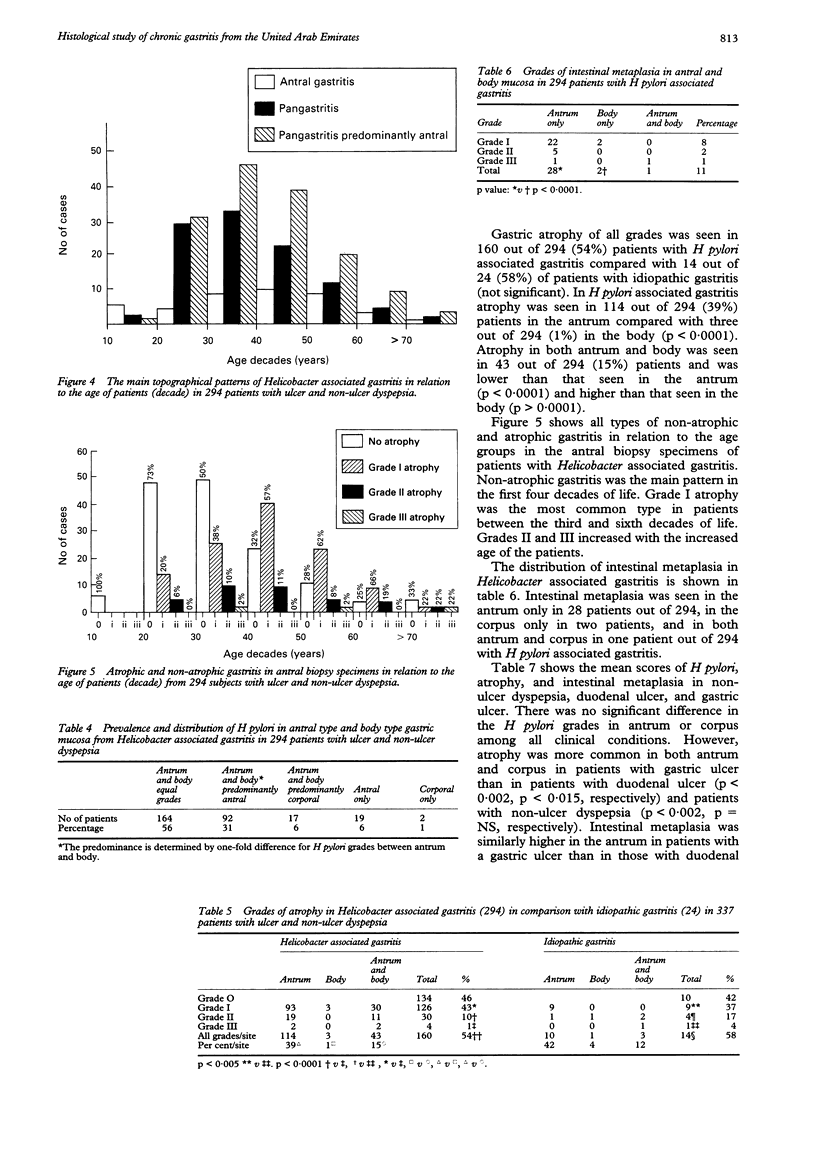
Abstract
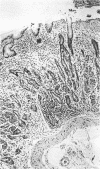
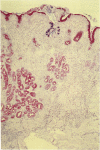
AIMS--To determine the prevalence of Helicobacter pylori in five main nationality groups with gastric ulcer, duodenal ulcer, and non-ulcer dyspepsia; and to determine the histopathological types of gastritis and assess the graded variables of Helicobacter associated gastritis. METHODS--Gastric antral and corpus biopsy specimens from 437 patients were examined for the prevalence of H pylori, 337 of which were classified and graded histologically according to the Sydney system. RESULTS--The overall colonisation rate of H pylori was 90%, and there was no significant difference between groups of different ethnic origins. The colonisation rates were 99%, 89%, and 78% in patients with duodenal ulcer, non-ulcer dyspepsia, and gastric ulcer, respectively. Helicobacter associated gastritis was the most common form of chronic gastritis (87%). H pylori density was greater in the antrum than the body. Gastric atrophy in helicobacter associated gastritis was seen in 54% of the cases (43% grade I, 10% grade II, 1% grade III) and increased the older the patients. Atrophy of the corpus alone was very rare (1%). Atrophy and intestinal metaplasia were more prevalent in patients with gastric ulcer than duodenal ulcer. CONCLUSION--The colonisation rate of H pylori was similar in the five groups studied and was almost invariably present in gastric biopsy specimens in patients with duodenal ulcer. H pylori associated gastritis was the most common form of gastritis. Atrophy was mainly of low grade and increased the older the patient.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blaser M. J. Gastric Campylobacter-like organisms, gastritis, and peptic ulcer disease. Gastroenterology. 1987 Aug;93(2):371–383. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(87)91028-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J. Helicobacter pylori and the pathogenesis of gastroduodenal inflammation. J Infect Dis. 1990 Apr;161(4):626–633. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.4.626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britt D. P., Barakat M. H., Tungekar M. F., Painchaud S. M., Adlouni M., Kern K., Malhas L. Helicobacter pylori in dyspeptic patients in Kuwait. J Clin Pathol. 1990 Dec;43(12):987–991. doi: 10.1136/jcp.43.12.987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheli R., Giacosa A. Chronic atrophic gastritis and gastric mucosal atrophy--one and the same. Gastrointest Endosc. 1983 Feb;29(1):23–25. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5107(83)72493-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Correa P. Chronic gastritis: a clinico-pathological classification. Am J Gastroenterol. 1988 May;83(5):504–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diomande M. I., Fléjou J. F., Potet F., Dago-Akribi A., Ouattara D., Kadjo K., Niamkey E., Beaumel A., Gbe K., Beda B. Y. Gastrite chronique et infection à Helicobacter pylori en Côte-d'Ivoire. Etude d'une série de 277 patients symptomatiques. Gastroenterol Clin Biol. 1991;15(10):711–716. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon M. F. Helicobacter pylori and peptic ulceration: histopathological aspects. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1991 Mar-Apr;6(2):125–130. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.1991.tb01451.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flejou J. F., Bahame P., Smith A. C., Stockbrugger R. W., Rode J., Price A. B. Pernicious anaemia and Campylobacter like organisms; is the gastric antrum resistant to colonisation? Gut. 1989 Jan;30(1):60–64. doi: 10.1136/gut.30.1.60. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong T. L., Dooley C. P., Dehesa M., Cohen H., Carmel R., Fitzgibbons P. L., Perez-Perez G. I., Blaser M. J. Helicobacter pylori infection in pernicious anemia: a prospective controlled study. Gastroenterology. 1991 Feb;100(2):328–332. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(91)90199-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin C. S., Armstrong J. A., Marshall B. J. Campylobacter pyloridis, gastritis, and peptic ulceration. J Clin Pathol. 1986 Apr;39(4):353–365. doi: 10.1136/jcp.39.4.353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham D. Y. Helicobacter pylori: its epidemiology and its role in duodenal ulcer disease. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1991 Mar-Apr;6(2):105–113. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.1991.tb01448.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haot J., Hamichi L., Wallez L., Mainguet P. Lymphocytic gastritis: a newly described entity: a retrospective endoscopic and histological study. Gut. 1988 Sep;29(9):1258–1264. doi: 10.1136/gut.29.9.1258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihamäki T., Kekki M., Sipponen P., Siurala M. The sequelae and course of chronic gastritis during a 30- to 34-year bioptic follow-up study. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1985 May;20(4):485–491. doi: 10.3109/00365528509089685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerzy Glass G. B., Pitchumoni C. S. Structural and ultrastructural alterations, exfoliative cytology and enzyme cytochemistry and histochemistry, proliferation kinetics, immunological derangements and other causes, and clinical associations and sequallae. Hum Pathol. 1975 Mar;6(2):219–250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karnes W. E., Jr, Samloff I. M., Siurala M., Kekki M., Sipponen P., Kim S. W., Walsh J. H. Positive serum antibody and negative tissue staining for Helicobacter pylori in subjects with atrophic body gastritis. Gastroenterology. 1991 Jul;101(1):167–174. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(91)90474-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kekki M., Siurala M., Varis K., Sipponen P., Sistonen P., Nevanlinna H. R. Classification principles and genetics of chronic gastritis. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1987;141:1–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein P. D., Graham D. Y., Gaillour A., Opekun A. R., Smith E. O. Water source as risk factor for Helicobacter pylori infection in Peruvian children. Gastrointestinal Physiology Working Group. Lancet. 1991 Jun 22;337(8756):1503–1506. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)93196-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maaroos H. I., Kekki M., Villako K., Sipponen P., Tamm A., Sadeniemi L. The occurrence and extent of Helicobacter pylori colonization and antral and body gastritis profiles in an Estonian population sample. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1990 Oct;25(10):1010–1017. doi: 10.3109/00365529008997627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall B. J., McGechie D. B., Rogers P. A., Glancy R. J. Pyloric Campylobacter infection and gastroduodenal disease. Med J Aust. 1985 Apr 15;142(8):439–444. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1985.tb113444.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor H. J., Axon A. T., Dixon M. F. Campylobacter-like organisms unusual in type A (pernicious anaemia) gastritis. Lancet. 1984 Nov 10;2(8411):1091–1091. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)91523-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price A. B. The Sydney System: histological division. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1991 May-Jun;6(3):209–222. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.1991.tb01468.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauws E. A., Langenberg W., Houthoff H. J., Zanen H. C., Tytgat G. N. Campylobacter pyloridis-associated chronic active antral gastritis. A prospective study of its prevalence and the effects of antibacterial and antiulcer treatment. Gastroenterology. 1988 Jan;94(1):33–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rugge M., Di Mario F., Cassaro M., Baffa R., Farinati F., Rubio J., Jr, Ninfo V. Pathology of the gastric antrum and body associated with Helicobacter pylori infection in non-ulcerous patients: is the bacterium a promoter of intestinal metaplasia? Histopathology. 1993 Jan;22(1):9–15. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1993.tb00062.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sipponen P., Seppälä K., Aärynen M., Helske T., Kettunen P. Chronic gastritis and gastroduodenal ulcer: a case control study on risk of coexisting duodenal or gastric ulcer in patients with gastritis. Gut. 1989 Jul;30(7):922–929. doi: 10.1136/gut.30.7.922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobala G. M., King R. F., Axon A. T., Dixon M. F. Reflux gastritis in the intact stomach. J Clin Pathol. 1990 Apr;43(4):303–306. doi: 10.1136/jcp.43.4.303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stolte M., Heilmann K. L. Neue Klassifikation und Graduierung der Gastritis. Leber Magen Darm. 1989 Sep;19(5):220–226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland R. G., Mackay I. R. A reappraisal of the nature and significance of chronic atrophic gastritis. Am J Dig Dis. 1973 May;18(5):426–440. doi: 10.1007/BF01071995. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland R. G. The Sydney System: auto-immune gastritis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1991 May-Jun;6(3):238–243. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.1991.tb01471.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taha A. S., Nakshabendi I., Lee F. D., Sturrock R. D., Russell R. I. Chemical gastritis and Helicobacter pylori related gastritis in patients receiving non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: comparison and correlation with peptic ulceration. J Clin Pathol. 1992 Feb;45(2):135–139. doi: 10.1136/jcp.45.2.135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trier J. S. Morphology of the gastric mucosa in patients with ulcer diseases. Am J Dig Dis. 1976 Feb;21(2):138–140. doi: 10.1007/BF01072059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitehead R., Truelove S. C., Gear M. W. The histological diagnosis of chronic gastritis in fibreoptic gastroscope biopsy specimens. J Clin Pathol. 1972 Jan;25(1):1–11. doi: 10.1136/jcp.25.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt J. I., Dixon M. F. Campylobacter-associated chronic gastritis. Pathol Annu. 1990;25(Pt 1):75–98. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt J. I., Dixon M. F. Chronic gastritis--a pathogenetic approach. J Pathol. 1988 Feb;154(2):113–124. doi: 10.1002/path.1711540203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yardley J. H., Paull G. Campylobacter pylori: a newly recognized infectious agent in the gastrointestinal tract. Am J Surg Pathol. 1988;12 (Suppl 1):89–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaitoun A. M. Use of Romanowsky type (Diff-3) stain for detecting Helicobacter pylori in smears and tissue sections. J Clin Pathol. 1992 May;45(5):448–449. doi: 10.1136/jcp.45.5.448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- al-Moagel M. A., Evans D. G., Abdulghani M. E., Adam E., Evans D. J., Jr, Malaty H. M., Graham D. Y. Prevalence of Helicobacter (formerly Campylobacter) pylori infection in Saudia Arabia, and comparison of those with and without upper gastrointestinal symptoms. Am J Gastroenterol. 1990 Aug;85(8):944–948. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Guneid A., el-Sherif A. M., Murray-Lyon I. M., Zureikat N., Shousha S. Effect of chewing Qat on mucosal histology and prevalence of Helicobacter pylori in the oesophagus, stomach and duodenum of Yemeni patients. Histopathology. 1991 Nov;19(5):437–443. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1991.tb00234.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]