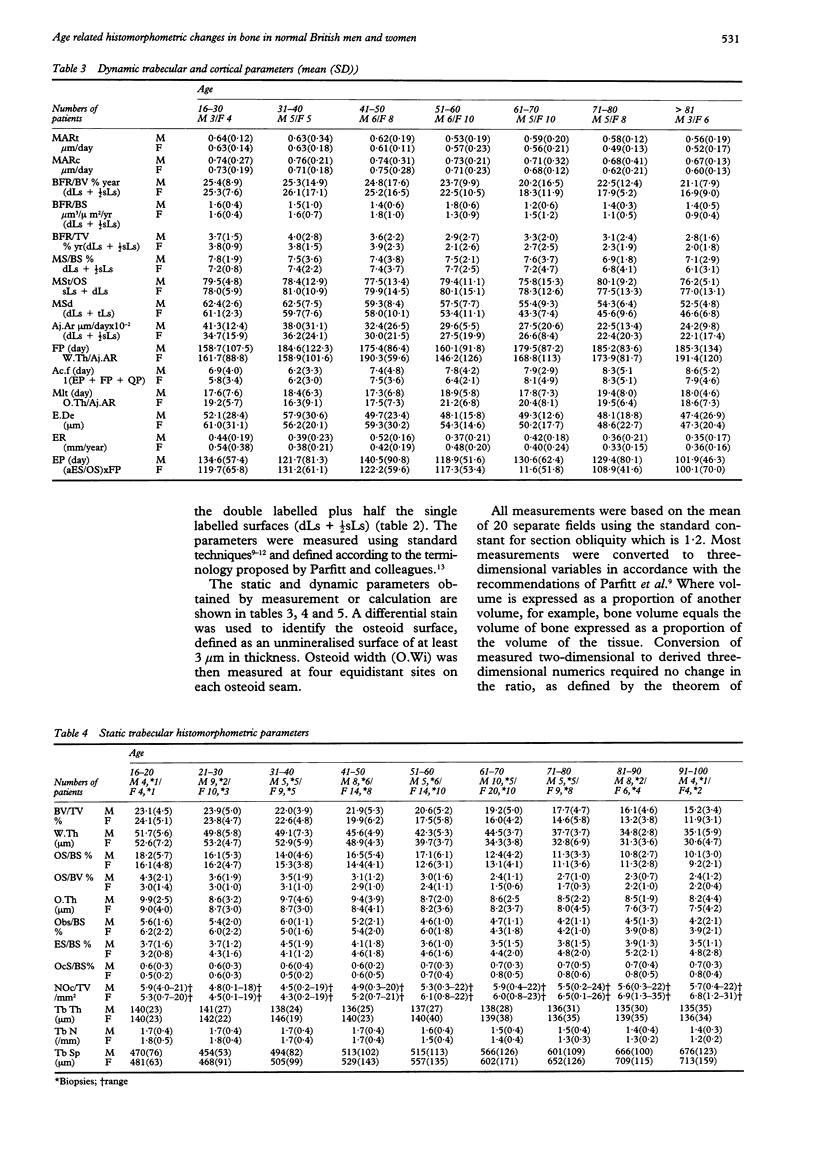
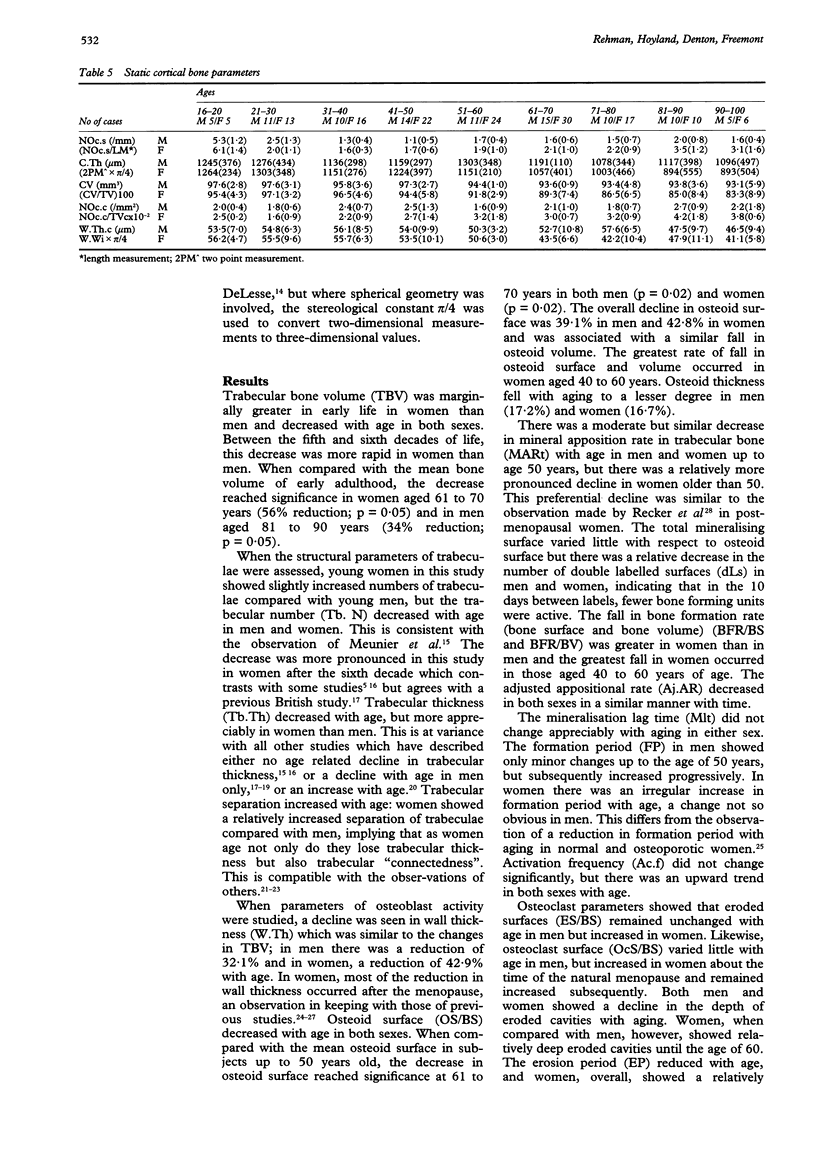
AIMS--To define the iliac crest histomorphometry of static variables in 234 individuals aged 16-100 years (91 men, 143 women) and of dynamic variables in 84 individuals aged 19-94 years (33 men, 51 women) from the North West of England. METHODS--Iliac crest biopsy specimens were sectioned, undecalcified, and examined using image analysis. RESULTS--The decrease in the quantity of cortical and trabecular bone and the connectivity of trabecular bone was more pronounced in women than men. This was associated with a reduction in bone formation and increased bone resorption which was greater in women at both the tissue and cellular level. Some of these histomorphometric differences first became evident at the natural menopause, and therefore provide clues as to the cause of the high prevalence of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women. CONCLUSIONS--These results show an age and sex dependent variation both in static and dynamic parameters, which differ, in some respects, from other studies and confirm the need for large regional studies to provide a database of normal morphometric results for a specific population.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aaron J. E., Makins N. B., Sagreiya K. The microanatomy of trabecular bone loss in normal aging men and women. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1987 Feb;(215):260–271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agerbaek M. O., Eriksen E. F., Kragstrup J., Mosekilde L., Melsen F. A reconstruction of the remodelling cycle in normal human cortical iliac bone. Bone Miner. 1991 Feb;12(2):101–112. doi: 10.1016/0169-6009(91)90039-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkenhäger-Frenkel D. H., Courpron P., Hüpscher E. A., Clermonts E., Coutinho M. F., Schmitz P. I., Meunier P. J. Age-related changes in cancellous bone structure. A two-dimensional study in the transiliac and iliac crest biopsy sites. Bone Miner. 1988 Jun;4(2):197–216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chavassieux P. M., Arlot M. E., Meunier P. J. Intermethod variation in bone histomorphometry: comparison between manual and computerized methods applied to iliac bone biopsies. Bone. 1985;6(4):221–229. doi: 10.1016/8756-3282(85)90004-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chavassieux P. M., Arlot M. E., Meunier P. J. Intersample variation in bone histomorphometry: comparison between parameter values measured on two contiguous transiliac bone biopsies. Calcif Tissue Int. 1985 Jul;37(4):345–350. doi: 10.1007/BF02553699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Compston J. E., Mellish R. W., Croucher P., Newcombe R., Garrahan N. J. Structural mechanisms of trabecular bone loss in man. Bone Miner. 1989 Jul;6(3):339–350. doi: 10.1016/0169-6009(89)90039-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Compston J. E., Mellish R. W., Garrahan N. J. Age-related changes in iliac crest trabecular microanatomic bone structure in man. Bone. 1987;8(5):289–292. doi: 10.1016/8756-3282(87)90004-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahl E., Nordal K. P., Halse J., Attramadal A. Histomorphometric analysis of normal bone from the iliac crest of Norwegian subjects. Bone Miner. 1988 Mar;3(4):369–377. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darby A. J., Meunier P. J. Mean wall thickness and formation periods of trabecular bone packets in idiopathic osteoporosis. Calcif Tissue Int. 1981;33(3):199–204. doi: 10.1007/BF02409438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriksen E. F., Hodgson S. F., Eastell R., Cedel S. L., O'Fallon W. M., Riggs B. L. Cancellous bone remodeling in type I (postmenopausal) osteoporosis: quantitative assessment of rates of formation, resorption, and bone loss at tissue and cellular levels. J Bone Miner Res. 1990 Apr;5(4):311–319. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.5650050402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FROST H. M. Mean formation time of human osteons. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1963 May;41:1307–1310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn M., Vogel M., Pompesius-Kempa M., Delling G. Trabecular bone pattern factor--a new parameter for simple quantification of bone microarchitecture. Bone. 1992;13(4):327–330. doi: 10.1016/8756-3282(92)90078-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keshawarz N. M., Recker R. R. Expansion of the medullary cavity at the expense of cortex in postmenopausal osteoporosis. Metab Bone Dis Relat Res. 1984;5(5):223–228. doi: 10.1016/0221-8747(84)90063-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimmel D. B., Recker R. R., Gallagher J. C., Vaswani A. S., Aloia J. F. A comparison of iliac bone histomorphometric data in post-menopausal osteoporotic and normal subjects. Bone Miner. 1990 Nov;11(2):217–235. doi: 10.1016/0169-6009(90)90061-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleerekoper M., Villanueva A. R., Stanciu J., Rao D. S., Parfitt A. M. The role of three-dimensional trabecular microstructure in the pathogenesis of vertebral compression fractures. Calcif Tissue Int. 1985 Dec;37(6):594–597. doi: 10.1007/BF02554913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kragstrup J., Melsen F., Mosekilde L. Thickness of bone formed at remodeling sites in normal human iliac trabecular bone: variations with age and sex. Metab Bone Dis Relat Res. 1983;5(1):17–21. doi: 10.1016/0221-8747(83)90046-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lips P., Courpron P., Meunier P. J. Mean wall thickness of trabecular bone packets in the human iliac crest: changes with age. Calcif Tissue Res. 1978 Nov 10;26(1):13–17. doi: 10.1007/BF02013227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malluche H. H., Meyer W., Sherman D., Massry S. G. Quantitative bone histology in 84 normal American subjects. Micromorphometric analysis and evaluation of variance in iliac bone. Calcif Tissue Int. 1982 Sep;34(5):449–455. doi: 10.1007/BF02411283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellish R. W., Garrahan N. J., Compston J. E. Age-related changes in trabecular width and spacing in human iliac crest biopsies. Bone Miner. 1989 Jul;6(3):331–338. doi: 10.1016/0169-6009(89)90038-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melsen F., Melsen B., Mosekilde L., Bergmann S. Histomorphometric analysis of normal bone from the iliac crest. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand A. 1978 Jan;86(1):70–81. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1978.tb02014.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melsen F., Mosekilde L. The role of bone biopsy in the diagnosis of metabolic bone disease. Orthop Clin North Am. 1981 Jul;12(3):571–602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosekilde L., Mosekilde L. Iliac crest trabecular bone volume as predictor for vertebral compressive strength, ash density and trabecular bone volume in normal individuals. Bone. 1988;9(4):195–199. doi: 10.1016/8756-3282(88)90030-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parfitt A. M., Drezner M. K., Glorieux F. H., Kanis J. A., Malluche H., Meunier P. J., Ott S. M., Recker R. R. Bone histomorphometry: standardization of nomenclature, symbols, and units. Report of the ASBMR Histomorphometry Nomenclature Committee. J Bone Miner Res. 1987 Dec;2(6):595–610. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.5650020617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parfitt A. M., Mathews C. H., Villanueva A. R., Kleerekoper M., Frame B., Rao D. S. Relationships between surface, volume, and thickness of iliac trabecular bone in aging and in osteoporosis. Implications for the microanatomic and cellular mechanisms of bone loss. J Clin Invest. 1983 Oct;72(4):1396–1409. doi: 10.1172/JCI111096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Recker R. R., Kimmel D. B., Parfitt A. M., Davies K. M., Keshawarz N., Hinders S. Static and tetracycline-based bone histomorphometric data from 34 normal postmenopausal females. J Bone Miner Res. 1988 Apr;3(2):133–144. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.5650030203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggs B. L., Wahner H. W., Melton L. J., 3rd, Richelson L. S., Judd H. L., Offord K. P. Rates of bone loss in the appendicular and axial skeletons of women. Evidence of substantial vertebral bone loss before menopause. J Clin Invest. 1986 May;77(5):1487–1491. doi: 10.1172/JCI112462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vedi S., Compston J. E. Direct and indirect measurements of osteoid seam width in human iliac crest trabecular bone. Metab Bone Dis Relat Res. 1984;5(6):269–274. doi: 10.1016/0221-8747(84)90013-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vesterby A., Gundersen H. J., Melsen F., Mosekilde L. Normal postmenopausal women show iliac crest trabecular thickening on vertical sections. Bone. 1989;10(5):333–339. doi: 10.1016/8756-3282(89)90129-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vesterby A., Gundersen H. J., Melsen F. Star volume of marrow space and trabeculae of the first lumbar vertebra: sampling efficiency and biological variation. Bone. 1989;10(1):7–13. doi: 10.1016/8756-3282(89)90140-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakamatsu E., Sissons H. A. The cancellous bone of the iliac crest. Calcif Tissue Res. 1969;4(2):147–161. doi: 10.1007/BF02279116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein R. S., Hutson M. S. Decreased trabecular width and increased trabecular spacing contribute to bone loss with aging. Bone. 1987;8(3):137–142. doi: 10.1016/8756-3282(87)90012-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright C. D., Vedi S., Garrahan N. J., Stanton M., Duffy S. W., Compston J. E. Combined inter-observer and inter-method variation in bone histomorphometry. Bone. 1992;13(3):205–208. doi: 10.1016/8756-3282(92)90198-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



