Abstract
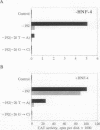
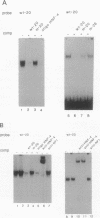
Hemophilia B Leyden is an X chromosome-linked bleeding disorder characterized by very low plasma levels of blood coagulation factor IX (fIX) during childhood. After puberty, plasma fIX levels gradually rise to a maximum of 60% of normal, probably under the influence of testosterone. Single point mutations in the fIX promoter region of hemophilia B Leyden patients have been reported at -20, -6, -5, +8 and +13. In addition, one promoter mutation (G----C at -26) has been detected that abolishes fIX expression throughout life (M. Ludwig, personal communication). We examined how one of the hemophilia B Leyden mutations (T----A at -20) and the G----C mutation at -26 interfere with fIX gene transcription. We report that the wild-type promoter of the human fIX gene contains a binding site (at nucleotides -34 to -10) for hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 (HNF-4), a member of the steroid hormone receptor superfamily of transcription factors. The binding of HNF-4 is disrupted by both the T----A mutation at -20 and the G----C mutation at -26. Whereas HNF-4 transactivates the wild-type promoter sequence in liver (HepG2) and non-liver (HeLa) cell types quite well, it transactivates the -20 mutated promoter to only a limited extent and the -26 mutated promoter not at all. These data suggest that HNF-4 is a major factor controlling fIX expression in the normal individual and that its inability to bind efficiently to the -20 T----A and the -26 G----C mutated promoter sequence results in hemophilia. Further, the severity of the hemophilia phenotype appears to be directly related to the degree of disruption of HNF-4 binding and transactivation.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Briët E., Bertina R. M., van Tilburg N. H., Veltkamp J. J. Hemophilia B Leyden: a sex-linked hereditary disorder that improves after puberty. N Engl J Med. 1982 Apr 1;306(13):788–790. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198204013061306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briët E., Wijnands M. C., Veltkamp J. J. The prophylactic treatment of hemophilia B Leyden with anabolic steroids. Ann Intern Med. 1985 Aug;103(2):225–226. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-103-2-225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa R. H., Grayson D. R., Darnell J. E., Jr Multiple hepatocyte-enriched nuclear factors function in the regulation of transthyretin and alpha 1-antitrypsin genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1415–1425. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crossley M., Brownlee G. G. Disruption of a C/EBP binding site in the factor IX promoter is associated with haemophilia B. Nature. 1990 May 31;345(6274):444–446. doi: 10.1038/345444a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edlund T., Walker M. D., Barr P. J., Rutter W. J. Cell-specific expression of the rat insulin gene: evidence for role of two distinct 5' flanking elements. Science. 1985 Nov 22;230(4728):912–916. doi: 10.1126/science.3904002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M. The steroid and thyroid hormone receptor superfamily. Science. 1988 May 13;240(4854):889–895. doi: 10.1126/science.3283939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forman B. M., Samuels H. H. Dimerization among nuclear hormone receptors. New Biol. 1990 Jul;2(7):587–594. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannelli F., Green P. M., High K. A., Sommer S., Lillicrap D. P., Ludwig M., Olek K., Reitsma P. H., Goossens M., Yoshioka A. Haemophilia B: database of point mutations and short additions and deletions--second edition. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Apr 25;19 (Suppl):2193–2219. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.suppl.2193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass C. K., Lipkin S. M., Devary O. V., Rosenfeld M. G. Positive and negative regulation of gene transcription by a retinoic acid-thyroid hormone receptor heterodimer. Cell. 1989 Nov 17;59(4):697–708. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90016-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorski K., Carneiro M., Schibler U. Tissue-specific in vitro transcription from the mouse albumin promoter. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):767–776. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90519-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbomel P., Bourachot B., Yaniv M. Two distinct enhancers with different cell specificities coexist in the regulatory region of polyoma. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):653–662. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90472-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Malley B. The steroid receptor superfamily: more excitement predicted for the future. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Mar;4(3):363–369. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-3-363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reijnen M. J., Bertina R. M., Reitsma P. H. Localization of transcription initiation sites in the human coagulation factor IX gene. FEBS Lett. 1990 Sep 17;270(1-2):207–210. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81269-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld P. J., Kelly T. J. Purification of nuclear factor I by DNA recognition site affinity chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 25;261(3):1398–1408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salier J. P., Hirosawa S., Kurachi K. Functional characterization of the 5'-regulatory region of human factor IX gene. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 25;265(12):7062–7068. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sladek F. M., Zhong W. M., Lai E., Darnell J. E., Jr Liver-enriched transcription factor HNF-4 is a novel member of the steroid hormone receptor superfamily. Genes Dev. 1990 Dec;4(12B):2353–2365. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.12b.2353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson A. R. Structure, function, and molecular defects of factor IX. Blood. 1986 Mar;67(3):565–572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L. H., Tsai S. Y., Sagami I., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Purification and characterization of chicken ovalbumin upstream promoter transcription factor from HeLa cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 25;262(33):16080–16086. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]