Abstract
The peripheral blood of a 3 month old boy with disseminated tuberculosis showed CD30 positive monocytes on flow cytometric analysis. His liver contained CD30 positive staining macrophages and giant cells. CD30 is an activation antigen which has not been previously found on peripheral blood monocytes.
Full text
PDF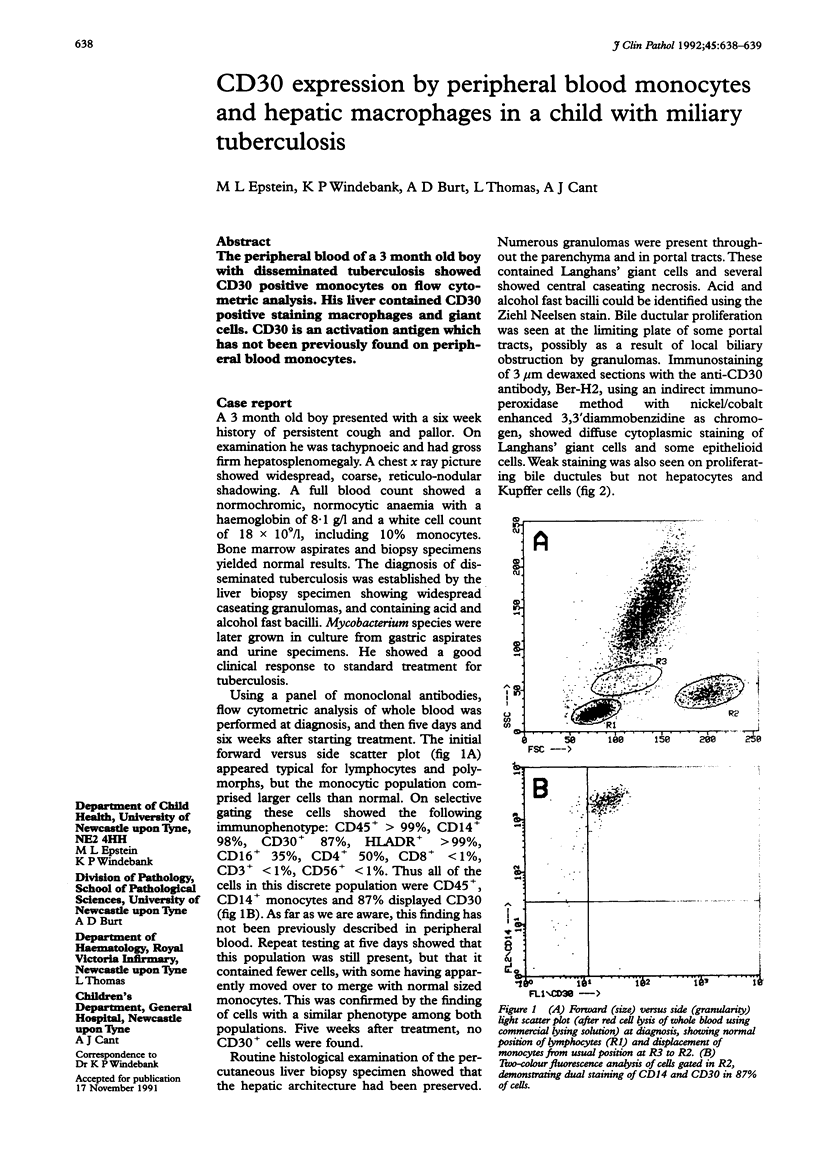

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andreesen R., Brugger W., Löhr G. W., Bross K. J. Human macrophages can express the Hodgkin's cell-associated antigen Ki-1 (CD30). Am J Pathol. 1989 Jan;134(1):187–192. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pallesen G. The diagnostic significance of the CD30 (Ki-1) antigen. Histopathology. 1990 Apr;16(4):409–413. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1990.tb01151.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwab U., Stein H., Gerdes J., Lemke H., Kirchner H., Schaadt M., Diehl V. Production of a monoclonal antibody specific for Hodgkin and Sternberg-Reed cells of Hodgkin's disease and a subset of normal lymphoid cells. Nature. 1982 Sep 2;299(5878):65–67. doi: 10.1038/299065a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarting R., Gerdes J., Dürkop H., Falini B., Pileri S., Stein H. BER-H2: a new anti-Ki-1 (CD30) monoclonal antibody directed at a formol-resistant epitope. Blood. 1989 Oct;74(5):1678–1689. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein H., Mason D. Y., Gerdes J., O'Connor N., Wainscoat J., Pallesen G., Gatter K., Falini B., Delsol G., Lemke H. The expression of the Hodgkin's disease associated antigen Ki-1 in reactive and neoplastic lymphoid tissue: evidence that Reed-Sternberg cells and histiocytic malignancies are derived from activated lymphoid cells. Blood. 1985 Oct;66(4):848–858. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





