Abstract
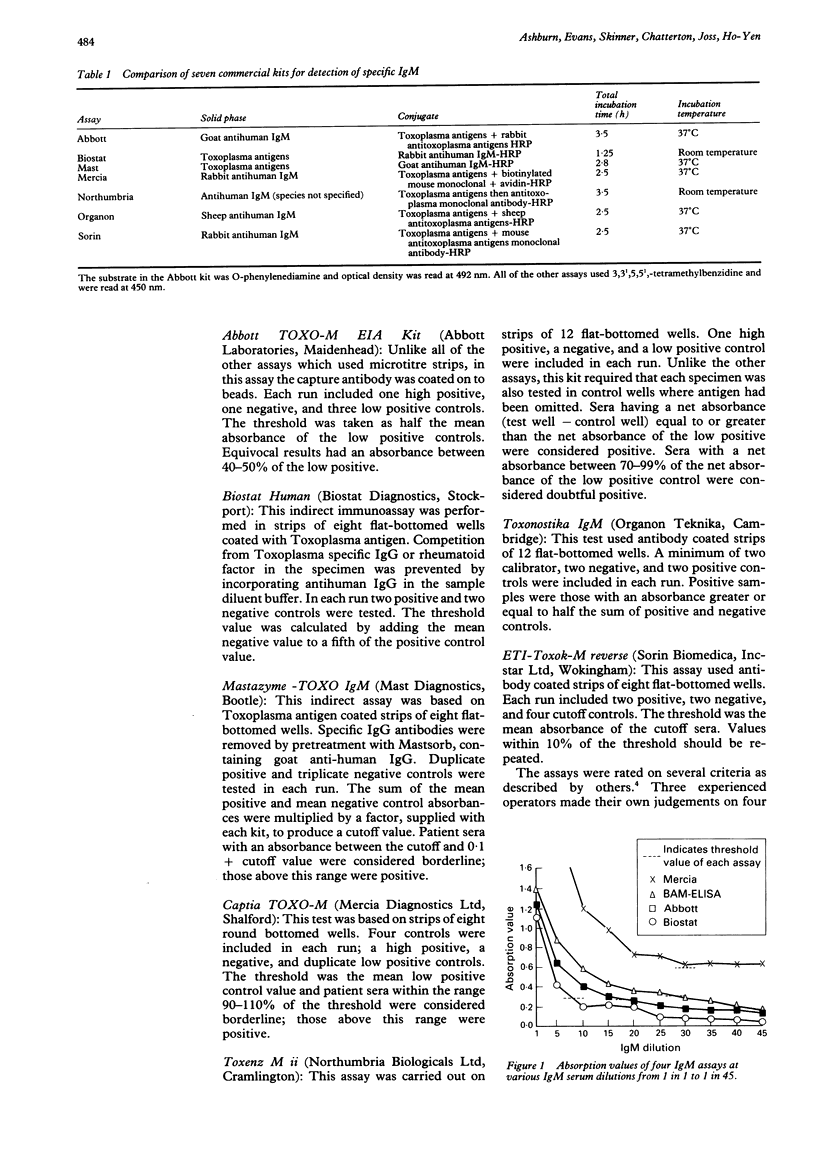
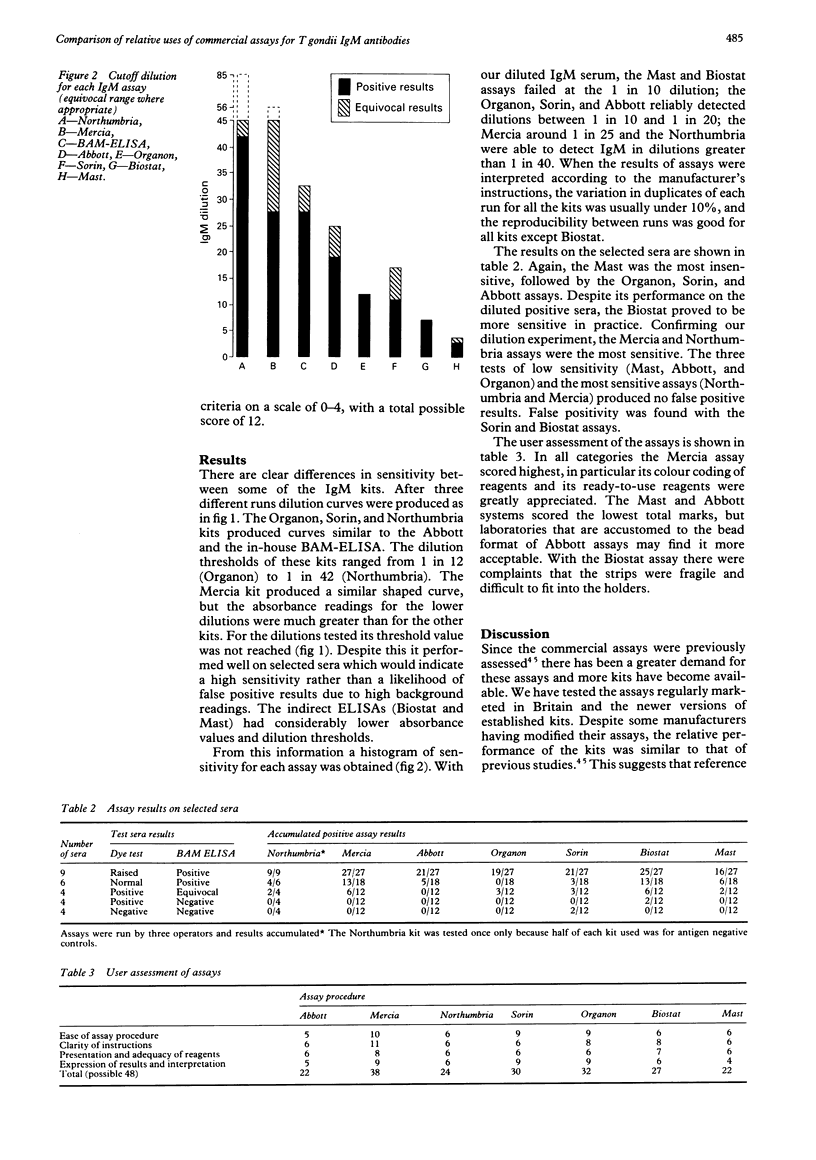
AIMS: To compare the sensitivity and user friendliness of seven commercially available enzyme linked immunoabsorbent assay (ELISA) kits for toxoplasma specific IgM. METHODS: Five antibody capture assays supplied by Abbott, Mercia, Northumbria, Organon and Sorin, and two indirect ELISA assays from Biostat and Mast, were assessed. Using defined dilutions of Toxoplasma gondii specific IgM, the performance and sensitivity of each assay was established. They were further assessed on a panel of 27 sera with a range of dye test and IgM results (as determined by the Scottish Toxoplasma Reference Laboratory). All of the assays were performed by three experienced operators and assessed for user satisfaction. RESULTS: The Mast, Organon, and Abbott assays were of low sensitivity; the Mercia and Northumbria were of high sensitivity; and the Biostat and Sorin assays produced too many false positive results. The Mercia kit provided most user satisfaction; the Mast and Abbott assays were most difficult to use. CONCLUSIONS: Local laboratories investigating toxoplasma infection should have three tests: one IgG and two IgM (high and low sensitivity) to help in the timing of infection. Alternatively, one sensitive IgM assay, such as that of Mercia, could be used by selecting appropriate high and low thresholds.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Herbrink P., van Loon A. M., Rotmans J. P., van Knapen F., van Dijk W. C. Interlaboratory evaluation of indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, antibody capture enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, and immunoblotting for detection of immunoglobulin M antibodies to Toxoplasma gondii. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Jan;25(1):100–105. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.1.100-105.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joss A. W., Skinner L. J., Moir I. L., Chatterton J. M., Williams H., Ho-Yen D. O. Biotin-labelled antigen screening test for toxoplasma IgM antibody. J Clin Pathol. 1989 Feb;42(2):206–209. doi: 10.1136/jcp.42.2.206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joynson D. H., Payne R. A., Balfour A. H., Prestage E. S., Fleck D. G., Chessum B. S. Five commercial enzyme linked immunosorbent assay kits for toxoplasma specific IgM antibody. J Clin Pathol. 1989 Jun;42(6):653–657. doi: 10.1136/jcp.42.6.653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne R. A., Joynson D. H., Balfour A. H., Harford J. P., Fleck D. G., Mythen M., Saunders R. J. Public Health Laboratory Service enzyme linked immunosorbent assay for detecting Toxoplasma specific IgM antibody. J Clin Pathol. 1987 Mar;40(3):276–281. doi: 10.1136/jcp.40.3.276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner L. J., Chatterton J. M., Joss A. W., Moir I. L., Ho-Yen D. O. The use of an IgM immunosorbent agglutination assay to diagnose congenital toxoplasmosis. J Med Microbiol. 1989 Feb;28(2):125–128. doi: 10.1099/00222615-28-2-125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verhofstede C., Van Renterghem L., Plum J. Comparison of six commercial enzyme linked immunosorbent assays for detecting IgM antibodies against Toxoplasma gondii. J Clin Pathol. 1989 Dec;42(12):1285–1290. doi: 10.1136/jcp.42.12.1285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wielaard F., van Gruijthuijsen H., Duermeyer W., Joss A. W., Skinner L., Williams H., van Elven E. H. Diagnosis of acute toxoplasmosis by an enzyme immunoassay for specific immunoglobulin m antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jun;17(6):981–987. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.6.981-987.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


