Abstract
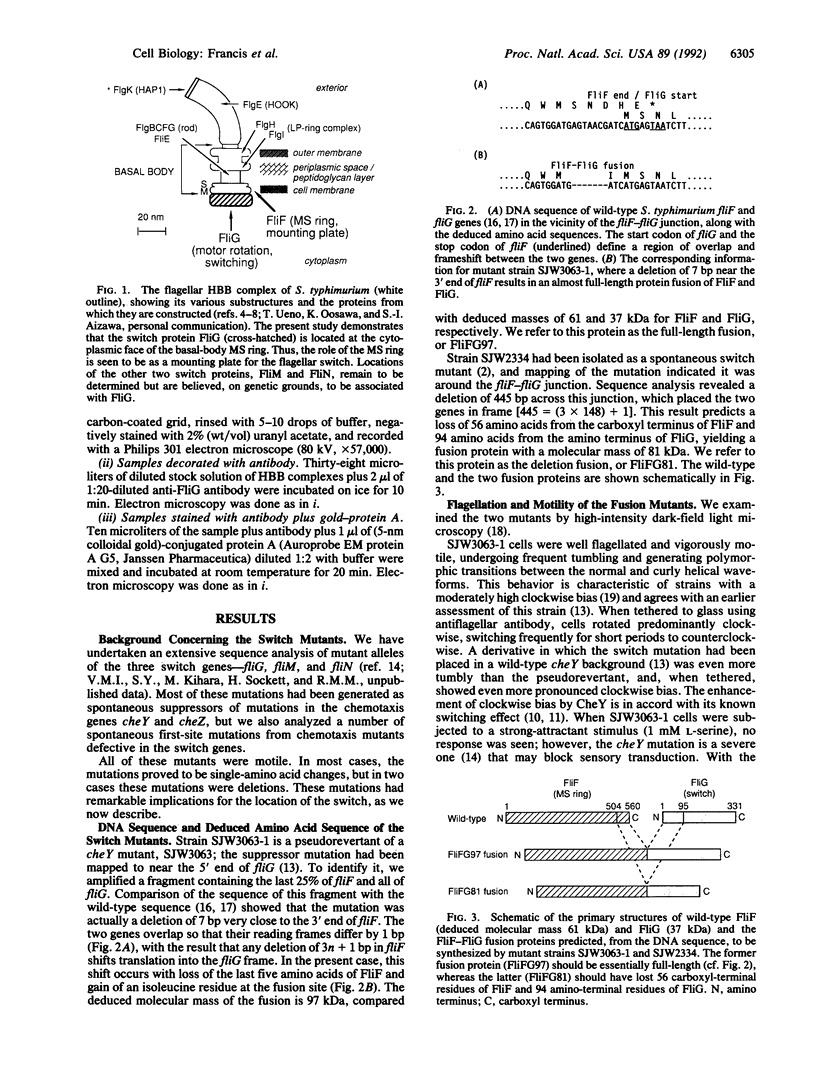
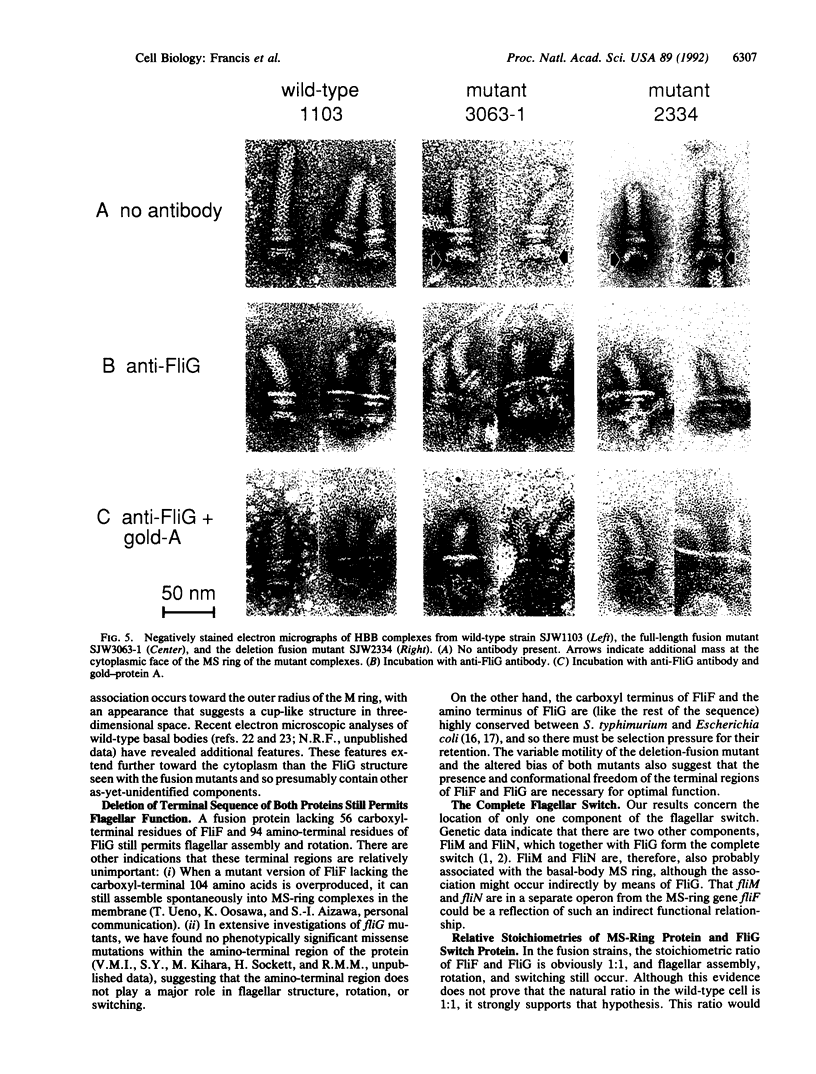
The direction of rotation of the bacterial flagellum is determined by the flagellar switch. We have localized FliG, one of the switch proteins of Salmonella typhimurium, to the cytoplasmic face of the M ring of the flagellar basal body. This localization was made possible by the discovery of two spontaneous mutants in which the fliF (M ring) and fliG (switch) genes were fused in-frame. In the first mutant, a deletion of 7 base pairs at the 3' end of fliF resulted in an essentially full-length fusion protein. In the second mutant, a larger deletion resulted in a fusion in which 56 amino acids from the carboxyl terminus of FliF and 94 amino acids from the amino terminus of FliG were lost. Both strains were motile and underwent switching; the first strain had a clockwise bias, and the second strain had a counterclockwise bias. Gel electrophoresis and immunoblotting of isolated hook-basal-body complexes verified that they contained the fusion proteins. Electron microscopy revealed additional mass at the cytoplasmic face of the M ring, which could be decorated with anti-FliG antibody. We conclude that the natural location for FliG is at the cytoplasmic face of the M ring and that the stoichiometric ratio between FliF and FliG in wild-type cells is probably 1:1.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aizawa S. I., Dean G. E., Jones C. J., Macnab R. M., Yamaguchi S. Purification and characterization of the flagellar hook-basal body complex of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1985 Mar;161(3):836–849. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.3.836-849.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg H. C. Bacterial behaviour. Nature. 1975 Apr 3;254(5499):389–392. doi: 10.1038/254389a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blair D. F., Berg H. C. Restoration of torque in defective flagellar motors. Science. 1988 Dec 23;242(4886):1678–1681. doi: 10.1126/science.2849208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blair D. F. The bacterial flagellar motor. Semin Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;1(2):75–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DePamphilis M. L., Adler J. Attachment of flagellar basal bodies to the cell envelope: specific attachment to the outer, lipopolysaccharide membrane and the cyoplasmic membrane. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jan;105(1):396–407. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.1.396-407.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driks A., DeRosier D. J. Additional structures associated with bacterial flagellar basal body. J Mol Biol. 1990 Feb 20;211(4):669–672. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90063-R. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homma M., Aizawa S., Dean G. E., Macnab R. M. Identification of the M-ring protein of the flagellar motor of Salmonella typhimurium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7483–7487. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homma M., Kutsukake K., Hasebe M., Iino T., Macnab R. M. FlgB, FlgC, FlgF and FlgG. A family of structurally related proteins in the flagellar basal body of Salmonella typhimurium. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jan 20;211(2):465–477. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90365-S. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C. J., Homma M., Macnab R. M. Identification of proteins of the outer (L and P) rings of the flagellar basal body of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1987 Apr;169(4):1489–1492. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.4.1489-1492.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C. J., Homma M., Macnab R. M. L-, P-, and M-ring proteins of the flagellar basal body of Salmonella typhimurium: gene sequences and deduced protein sequences. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jul;171(7):3890–3900. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.7.3890-3900.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C. J., Macnab R. M. Flagellar assembly in Salmonella typhimurium: analysis with temperature-sensitive mutants. J Bacteriol. 1990 Mar;172(3):1327–1339. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.3.1327-1339.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C. J., Macnab R. M., Okino H., Aizawa S. Stoichiometric analysis of the flagellar hook-(basal-body) complex of Salmonella typhimurium. J Mol Biol. 1990 Mar 20;212(2):377–387. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90132-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan S., Khan I. H., Reese T. S. New structural features of the flagellar base in Salmonella typhimurium revealed by rapid-freeze electron microscopy. J Bacteriol. 1991 May;173(9):2888–2896. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.9.2888-2896.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kihara M., Homma M., Kutsukake K., Macnab R. M. Flagellar switch of Salmonella typhimurium: gene sequences and deduced protein sequences. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jun;171(6):3247–3257. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.6.3247-3257.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo S. C., Koshland D. E., Jr Roles of cheY and cheZ gene products in controlling flagellar rotation in bacterial chemotaxis of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1987 Mar;169(3):1307–1314. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.3.1307-1314.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macnab R. M. Examination of bacterial flagellation by dark-field microscopy. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Sep;4(3):258–265. doi: 10.1128/jcm.4.3.258-265.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macnab R. M., Ornston M. K. Normal-to-curly flagellar transitions and their role in bacterial tumbling. Stabilization of an alternative quaternary structure by mechanical force. J Mol Biol. 1977 May 5;112(1):1–30. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80153-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magariyama Y., Yamaguchi S., Aizawa S. Genetic and behavioral analysis of flagellar switch mutants of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1990 Aug;172(8):4359–4369. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.8.4359-4369.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller V., Jones C. J., Kawagishi I., Aizawa S., Macnab R. M. Characterization of the fliE genes of Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium and identification of the FliE protein as a component of the flagellar hook-basal body complex. J Bacteriol. 1992 Apr;174(7):2298–2304. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.7.2298-2304.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson J. S., Parker S. R., Talbert P. B., Houts S. E. Interactions between chemotaxis genes and flagellar genes in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jul;155(1):265–274. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.1.265-274.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravid S., Matsumura P., Eisenbach M. Restoration of flagellar clockwise rotation in bacterial envelopes by insertion of the chemotaxis protein CheY. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7157–7161. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sockett H., Yamaguchi S., Kihara M., Irikura V. M., Macnab R. M. Molecular analysis of the flagellar switch protein FliM of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1992 Feb;174(3):793–806. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.3.793-806.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sosinsky G. E., Francis N. R., DeRosier D. J., Wall J. S., Simon M. N., Hainfeld J. Mass determination and estimation of subunit stoichiometry of the bacterial hook-basal body flagellar complex of Salmonella typhimurium by scanning transmission electron microscopy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 1;89(11):4801–4805. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.11.4801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stallmeyer M. J., Aizawa S., Macnab R. M., DeRosier D. J. Image reconstruction of the flagellar basal body of Salmonella typhimurium. J Mol Biol. 1989 Feb 5;205(3):519–528. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90223-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi S., Aizawa S., Kihara M., Isomura M., Jones C. J., Macnab R. M. Genetic evidence for a switching and energy-transducing complex in the flagellar motor of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1986 Dec;168(3):1172–1179. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.3.1172-1179.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi S., Fujita H., Ishihara A., Aizawa S., Macnab R. M. Subdivision of flagellar genes of Salmonella typhimurium into regions responsible for assembly, rotation, and switching. J Bacteriol. 1986 Apr;166(1):187–193. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.1.187-193.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]