Abstract
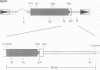
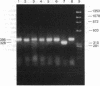
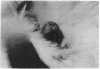
The transforming (onc) genes of oncogenic retroviruses share most or all of their coding sequences with normal cellular genes termed proto-onc genes. The viral genes differ from proto-onc genes in virus-specific promoters and in various point mutations and substitutions of cell-derived coding regions. In view of the structural similarities between viral oncogenes and cellular proto-onc genes, the hypothesis has been advanced that proto-onc genes become cellular cancer genes if they have suffered mutations. Indeed, point mutations and substitutions have been observed in the proto-onc genes of some cancers. However, the hypothesis has been difficult to prove because mutated proto-onc genes from tumors do not transform diploid cells. Moreover, owing to the popularity of this hypothesis, even viral oncogenes are thought to derive transforming function from mutations of this cell-derived coding region. A competing hypothesis proposes that enhanced expression from retroviral promoters is necessary and sufficient for oncogenic function of proto-onc genes. To distinguish between these hypotheses we have tested tumorigenicity of RpSV, a synthetic retrovirus with the normal proto-src coding region in a vector derived from Rous sarcoma virus (RSV). In addition, we have tested the role of RSV-specific src point mutations on the tumorigenicity of RpSV. It was found that RpSV with an unmutated proto-src coding region is tumorigenic in chickens and that tumorigenicity is enhanced by RSV-specific src point mutations. It is concluded that retroviral promoters are essential for the transforming function of viral oncogenes and that certain point mutations merely supplement their transforming function. Thus retroviral onc genes are not models for the hypothesis that mutated, but transcriptionally normal, proto-onc genes of certain tumors are cancer genes.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ames B. N. Identifying environmental chemicals causing mutations and cancer. Science. 1979 May 11;204(4393):587–593. doi: 10.1126/science.373122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbacid M. ras genes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:779–827. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.004023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. M. Enemies within: the genesis of retrovirus oncogenes. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):5–6. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90263-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. M. Molecular themes in oncogenesis. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):235–248. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90636-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. M. Retroviruses and cancer genes. Adv Cancer Res. 1982;37:1–32. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60880-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. M. The molecular genetics of cancer. Science. 1987 Jan 16;235(4786):305–311. doi: 10.1126/science.3541204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cairns J. The origin of human cancers. Nature. 1981 Jan 29;289(5796):353–357. doi: 10.1038/289353a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canaani E., Helm K. V., Duesberg P. Evidence for 30-40S RNA as precursor of the 60-70S RNA of Rous sarcoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Feb;70(2):401–405. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.2.401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborty A. K., Cichutek K., Duesberg P. H. Transforming function of proto-ras genes depends on heterologous promoters and is enhanced by specific point mutations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2217–2221. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cichutek K., Duesberg P. H. Harvey ras genes transform without mutant codons, apparently activated by truncation of a 5' exon (exon -1). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2340–2344. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cichutek K., Duesberg P. H. Recombinant BALB and Harvey sarcoma viruses with normal proto-ras-coding regions transform embryo cells in culture and cause tumors in mice. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1377–1383. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1377-1383.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duesberg P. H. Cancer genes: rare recombinants instead of activated oncogenes (a review). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2117–2124. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duesberg P. H. Physical properties of Rous Sarcoma Virus RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Aug;60(4):1511–1518. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.4.1511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duesberg P. H., Schwartz J. R. Latent viruses and mutated oncogenes: no evidence for pathogenicity. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1992;43:135–204. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)61047-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodrich D. W., Duesberg P. H. Retroviral recombination during reverse transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(6):2052–2056. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.6.2052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T. A tail of two src's: mutatis mutandis. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):1–4. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90745-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iba H., Takeya T., Cross F. R., Hanafusa T., Hanafusa H. Rous sarcoma virus variants that carry the cellular src gene instead of the viral src gene cannot transform chicken embryo fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(14):4424–4428. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.14.4424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. H., Bister K., Pawson A., Robins T., Moscovici C., Duesberg P. H. Fujinami sarcoma virus: an avian RNA tumor virus with a unique transforming gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):2018–2022. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.2018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker R. C., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Expression of v-src and chicken c-src in rat cells demonstrates qualitative differences between pp60v-src and pp60c-src. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):131–139. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90308-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROUS P. Surmise and fact on the nature of cancer. Nature. 1959 May 16;183(4672):1357–1361. doi: 10.1038/1831357a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy E. P., Reynolds R. K., Santos E., Barbacid M. A point mutation is responsible for the acquisition of transforming properties by the T24 human bladder carcinoma oncogene. Nature. 1982 Nov 11;300(5888):149–152. doi: 10.1038/300149a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rous P. The challenge to man of the neoplastic cell. Science. 1967 Jul 7;157(3784):24–28. doi: 10.1126/science.157.3784.24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin H. Is somatic mutation the major mechanism of malignant transformation? J Natl Cancer Inst. 1980 May;64(5):995–1000. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeburg P. H., Colby W. W., Capon D. J., Goeddel D. V., Levinson A. D. Biological properties of human c-Ha-ras1 genes mutated at codon 12. Nature. 1984 Nov 1;312(5989):71–75. doi: 10.1038/312071a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanbridge E. J. Human tumor suppressor genes. Annu Rev Genet. 1990;24:615–657. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.24.120190.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanbridge E. J. Identifying tumor suppressor genes in human colorectal cancer. Science. 1990 Jan 5;247(4938):12–13. doi: 10.1126/science.2403692. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss B. S. The origin of point mutations in human tumor cells. Cancer Res. 1992 Jan 15;52(2):249–253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabin C. J., Bradley S. M., Bargmann C. I., Weinberg R. A., Papageorge A. G., Scolnick E. M., Dhar R., Lowy D. R., Chang E. H. Mechanism of activation of a human oncogene. Nature. 1982 Nov 11;300(5888):143–149. doi: 10.1038/300143a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabin C. J., Weinberg R. A. Analysis of viral and somatic activations of the cHa-ras gene. J Virol. 1985 Jan;53(1):260–265. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.1.260-265.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temin H. M. Evolution of cancer genes as a mutation-driven process. Cancer Res. 1988 Apr 1;48(7):1697–1701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varmus H. E. The molecular genetics of cellular oncogenes. Annu Rev Genet. 1984;18:553–612. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.18.120184.003005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velu T. J., Vass W. C., Lowy D. R., Tambourin P. E. Harvey murine sarcoma virus: influences of coding and noncoding sequences on cell transformation in vitro and oncogenicity in vivo. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1384–1392. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1384-1392.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelstein B., Fearon E. R., Hamilton S. R., Kern S. E., Preisinger A. C., Leppert M., Nakamura Y., White R., Smits A. M., Bos J. L. Genetic alterations during colorectal-tumor development. N Engl J Med. 1988 Sep 1;319(9):525–532. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198809013190901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg R. A. Tumor suppressor genes. Science. 1991 Nov 22;254(5035):1138–1146. doi: 10.1126/science.1659741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkerson V. W., Bryant D. L., Parsons J. T. Rous sarcoma virus variants that encode src proteins with an altered carboxy terminus are defective for cellular transformation. J Virol. 1985 Aug;55(2):314–321. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.2.314-321.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou H., Duesberg P. H. A retroviral promoter is sufficient to convert proto-src to a transforming gene that is distinct from the src gene of Rous sarcoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(23):9128–9132. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.23.9128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou R. P., Duesberg P. H. Avian proto-myc genes promoted by defective or nondefective retroviruses are single-hit transforming genes in primary cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):7721–7725. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.7721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou R. P., Duesberg P. H. myc protooncogene linked to retroviral promoter, but not to enhancer, transforms embryo cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):2924–2928. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.2924. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]