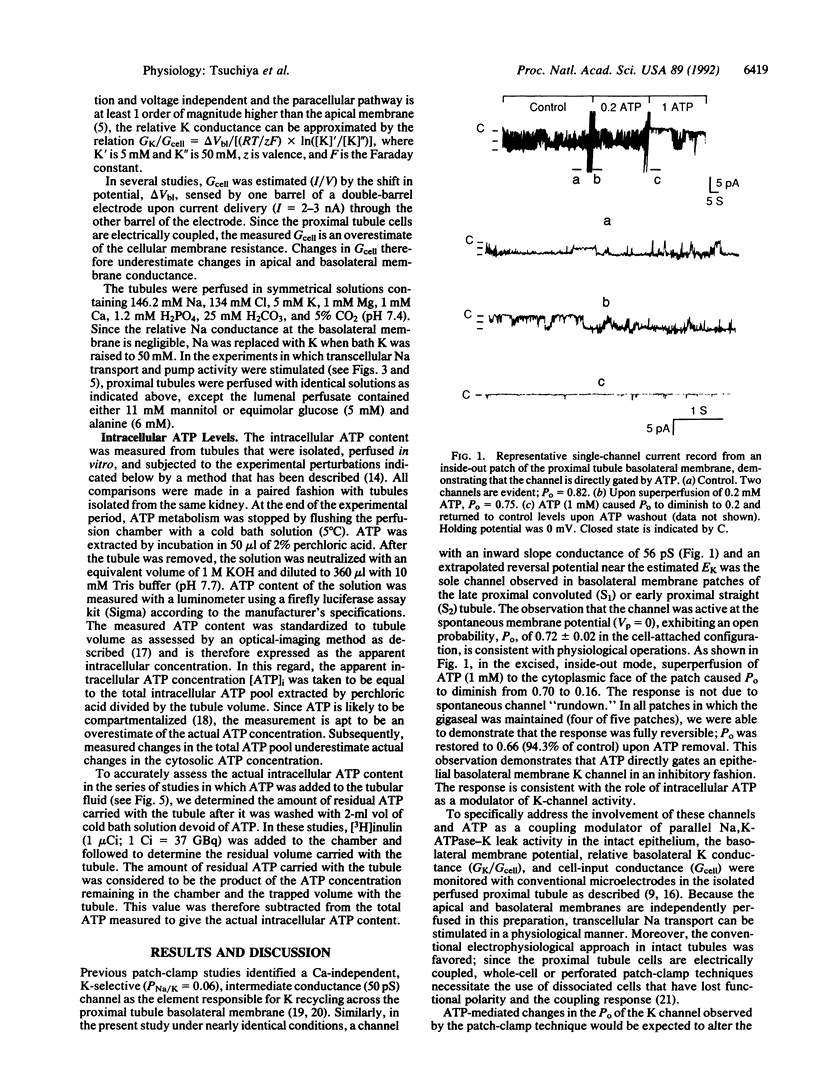
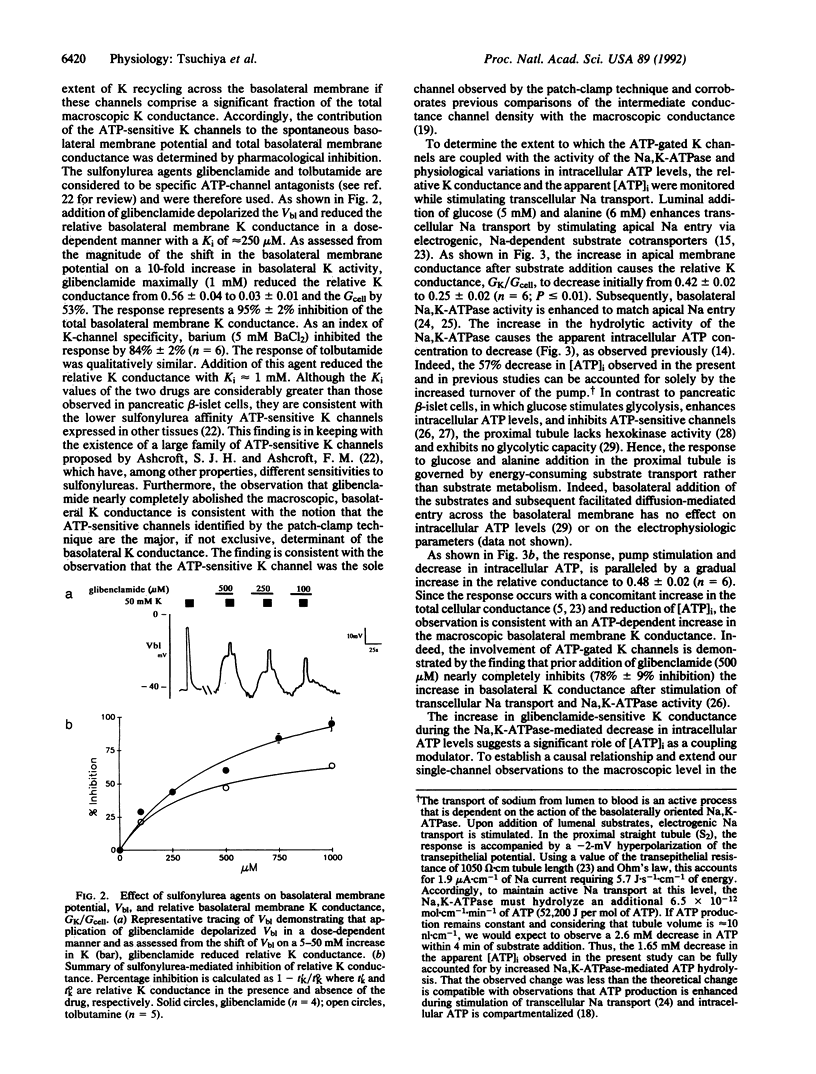
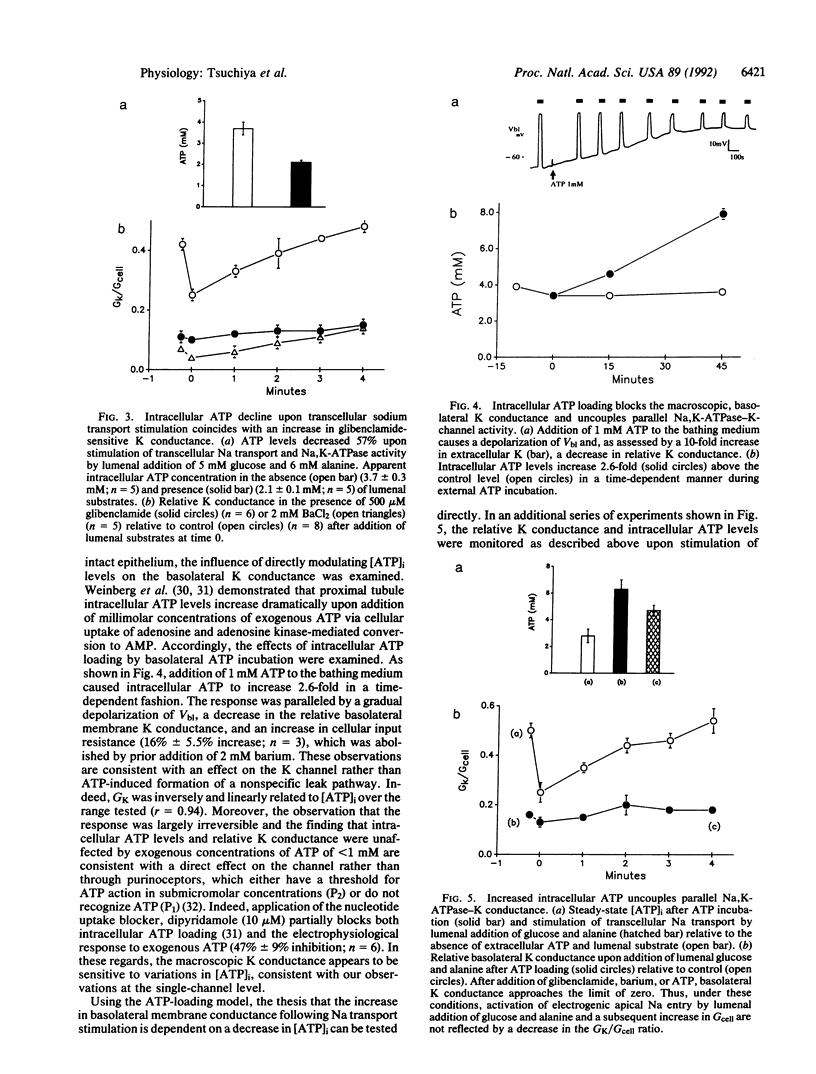
Abstract
A fundamental and essential property of nearly all salt-transporting epithelia is the tight parallel coupling between the magnitude of the K-conductive pathway at the basolateral membrane and the activity of the Na,K-dependent ATPase (Na,K-ATPase). In the present study, we demonstrate that the coupling response in the renal proximal tubule is governed, at least in part, through the interaction between ATP-sensitive K channels and Na,K-ATPase-mediated changes in intracellular ATP levels. First, we identified a K-selective channel at the basolateral membrane, which is inhibited by the cytosolic addition of ATP. Second, conventional microelectrode analysis in the isolated perfused proximal straight tubule revealed that these channels are the major determinant of the macroscopic K conductance so that ATP-mediated changes in the open probability of the K channel could alter the extent of K recycling. Indeed, the increase in the macroscopic K conductance upon stimulation of transcellular Na transport and pump activity was found to be paralleled by a decrease in intracellular ATP. Finally, a causal link between parallel Na,K-ATPase-K-channel activity and ATP was established by the finding that intracellular ATP loading uncoupled the response. With our recent observations that similar ATP-sensitive K channels are expressed abundantly in other epithelia, we postulate that ATP may act as a universal coupling modulator of parallel Na,K-ATPase-K-channel activity.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashcroft F. M., Harrison D. E., Ashcroft S. J. Glucose induces closure of single potassium channels in isolated rat pancreatic beta-cells. 1984 Nov 29-Dec 5Nature. 312(5993):446–448. doi: 10.1038/312446a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashcroft S. J., Ashcroft F. M. Properties and functions of ATP-sensitive K-channels. Cell Signal. 1990;2(3):197–214. doi: 10.1016/0898-6568(90)90048-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balaban R. S., Mandel L. J., Soltoff S. P., Storey J. M. Coupling of active ion transport and aerobic respiratory rate in isolated renal tubules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):447–451. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck J. S., Breton S., Laprade R., Giebisch G. Volume regulation and intracellular calcium in the rabbit proximal convoluted tubule. Am J Physiol. 1991 Jun;260(6 Pt 2):F861–F867. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1991.260.6.F861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck J. S., Breton S., Mairbäurl H., Laprade R., Giebisch G. Relationship between sodium transport and intracellular ATP in isolated perfused rabbit proximal convoluted tubule. Am J Physiol. 1991 Oct;261(4 Pt 2):F634–F639. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1991.261.4.F634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck J. S., Potts D. J. Cell swelling, co-transport activation and potassium conductance in isolated perfused rabbit kidney proximal tubules. J Physiol. 1990 Jun;425:369–378. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook D. L., Hales C. N. Intracellular ATP directly blocks K+ channels in pancreatic B-cells. Nature. 1984 Sep 20;311(5983):271–273. doi: 10.1038/311271a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson D. C., Richards N. W. Basolateral K conductance: role in regulation of NaCl absorption and secretion. Am J Physiol. 1990 Aug;259(2 Pt 1):C181–C195. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1990.259.2.C181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gullans S. R., Harris S. I., Mandel L. J. Glucose-dependent respiration in suspensions of rabbit cortical tubules. J Membr Biol. 1984;78(3):257–262. doi: 10.1007/BF01925973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gögelein H., Greger R. Properties of single K+ channels in the basolateral membrane of rabbit proximal straight tubules. Pflugers Arch. 1987 Oct;410(3):288–295. doi: 10.1007/BF00580279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henquin J. C. D-glucose inhibits potassium efflux from pancreatic islet cells. Nature. 1978 Jan 19;271(5642):271–273. doi: 10.1038/271271a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson R. L., Schultz S. G. Sodium-coupled sugar transport: effects on intracellular sodium activities and sodium-pump activity. Science. 1984 Jun 15;224(4654):1237–1239. doi: 10.1126/science.6328650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter M. Potassium-selective channels in the basolateral membrane of single proximal tubule cells of frog kidney. Pflugers Arch. 1991 Mar;418(1-2):26–34. doi: 10.1007/BF00370448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang F., Messner G., Rehwald W. Electrophysiology of sodium-coupled transport in proximal renal tubules. Am J Physiol. 1986 Jun;250(6 Pt 2):F953–F962. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1986.250.6.F953. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapointe J. Y., Duplain M. Regulation of basolateral membrane potential after stimulation of Na+ transport in proximal tubules. J Membr Biol. 1991 Mar;120(2):165–172. doi: 10.1007/BF01872399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapointe J. Y., Garneau L., Bell P. D., Cardinal J. Membrane crosstalk in the mammalian proximal tubule during alterations in transepithelial sodium transport. Am J Physiol. 1990 Feb;258(2 Pt 2):F339–F345. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1990.258.2.F339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapointe J. Y., Laprade R., Cardinal J. Transepithelial and cell membrane electrical resistances of the rabbit proximal convoluted tubule. Am J Physiol. 1984 Oct;247(4 Pt 2):F637–F649. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1984.247.4.F637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLennan W. L., Machen T. E., Zeuthen T. Ba2+ inhibition of electrogenic Cl- secretion in vitro frog and piglet gastric mucosa. Am J Physiol. 1980 Sep;239(3):G151–G160. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1980.239.3.G151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noma A. ATP-regulated K+ channels in cardiac muscle. Nature. 1983 Sep 8;305(5930):147–148. doi: 10.1038/305147a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parent L., Cardinal J., Sauvé R. Single-channel analysis of a K channel at basolateral membrane of rabbit proximal convoluted tubule. Am J Physiol. 1988 Jan;254(1 Pt 2):F105–F113. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1988.254.1.F105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfaller W., Guder W. G., Gstraunthaler G., Kotanko P., Jehart I., Pürschel S. Compartmentation of ATP within renal proximal tubular cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Oct 12;805(2):152–157. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(84)90162-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz S. G. Homocellular regulatory mechanisms in sodium-transporting epithelia: avoidance of extinction by "flush-through". Am J Physiol. 1981 Dec;241(6):F579–F590. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1981.241.6.F579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. L., Frizzell R. A. Chloride secretion by canine tracheal epithelium: IV. Basolateral membrane K permeability parallels secretion rate. J Membr Biol. 1984;77(3):187–199. doi: 10.1007/BF01870568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchida S., Endou H. Substrate specificity to maintain cellular ATP along the mouse nephron. Am J Physiol. 1988 Nov;255(5 Pt 2):F977–F983. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1988.255.5.F977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandewalle A., Wirthensohn G., Heidrich H. G., Guder W. G. Distribution of hexokinase and phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase along the rabbit nephron. Am J Physiol. 1981 Jun;240(6):F492–F500. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1981.240.6.F492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang W. H., Giebisch G. Dual modulation of renal ATP-sensitive K+ channel by protein kinases A and C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9722–9725. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang W. H., Schwab A., Giebisch G. Regulation of small-conductance K+ channel in apical membrane of rat cortical collecting tubule. Am J Physiol. 1990 Sep;259(3 Pt 2):F494–F502. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1990.259.3.F494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang W. H., White S., Geibel J., Giebisch G. A potassium channel in the apical membrane of rabbit thick ascending limb of Henle's loop. Am J Physiol. 1990 Feb;258(2 Pt 2):F244–F253. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1990.258.2.F244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang W., Giebisch G. Dual effect of adenosine triphosphate on the apical small conductance K+ channel of the rat cortical collecting duct. J Gen Physiol. 1991 Jul;98(1):35–61. doi: 10.1085/jgp.98.1.35. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg J. M., Davis J. A., Lawton A., Abarzua M. Modulation of cell nucleotide levels of isolated kidney tubules. Am J Physiol. 1988 Mar;254(3 Pt 2):F311–F322. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1988.254.3.F311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg J. M., Humes H. D. Increases of cell ATP produced by exogenous adenine nucleotides in isolated rabbit kidney tubules. Am J Physiol. 1986 Apr;250(4 Pt 2):F720–F733. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1986.250.4.F720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welling P. A., O'Neil R. G. Cell swelling activates basolateral membrane Cl and K conductances in rabbit proximal tubule. Am J Physiol. 1990 Apr;258(4 Pt 2):F951–F962. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1990.258.4.F951. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welling P. A., O'Neil R. G. Ionic conductive properties of rabbit proximal straight tubule basolateral membrane. Am J Physiol. 1990 Apr;258(4 Pt 2):F940–F950. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1990.258.4.F940. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



