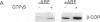Abstract
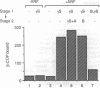
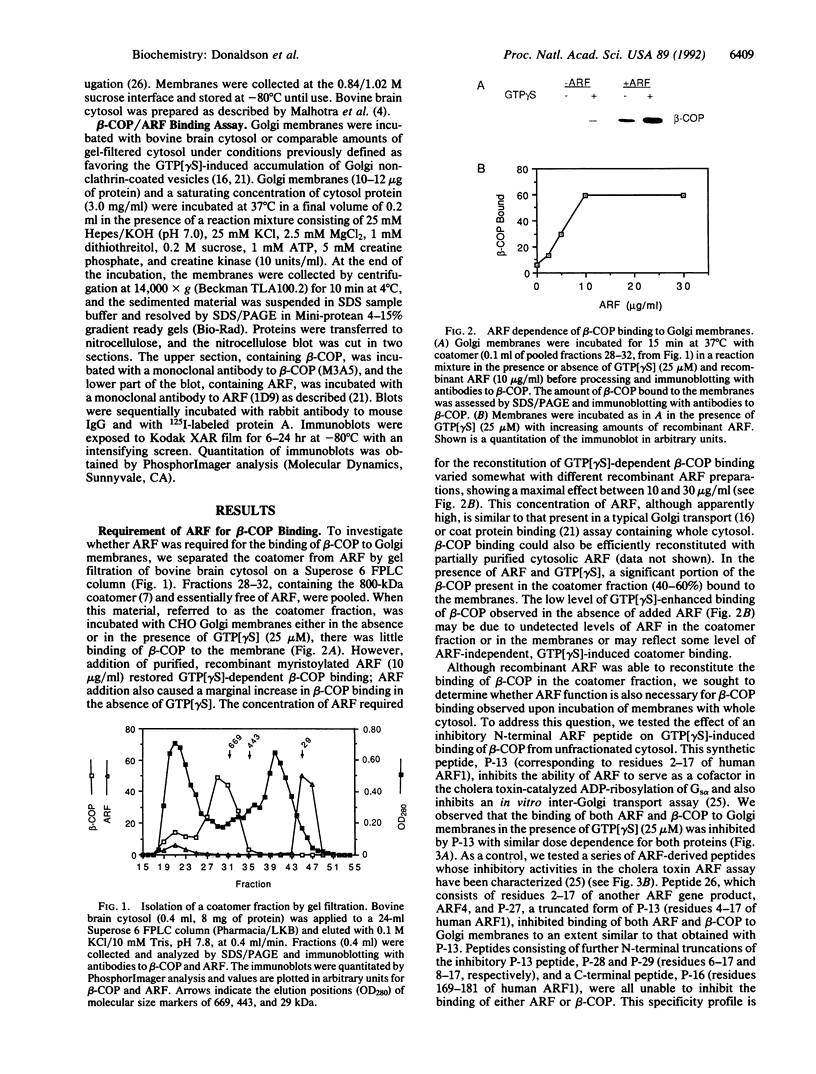
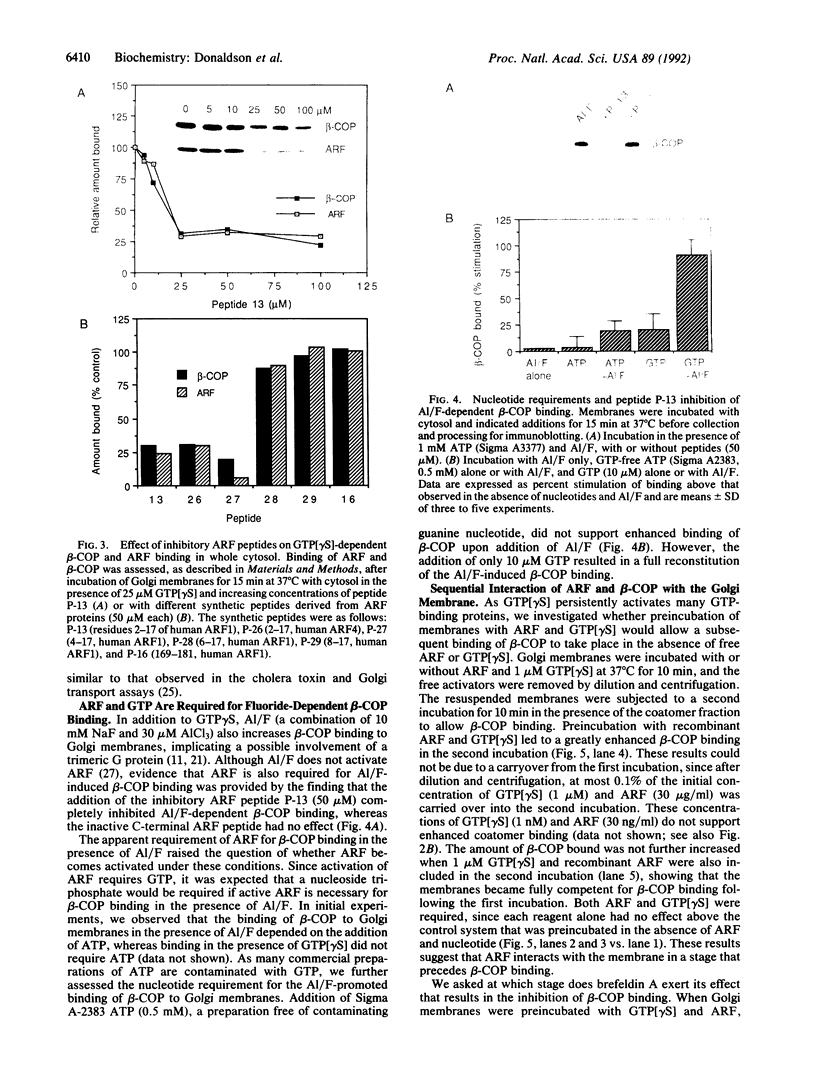
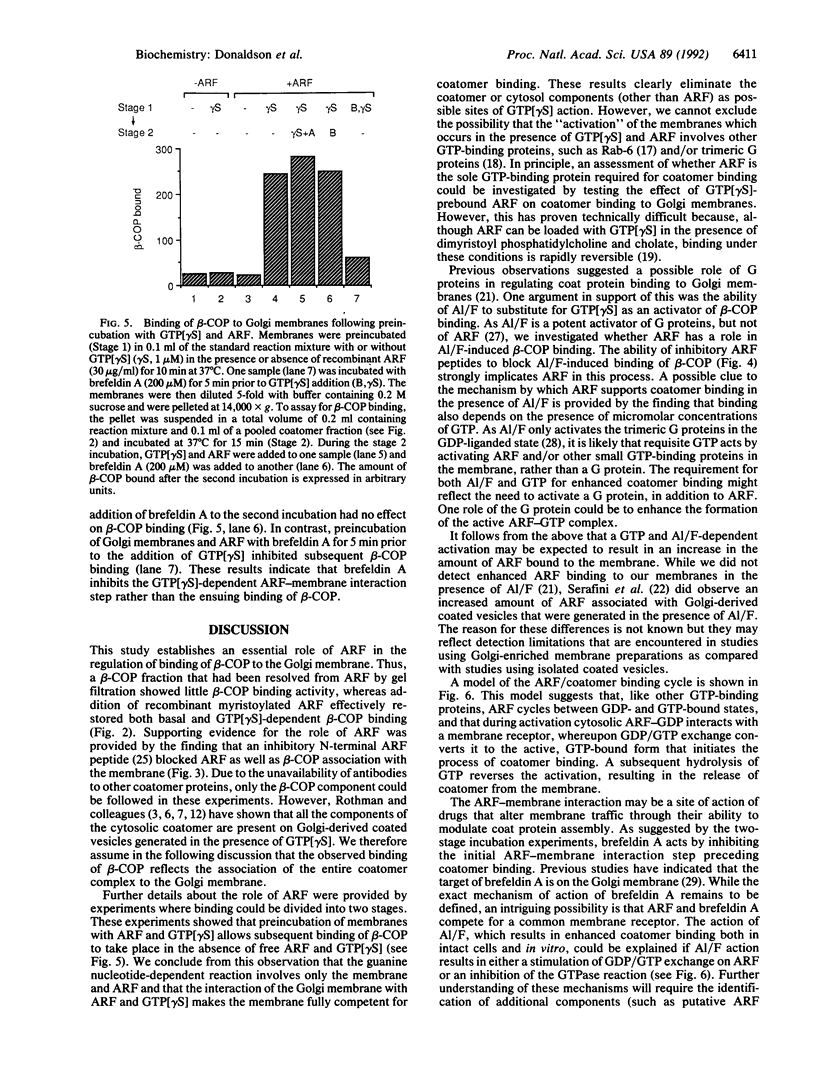
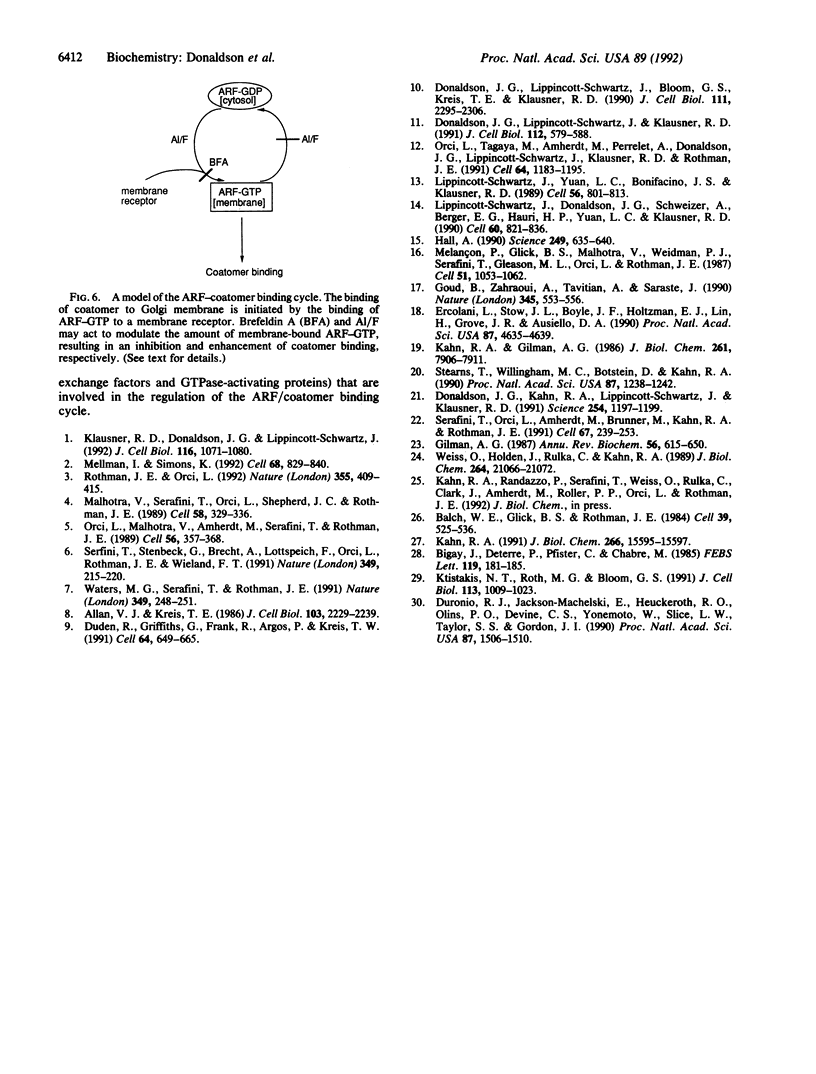
The coatomer is a cytosolic protein complex that reversibly associates with Golgi membranes and is implicated in modulating Golgi membrane transport. The association of beta-COP, a component of coatomer, with Golgi membranes is enhanced by guanosine 5'-[gamma-thio]triphosphate (GTP[gamma S]), a nonhydrolyzable analogue of GTP, and by a mixture of aluminum and fluoride ions (Al/F). Here we show that the ADP-ribosylation factor (ARF) is required for the binding of beta-COP. Thus, beta-COP contained in a coatomer fraction that has been resolved from ARF does not bind to Golgi membranes, whereas binding can be reconstituted by the addition of recombinant ARF. Furthermore, an N-terminal peptide of ARF, which blocks ARF binding to Golgi membranes, inhibits GTP[gamma S]- as well as the Al/F-enhanced binding of beta-COP. We show that Golgi coat protein binding involves a sequential reaction where an initial interaction of ARF and GTP[gamma S] with the membrane allows subsequent binding of beta-COP to take place in the absence of free ARF and GTP[gamma S]. The fungal metabolite brefeldin A, which is known to prevent the association of coat proteins with Golgi membrane, is shown to exert this effect by interfering with the initial ARF-membrane interaction step.
Full text
PDF
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allan V. J., Kreis T. E. A microtubule-binding protein associated with membranes of the Golgi apparatus. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 1):2229–2239. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balch W. E., Glick B. S., Rothman J. E. Sequential intermediates in the pathway of intercompartmental transport in a cell-free system. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):525–536. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90459-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bigay J., Deterre P., Pfister C., Chabre M. Fluoroaluminates activate transducin-GDP by mimicking the gamma-phosphate of GTP in its binding site. FEBS Lett. 1985 Oct 28;191(2):181–185. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80004-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson J. G., Kahn R. A., Lippincott-Schwartz J., Klausner R. D. Binding of ARF and beta-COP to Golgi membranes: possible regulation by a trimeric G protein. Science. 1991 Nov 22;254(5035):1197–1199. doi: 10.1126/science.1957170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson J. G., Lippincott-Schwartz J., Bloom G. S., Kreis T. E., Klausner R. D. Dissociation of a 110-kD peripheral membrane protein from the Golgi apparatus is an early event in brefeldin A action. J Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;111(6 Pt 1):2295–2306. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.6.2295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson J. G., Lippincott-Schwartz J., Klausner R. D. Guanine nucleotides modulate the effects of brefeldin A in semipermeable cells: regulation of the association of a 110-kD peripheral membrane protein with the Golgi apparatus. J Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;112(4):579–588. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.4.579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duden R., Griffiths G., Frank R., Argos P., Kreis T. E. Beta-COP, a 110 kd protein associated with non-clathrin-coated vesicles and the Golgi complex, shows homology to beta-adaptin. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):649–665. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90248-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duronio R. J., Jackson-Machelski E., Heuckeroth R. O., Olins P. O., Devine C. S., Yonemoto W., Slice L. W., Taylor S. S., Gordon J. I. Protein N-myristoylation in Escherichia coli: reconstitution of a eukaryotic protein modification in bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(4):1506–1510. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.4.1506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ercolani L., Stow J. L., Boyle J. F., Holtzman E. J., Lin H., Grove J. R., Ausiello D. A. Membrane localization of the pertussis toxin-sensitive G-protein subunits alpha i-2 and alpha i-3 and expression of a metallothionein-alpha i-2 fusion gene in LLC-PK1 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4635–4639. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:615–649. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goud B., Zahraoui A., Tavitian A., Saraste J. Small GTP-binding protein associated with Golgi cisternae. Nature. 1990 Jun 7;345(6275):553–556. doi: 10.1038/345553a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall A. The cellular functions of small GTP-binding proteins. Science. 1990 Aug 10;249(4969):635–640. doi: 10.1126/science.2116664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn R. A. Fluoride is not an activator of the smaller (20-25 kDa) GTP-binding proteins. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 25;266(24):15595–15597. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn R. A., Gilman A. G. The protein cofactor necessary for ADP-ribosylation of Gs by cholera toxin is itself a GTP binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 15;261(17):7906–7911. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klausner R. D., Donaldson J. G., Lippincott-Schwartz J. Brefeldin A: insights into the control of membrane traffic and organelle structure. J Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;116(5):1071–1080. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.5.1071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ktistakis N. T., Roth M. G., Bloom G. S. PtK1 cells contain a nondiffusible, dominant factor that makes the Golgi apparatus resistant to brefeldin A. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;113(5):1009–1023. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.5.1009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lippincott-Schwartz J., Donaldson J. G., Schweizer A., Berger E. G., Hauri H. P., Yuan L. C., Klausner R. D. Microtubule-dependent retrograde transport of proteins into the ER in the presence of brefeldin A suggests an ER recycling pathway. Cell. 1990 Mar 9;60(5):821–836. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90096-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lippincott-Schwartz J., Yuan L. C., Bonifacino J. S., Klausner R. D. Rapid redistribution of Golgi proteins into the ER in cells treated with brefeldin A: evidence for membrane cycling from Golgi to ER. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):801–813. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90685-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malhotra V., Serafini T., Orci L., Shepherd J. C., Rothman J. E. Purification of a novel class of coated vesicles mediating biosynthetic protein transport through the Golgi stack. Cell. 1989 Jul 28;58(2):329–336. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90847-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melançon P., Glick B. S., Malhotra V., Weidman P. J., Serafini T., Gleason M. L., Orci L., Rothman J. E. Involvement of GTP-binding "G" proteins in transport through the Golgi stack. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):1053–1062. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90591-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellman I., Simons K. The Golgi complex: in vitro veritas? Cell. 1992 Mar 6;68(5):829–840. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90027-A. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orci L., Malhotra V., Amherdt M., Serafini T., Rothman J. E. Dissection of a single round of vesicular transport: sequential intermediates for intercisternal movement in the Golgi stack. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):357–368. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90239-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orci L., Tagaya M., Amherdt M., Perrelet A., Donaldson J. G., Lippincott-Schwartz J., Klausner R. D., Rothman J. E. Brefeldin A, a drug that blocks secretion, prevents the assembly of non-clathrin-coated buds on Golgi cisternae. Cell. 1991 Mar 22;64(6):1183–1195. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90273-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman J. E., Orci L. Molecular dissection of the secretory pathway. Nature. 1992 Jan 30;355(6359):409–415. doi: 10.1038/355409a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serafini T., Orci L., Amherdt M., Brunner M., Kahn R. A., Rothman J. E. ADP-ribosylation factor is a subunit of the coat of Golgi-derived COP-coated vesicles: a novel role for a GTP-binding protein. Cell. 1991 Oct 18;67(2):239–253. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90176-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serafini T., Stenbeck G., Brecht A., Lottspeich F., Orci L., Rothman J. E., Wieland F. T. A coat subunit of Golgi-derived non-clathrin-coated vesicles with homology to the clathrin-coated vesicle coat protein beta-adaptin. Nature. 1991 Jan 17;349(6306):215–220. doi: 10.1038/349215a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stearns T., Willingham M. C., Botstein D., Kahn R. A. ADP-ribosylation factor is functionally and physically associated with the Golgi complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):1238–1242. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.1238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waters M. G., Serafini T., Rothman J. E. 'Coatomer': a cytosolic protein complex containing subunits of non-clathrin-coated Golgi transport vesicles. Nature. 1991 Jan 17;349(6306):248–251. doi: 10.1038/349248a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss O., Holden J., Rulka C., Kahn R. A. Nucleotide binding and cofactor activities of purified bovine brain and bacterially expressed ADP-ribosylation factor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 15;264(35):21066–21072. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]