Abstract
AIMS: To evaluate serum secretory component in relation to early detection and clinical management of liver metastasis in patients with colorectal cancer. METHODS: Secretory component and carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) were analysed in serial serum samples from 23 patients who had liver metastases as the only apparent recurrence, and in sera from 54 matched controls. Results of surgical treatment of recurrences were classified peroperatively as radical when no residual tumour was apparent and resection margins were free of disease. RESULTS: In total, 18 (78%) patients had increased secretory component during the whole follow up period (median 16 months); 12 (52%) had raised secretory component concentrations before clinical recurrence (median lead time 5.2 months). There was no difference before recurrence between circulating secretory component and CEA in sensitivity and lead times. Seventeen patients underwent surgery for hepatic metastasis; seven had radical hepatic resection of which only two (29%) showed increased secretory component concentrations before clinical recurrence; both had concurrent raised CEA values. By contrast, secretory component was raised in 83% of those cases considered inoperable. CONCLUSIONS: Although serum secretory component clearly increases in most patients with liver metastases, its clinical value seems questionable because secretory component apparently indicates mainly inoperable hepatic metastases.
Full text
PDF
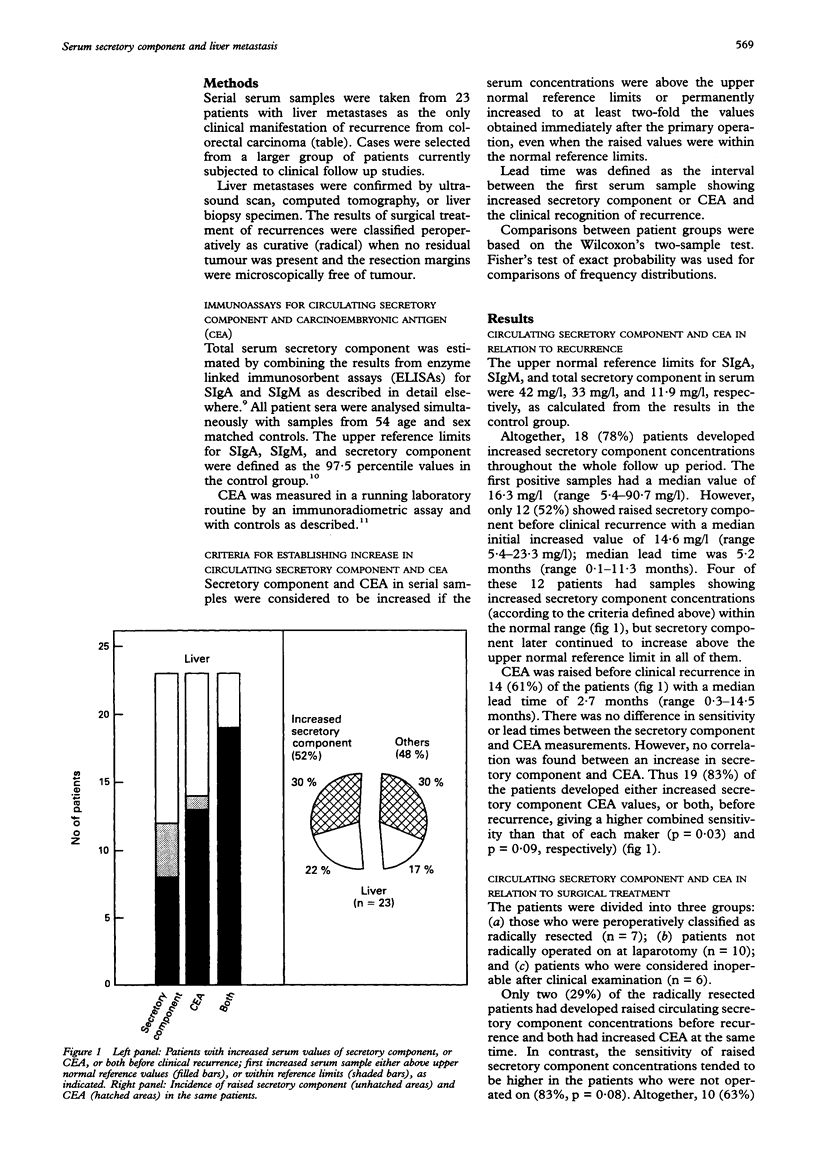

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brandtzaeg P., Halstensen T. S., Kett K., Krajci P., Kvale D., Rognum T. O., Scott H., Sollid L. M. Immunobiology and immunopathology of human gut mucosa: humoral immunity and intraepithelial lymphocytes. Gastroenterology. 1989 Dec;97(6):1562–1584. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(89)90406-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks J. J., Ernst C. S. Immunoreactive secretory component of IgA in human tissues and tumors. Am J Clin Pathol. 1984 Dec;82(6):660–665. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/82.6.660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Börmer O. P., Nustad K. Selection of monoclonal antibodies for use in an immunometric assay for carcinoembryonic antigen. J Immunol Methods. 1990 Mar 9;127(2):171–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(90)90066-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. K., Yasaka T., Horton M. R., Shakarji G. Comparing multivariate and univariate subject-specific reference regions for blood constituents in healthy persons. Clin Chem. 1982 Mar;28(3):422–426. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. K., Yasaka T. On the calculation of a "reference change" for comparing two consecutive measurements. Clin Chem. 1983 Jan;29(1):25–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes K. S., Rosenstein R. B., Songhorabodi S., Adson M. A., Ilstrup D. M., Fortner J. G., Maclean B. J., Foster J. H., Daly J. M., Fitzherbert D. Resection of the liver for colorectal carcinoma metastases. A multi-institutional study of long-term survivors. Dis Colon Rectum. 1988 Jan;31(1):1–4. doi: 10.1007/bf02552560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kvale D., Brandtzaeg P. An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for differential quantitation of secretory immunoglobulins of the A and M isotypes in human serum. J Immunol Methods. 1986 Jan 22;86(1):107–114. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(86)90272-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kvale D., Brandtzaeg P. Does secretory component (SC) exist as free SC in human serum? J Immunol Methods. 1988 Oct 26;113(2):279-81, 87-88. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(88)90342-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kvale D., Rognum T. O., Brandtzaeg P. Early detection of liver metastasis in patients with colorectal carcinoma by increased levels of circulating IgA- and IgM-associated secretory component. Br J Cancer. 1987 Nov;56(5):629–632. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1987.256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kvale D., Rognum T. O., Brandtzaeg P. Elevated levels of secretory immunoglobulins A and M in serum of patients with large bowel carcinoma indicate liver metastasis. Cancer. 1987 Jan 15;59(2):203–207. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19870115)59:2<203::aid-cncr2820590204>3.0.co;2-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rognum T., Elgjo K., Brandtzaeg P., Orjasaeter H., Bergan A. Plasma carcinoembryonic antigen concentrations and immunohistochemical patterns of epithelial marker antigens in patients with large bowel carcinoma. J Clin Pathol. 1982 Sep;35(9):922–933. doi: 10.1136/jcp.35.9.922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheele J., Stangl R., Altendorf-Hofmann A. Hepatic metastases from colorectal carcinoma: impact of surgical resection on the natural history. Br J Surg. 1990 Nov;77(11):1241–1246. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800771115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solberg H. E. The theory of reference values Part 5. Statistical treatment of collected reference values. Determination of reference limits. J Clin Chem Clin Biochem. 1983 Nov;21(11):749–760. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnbull R. B., Jr, Kyle K., Watson F. R., Spratt J. Cancer of the colon: the influence of the no-touch isolation technic on survival rates. Ann Surg. 1967 Sep;166(3):420–427. doi: 10.1097/00000658-196709000-00010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]