Abstract
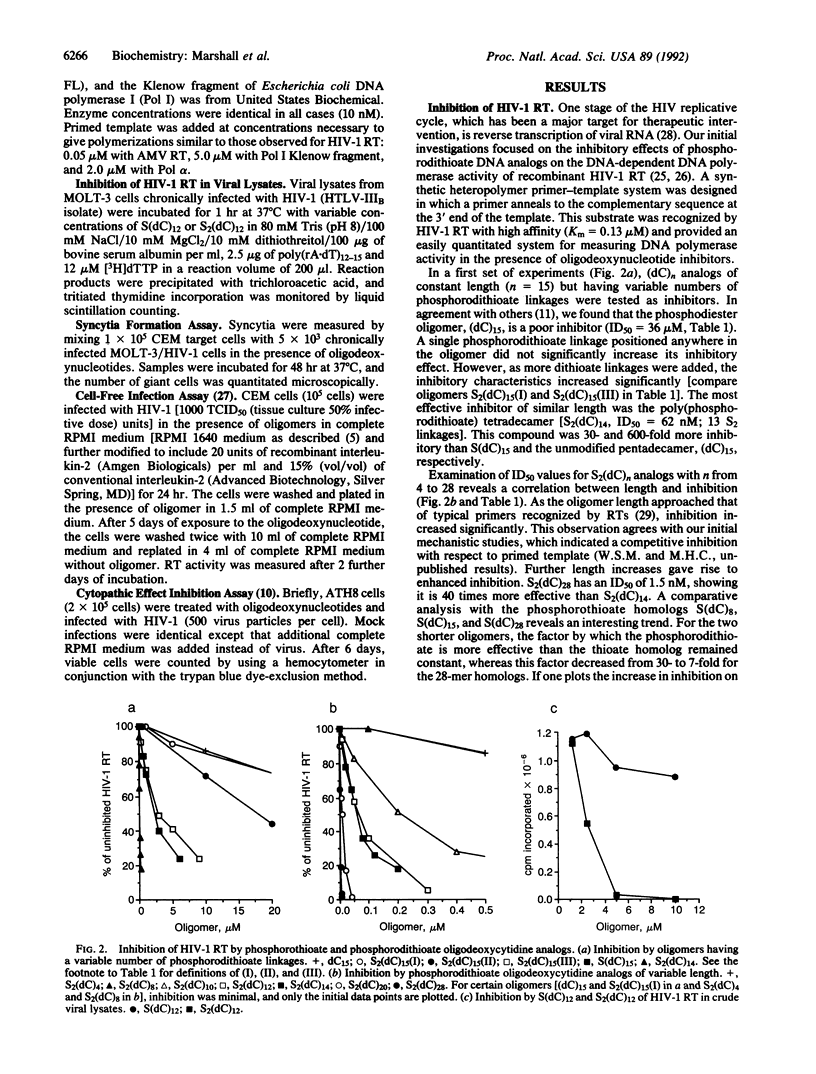
Phosphorothioate oligodeoxynucleotides exert a sequence-independent cytoprotective effect against human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1). We now report that phosphorodithioate-containing oligodeoxycytidines are very potent inhibitors of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase in vitro, as they exhibit an increasing inhibitory effect with length and number of phosphorodithioate internucleotide linkages. This inhibitory effect can be at least 30-fold greater with phosphorodithioate oligodeoxycytidine than for the corresponding phosphorothioate analog of similar length. In cell culture, phosphorodithioate oligodeoxycytidines are active inhibitors of syncytia formation and effectively inhibit de novo infection of target cells by HIV-1. Moreover, comparative experiments show that a deoxycytidine phosphorodithioate 14-mer is as effective an inhibitor of de novo infection as a phosphorothioate-containing 28-mer. Such potent inhibition by oligomers of relatively short length makes dithioate analogs an additional class of potential therapeutic agents against acquired immunodeficiency syndrome.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agrawal S., Goodchild J., Civeira M. P., Thornton A. H., Sarin P. S., Zamecnik P. C. Oligodeoxynucleoside phosphoramidates and phosphorothioates as inhibitors of human immunodeficiency virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7079–7083. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agrawal S., Ikeuchi T., Sun D., Sarin P. S., Konopka A., Maizel J., Zamecnik P. C. Inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus in early infected and chronically infected cells by antisense oligodeoxynucleotides and their phosphorothioate analogues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):7790–7794. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.7790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caruthers M. H. Gene synthesis machines: DNA chemistry and its uses. Science. 1985 Oct 18;230(4723):281–285. doi: 10.1126/science.3863253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cazenave C., Stein C. A., Loreau N., Thuong N. T., Neckers L. M., Subasinghe C., Hélène C., Cohen J. S., Toulmé J. J. Comparative inhibition of rabbit globin mRNA translation by modified antisense oligodeoxynucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jun 12;17(11):4255–4273. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.11.4255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark P. K., Ferris A. L., Miller D. A., Hizi A., Kim K. W., Deringer-Boyer S. M., Mellini M. L., Clark A. D., Jr, Arnold G. F., Lebherz W. B., 3rd HIV-1 reverse transcriptase purified from a recombinant strain of Escherichia coli. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1990 Jun;6(6):753–764. doi: 10.1089/aid.1990.6.753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalgleish A. G., Beverley P. C., Clapham P. R., Crawford D. H., Greaves M. F., Weiss R. A. The CD4 (T4) antigen is an essential component of the receptor for the AIDS retrovirus. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):763–767. doi: 10.1038/312763a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hizi A., McGill C., Hughes S. H. Expression of soluble, enzymatically active, human immunodeficiency virus reverse transcriptase in Escherichia coli and analysis of mutants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):1218–1222. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.1218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulka M., Smith C. C., Aurelian L., Fishelevich R., Meade K., Miller P., Ts'o P. O. Site specificity of the inhibitory effects of oligo(nucleoside methylphosphonate)s complementary to the acceptor splice junction of herpes simplex virus type 1 immediate early mRNA 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):6868–6872. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.6868. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loke S. L., Stein C. A., Zhang X. H., Mori K., Nakanishi M., Subasinghe C., Cohen J. S., Neckers L. M. Characterization of oligonucleotide transport into living cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3474–3478. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majumdar C., Stein C. A., Cohen J. S., Broder S., Wilson S. H. Stepwise mechanism of HIV reverse transcriptase: primer function of phosphorothioate oligodeoxynucleotide. Biochemistry. 1989 Feb 7;28(3):1340–1346. doi: 10.1021/bi00429a060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsukura M., Shinozuka K., Zon G., Mitsuya H., Reitz M., Cohen J. S., Broder S. Phosphorothioate analogs of oligodeoxynucleotides: inhibitors of replication and cytopathic effects of human immunodeficiency virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7706–7710. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsukura M., Zon G., Shinozuka K., Robert-Guroff M., Shimada T., Stein C. A., Mitsuya H., Wong-Staal F., Cohen J. S., Broder S. Regulation of viral expression of human immunodeficiency virus in vitro by an antisense phosphorothioate oligodeoxynucleotide against rev (art/trs) in chronically infected cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(11):4244–4248. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.4244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsuya H., Yarchoan R., Broder S. Molecular targets for AIDS therapy. Science. 1990 Sep 28;249(4976):1533–1544. doi: 10.1126/science.1699273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sodroski J., Goh W. C., Rosen C., Campbell K., Haseltine W. A. Role of the HTLV-III/LAV envelope in syncytium formation and cytopathicity. 1986 Jul 31-Aug 6Nature. 322(6078):470–474. doi: 10.1038/322470a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein C. A., Cohen J. S. Oligodeoxynucleotides as inhibitors of gene expression: a review. Cancer Res. 1988 May 15;48(10):2659–2668. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein C. A., Matsukura M., Subasinghe C., Broder S., Cohen J. S. Phosphorothioate oligodeoxynucleotides are potent sequence nonspecific inhibitors of de novo infection by HIV. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1989 Dec;5(6):639–646. doi: 10.1089/aid.1989.5.639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein C. A., Subasinghe C., Shinozuka K., Cohen J. S. Physicochemical properties of phosphorothioate oligodeoxynucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Apr 25;16(8):3209–3221. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.8.3209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson M. L., Zamecnik P. C. Inhibition of Rous sarcoma viral RNA translation by a specific oligodeoxyribonucleotide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):285–288. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamecnik P. C., Stephenson M. L. Inhibition of Rous sarcoma virus replication and cell transformation by a specific oligodeoxynucleotide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):280–284. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]