Abstract
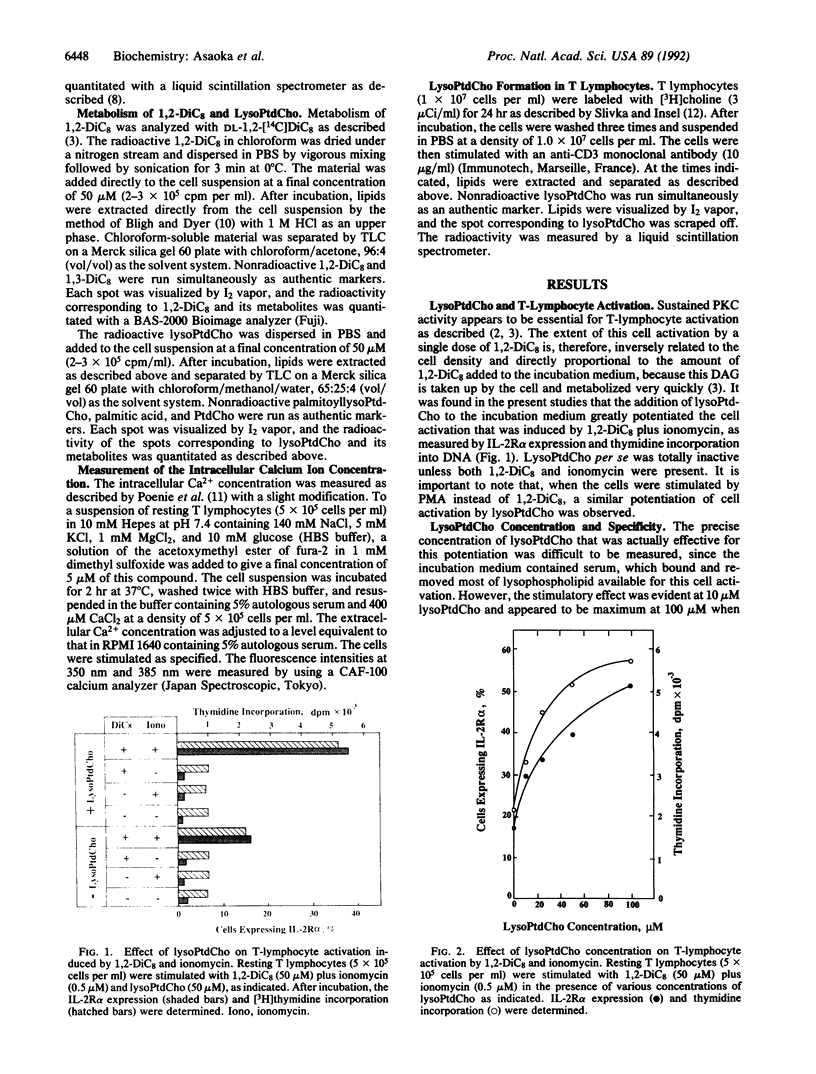
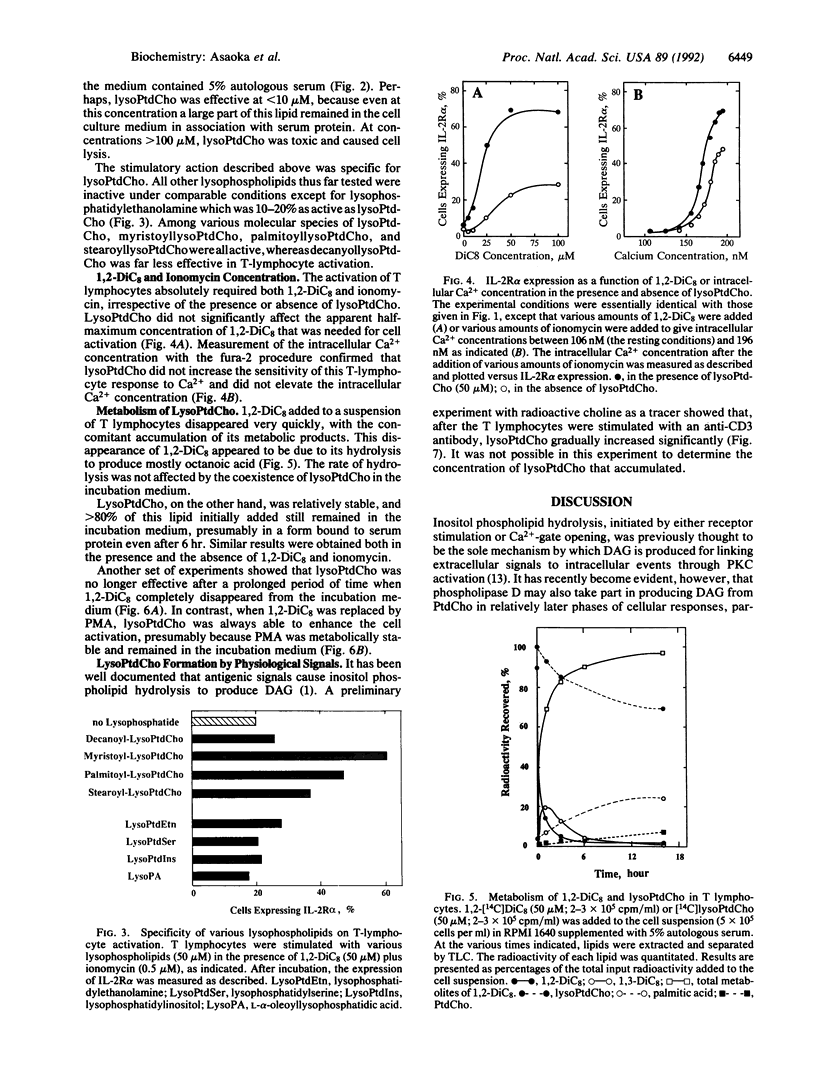
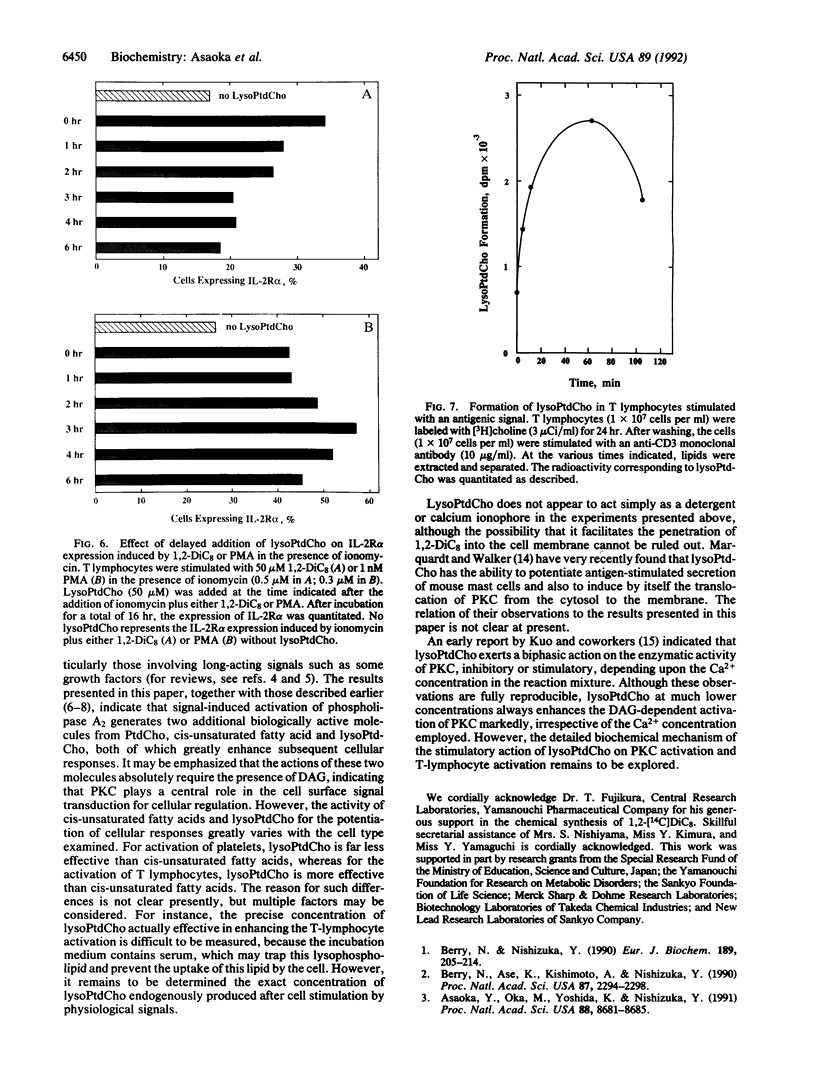
2-Lysophosphatidylcholine (lysoPtdCho), a product of the hydrolysis of phosphatidylcholine catalyzed by phospholipase A2, greatly potentiates the activation of human resting T lymphocytes that is induced by a membrane-permeant diacylglycerol plus a calcium ionophore, as determined by the expression of the alpha subunit of the interleukin 2 receptor and thymidine incorporation into DNA. LysoPtdCho per se is inactive unless both diacylglycerol and a calcium ionophore are present. This effect of lysoPtdCho is also observed when diacylglycerol is replaced by a tumor-promoting phorbol ester. Other lysophosphatides including lysophosphatidylserine, lysophosphatidylinositol, and lysophosphatidic acid are inert except for lysophosphatidylethanolamine, which is far less effective than lysoPtdCho. Tracer experiments with radioactive choline indicate that, when T lymphocytes are stimulated with an antigenic signal, lysoPtdCho is indeed produced in a time-dependent fashion, although the concentration of this lysophospholipid accumulated remains to be quantitated. It suggests that phospholipase A2 is directly involved in the signal transduction pathway through protein kinase C to induce long-term cellular responses.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asaoka Y., Oka M., Yoshida K., Nishizuka Y. Lysophosphatidylcholine as a possible second messenger synergistic to diacylglycerol and calcium ion for T-lymphocyte activation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Aug 15;178(3):1378–1385. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91046-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asaoka Y., Oka M., Yoshida K., Nishizuka Y. Metabolic rate of membrane-permeant diacylglycerol and its relation to human resting T-lymphocyte activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8681–8685. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry N., Ase K., Kishimoto A., Nishizuka Y. Activation of resting human T cells requires prolonged stimulation of protein kinase C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(6):2294–2298. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.6.2294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry N., Nishizuka Y. Protein kinase C and T cell activation. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Apr 30;189(2):205–214. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb15478.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billah M. M., Anthes J. C. The regulation and cellular functions of phosphatidylcholine hydrolysis. Biochem J. 1990 Jul 15;269(2):281–291. doi: 10.1042/bj2690281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burch R. M., Luini A., Axelrod J. Phospholipase A2 and phospholipase C are activated by distinct GTP-binding proteins in response to alpha 1-adrenergic stimulation in FRTL5 thyroid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7201–7205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exton J. H. Signaling through phosphatidylcholine breakdown. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 5;265(1):1–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marquardt D. L., Walker L. L. Lysophosphatidylcholine induces mast cell secretion and protein kinase C activation. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1991 Nov;88(5):721–730. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(91)90178-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The role of protein kinase C in cell surface signal transduction and tumour promotion. Nature. 1984 Apr 19;308(5961):693–698. doi: 10.1038/308693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oishi K., Raynor R. L., Charp P. A., Kuo J. F. Regulation of protein kinase C by lysophospholipids. Potential role in signal transduction. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 15;263(14):6865–6871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poenie M., Alderton J., Tsien R. Y., Steinhardt R. A. Changes of free calcium levels with stages of the cell division cycle. Nature. 1985 May 9;315(6015):147–149. doi: 10.1038/315147a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinomura T., Asaoka Y., Oka M., Yoshida K., Nishizuka Y. Synergistic action of diacylglycerol and unsaturated fatty acid for protein kinase C activation: its possible implications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 15;88(12):5149–5153. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.12.5149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slivka S. R., Insel P. A. Phorbol ester and neomycin dissociate bradykinin receptor-mediated arachidonic acid release and polyphosphoinositide hydrolysis in Madin-Darby canine kidney cells. Evidence that bradykinin mediates noninterdependent activation of phospholipases A2 and C. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 15;263(29):14640–14647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida K., Asaoka Y., Nishizuka Y. Platelet activation by simultaneous actions of diacylglycerol and unsaturated fatty acids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 15;89(14):6443–6446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.14.6443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]