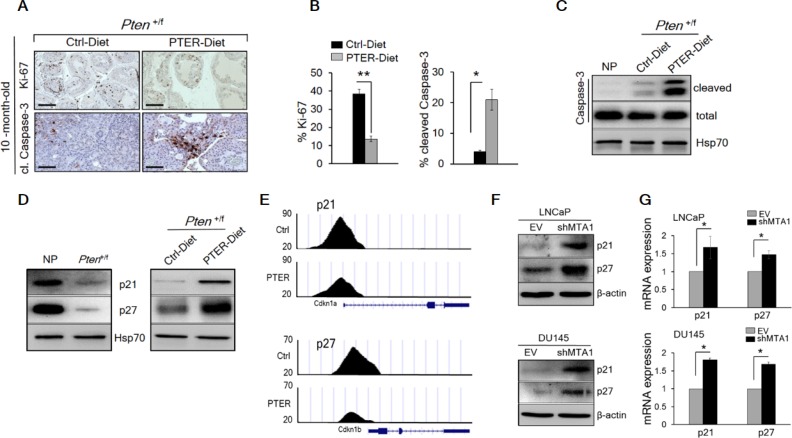
Figure 7. Pterostilbene significantly inhibits MTA1-dependent cell proliferation and induces MTA1-targeted apoptosis in Pten+/f mice.
(A) Representative Ki-67 (top) and cleaved Caspase-3 (bottom) staining of prostate tissues from 10-month-old Pten+/f mice on Ctrl- and PTER-Diet. Scale bars, 100 μm (Ki-67) and 50 μm (cleaved Caspase-3). (B) Quantitation of Ki-67 (left) and cleaved Caspase-3 (right) positive cells of prostate tissues from 10-month-old Pten+/f mice on Ctrl- and PTER-Diet (n = 5/group). (C) Immunoblots of total and cleaved Caspase-3 in prostate tissues of 10-month-old Pten+/f mice on Ctrl- and PTER-Diet. (D) Immunoblots of p21 and p27 in the prostate tissues of 10-month-old Pten+/f mice compared to NP controls (left) and mice on Ctrl- and PTER-Diet (right). (E) Comparative analysis of MTA1 binding in the prostate tissues of Pten+/f mice on Ctrl- and PTER-Diet. Representative ChIP-Seq tracks for p21 and p27 gene loci at 10 kb resolution are shown. (F) Immunoblots of p21 and p27 in LNCaP (top) and DU145 (bottom) cells expressing (EV) and silenced for MTA1 (shMTA1). (G) qRT-PCR of p21 and p27 mRNA levels in cells expressing MTA1 and silenced for MTA1 (shMTA1). Data are mean ± SEM (n = 3), *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01 (two-tailed, two-sample t-test).