Abstract
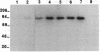
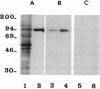
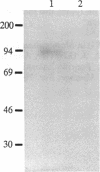
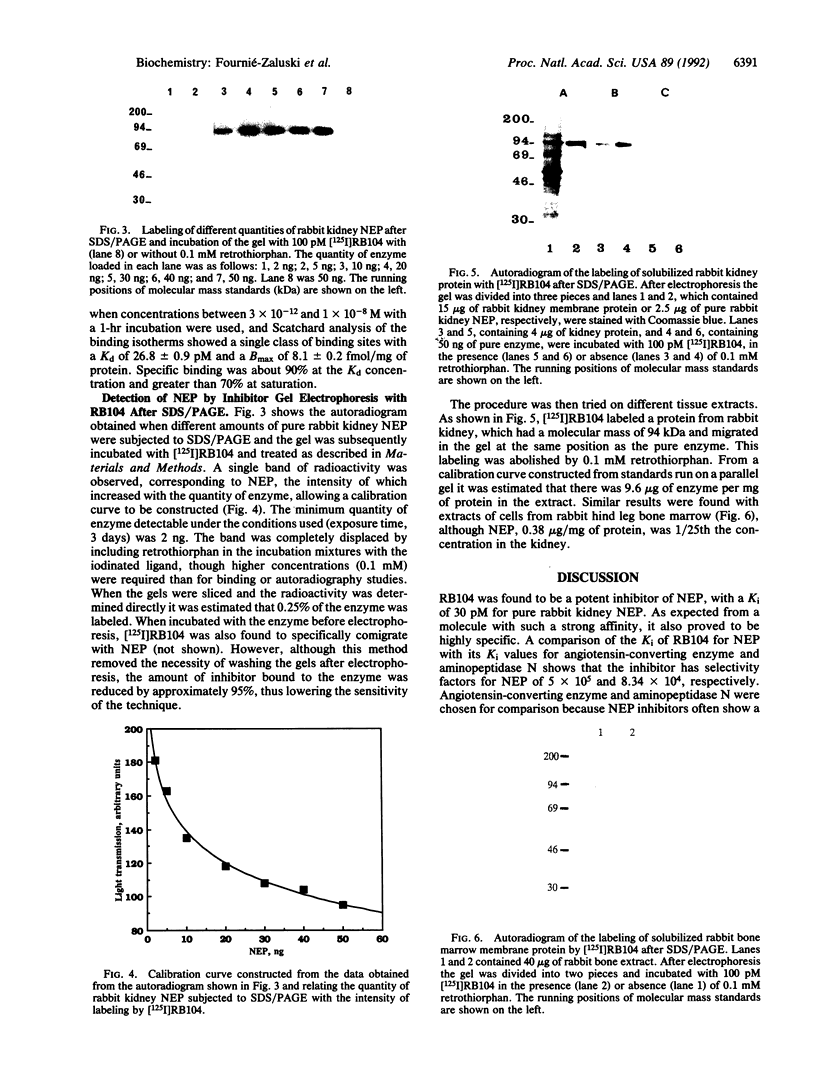
Neutral endopeptidase 24.11, also known as the common acute lymphoblastic leukemia antigen, is a zinc metallopeptidase involved in the inactivation of biologically active peptides, such as the enkephalins and atrial natriuretic peptide. The highly potent radiolabeled inhibitor 2-((3-[125I]iodo-4-hydroxy)phenylmethyl)-4-N-[3-(hydroxyamino-3-oxo-1- phenylmethyl)propyl]amino-4-oxobutanoic acid ([125I]RB104; Ki = 30 pM) has been developed for the enzyme. [125I]RB104 is highly specific, its Ki for another widely distributed zinc peptidase, angiotensin-converting enzyme, being 15 microM. In binding studies using rat brain slices, [125I]RB104 was shown to have a high affinity (Kd = 300 +/- 20 pM) and high specific binding at the Kd concentration (90%). With rat brain homogenates the Kd of [125I]RB104 was 26.8 +/- 0.9 pM, close to the kinetically derived Kd, 7.0 +/- 0.8 pM. Using the inhibitor, we have developed a simple, rapid, and quantitative technique to detect low nanogram quantities of the endopeptidase directly from tissue extracts after SDS/PAGE. The method has been used to show the presence of low quantities of the enzyme in rabbit bone marrow. Apart from its sensitivity, "inhibitor gel electrophoresis" using [125I]RB104 has the advantage over immunohistochemical methods of being able to label the enzyme in all tissues and species. It will therefore be of great value in determining the exact role of this important regulatory peptidase in a number of biological systems. Moreover, this one-step characterization of neutral endopeptidase 24.11 could be extended to other zinc metallopeptidases such as angiotensin-converting enzyme or collagenases, and inhibitors with affinities as high as RB104 could open the way to visualization of zinc metallopeptidases in different tissues by electron microscopy.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aubry M., Berteloot A., Beaumont A., Roques B. P., Crine P. The use of a monoclonal antibody for the rapid purification of kidney neutral endopeptidase ("enkephalinase") solubilized in octyl glucoside. Biochem Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;65(4):398–404. doi: 10.1139/o87-050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaumont A., Brouet J. C., Roques B. P. Neutral endopeptidase 24.11 and angiotensin converting enzyme like activity in CALLA positive and CALLA negative lymphoid cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 May 15;160(3):1323–1329. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(89)80148-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fournie-Zaluski M. C., Lucas E., Waksman G., Roques B. P. Differences in the structural requirements for selective interaction with neutral metalloendopeptidase (enkephalinase) or angiotensin-converting enzyme. Molecular investigation by use of new thiol inhibitors. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Mar 1;139(2):267–274. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08003.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fournié-Zaluski M. C., Hernandez J. F., Soleilhac J. M., Renwart N., Peyroux J., Xie J., Roques B. P. Enkephalin-degrading enzyme inhibitors. Crucial role of the C-terminal residue on the inhibitory potencies of retro-hydroxamate dipeptides. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1989 Feb;33(2):146–153. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1989.tb00200.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gee N. S., Bowes M. A., Buck P., Kenny A. J. An immunoradiometric assay for endopeptidase-24.11 shows it to be a widely distributed enzyme in pig tissues. Biochem J. 1985 May 15;228(1):119–126. doi: 10.1042/bj2280119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helene A., Milhiet P. E., Haouas H., Boucheix C., Beaumont A., Roques B. P. Effects of monoclonal antibodies raised against the common acute lymphoblastic leukemia antigen on endopeptidase-24.11 activity. Biochem Pharmacol. 1992 Feb 18;43(4):809–814. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(92)90247-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeBien T. W., McCormack R. T. The common acute lymphoblastic leukemia antigen (CD10)--emancipation from a functional enigma. Blood. 1989 Feb 15;73(3):625–635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letarte M., Vera S., Tran R., Addis J. B., Onizuka R. J., Quackenbush E. J., Jongeneel C. V., McInnes R. R. Common acute lymphocytic leukemia antigen is identical to neutral endopeptidase. J Exp Med. 1988 Oct 1;168(4):1247–1253. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.4.1247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mailleux P., Przedborski S., Beaumont A., Verslijpe M., Depierreux M., Levivier M., Kitabgi P., Roques B. P., Vanderhaeghen J. J. Neurotensin high affinity binding sites and endopeptidase 24.11 are present respectively in the meningothelial and in the fibroblastic components of human meningiomas. Peptides. 1990 Nov-Dec;11(6):1245–1253. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(90)90159-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malfroy B., Kuang W. J., Seeburg P. H., Mason A. J., Schofield P. R. Molecular cloning and amino acid sequence of human enkephalinase (neutral endopeptidase). FEBS Lett. 1988 Feb 29;229(1):206–210. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80828-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsas R., Kenny A. J., Turner A. J. An immunohistochemical study of endopeptidase-24.11 ("enkephalinase") in the pig nervous system. Neuroscience. 1986 Aug;18(4):991–1012. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(86)90113-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murthy K. K., Thibault G., Schiffrin E. L., Garcia R., Chartier L., Gutkowska J., Genest J., Cantin M. Disappearance of atrial natriuretic factor from circulation in the rat. Peptides. 1986 Mar-Apr;7(2):241–246. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(86)90220-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard H., De la Baume S., Bouthenet M. L., Schwartz J. C., Ronco P., Verroust P. Characterisation of two probes for the localisation of enkephalinase in rat brain: [3H]thiorphan and a 125I-labeled monoclonal antibody. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Jan 13;133(2):155–164. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90146-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Relton J. M., Gee N. S., Matsas R., Turner A. J., Kenny A. J. Purification of endopeptidase-24.11 ('enkephalinase') from pig brain by immunoadsorbent chromatography. Biochem J. 1983 Dec 1;215(3):519–523. doi: 10.1042/bj2150519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronco P., Pollard H., Galceran M., Delauche M., Schwartz J. C., Verroust P. Distribution of enkephalinase (membrane metalloendopeptidase, E.C. 3.4.24.11) in rat organs. Detection using a monoclonal antibody. Lab Invest. 1988 Feb;58(2):210–217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roques B. P., Beaumont A. Neutral endopeptidase-24.11 inhibitors: from analgesics to antihypertensives? Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1990 Jun;11(6):245–249. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(90)90252-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roques B. P., Fournie-Zaluski M. C. Enkephalin degrading enzyme inhibitors: a physiological way to new analgesics and psychoactive agents. NIDA Res Monogr. 1986;70:128–154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roques B. P., Fournié-Zaluski M. C., Soroca E., Lecomte J. M., Malfroy B., Llorens C., Schwartz J. C. The enkephalinase inhibitor thiorphan shows antinociceptive activity in mice. Nature. 1980 Nov 20;288(5788):286–288. doi: 10.1038/288286a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roques B. P., Lucas-Soroca E., Chaillet P., Costentin J., Fournié-Zaluski M. C. Complete differentiation between enkephalinase and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition by retro-thiorphan. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3178–3182. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sales N., Dutriez I., Maziere B., Ottaviani M., Roques B. P. Neutral endopeptidase 24.11 in rat peripheral tissues: comparative localization by 'ex vivo' and 'in vitro' autoradiography. Regul Pept. 1991 Apr 25;33(2):209–222. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(91)90215-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato M., Ikeda K., Haga S., Allsop D., Ishii T. A monoclonal antibody to common acute lymphoblastic leukemia antigen (neutral endopeptidase) immunostains senile plaques in the brains of patients with Alzheimer's disease. Neurosci Lett. 1991 Jan 2;121(1-2):271–273. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(91)90702-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan J., Johnson A. R. Detection and analysis of neutral endopeptidase from tissues with substrate gel electrophoresis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Jul 14;162(1):300–307. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)91996-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel Z., Altstein M. The adsorption of enkephalin to porous polystyrene beads: a simple assay for enkephalin hydrolysis. FEBS Lett. 1977 Aug 15;80(2):332–336. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80469-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waksman G., Bouboutou R., Devin J., Besselievre R., Fournie-Zaluski M. C., Roques B. P. Binding of the bidentate inhibitor [3H]HACBO-Gly to the rat brain neutral endopeptidase "enkephalinase". Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Aug 30;131(1):262–268. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91797-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waksman G., Hamel E., Bouboutou R., Besselièvre R., Fournié-Zaluski M. C., Roques B. P. Distribution régionale de l'enképhalinase dans le cerveau du rat par autoradiographie. C R Acad Sci III. 1984;299(14):613–615. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waksman G., Hamel E., Fournié-Zaluski M. C., Roques B. P. Autoradiographic comparison of the distribution of the neutral endopeptidase "enkephalinase" and of mu and delta opioid receptors in rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1523–1527. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]