Abstract
Background:
T2R bitter taste receptors play a crucial role in sinonasal innate immunity by upregulating mucociliary clearance and nitric oxide (NO) production in response to bitter gram-negative quorum-sensing molecules in the airway surface liquid. Previous studies showed that phytochemical flavonoid metabolites, known as anthocyanidins, taste bitter and have antibacterial effects. Our objectives were to examine the effects of anthocyanidins on NO production by human sinonasal epithelial cells and ciliary beat frequency, and their impact on common sinonasal pathogens Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus.
Methods:
Ciliary beat frequency and NO production were measured by using digital imaging of differentiated air-liquid interface cultures prepared from primary human cells isolated from residual surgical material. Plate-based assays were used to determine the effects of anthocyanidins on bacterial swimming and swarming motility. Biofilm formation and planktonic growth were also assessed.
Results:
Anthocyanidin compounds triggered epithelial cells to produce NO but not through T2R receptors. However, anthocyanidins did not impact ciliary beat frequency. Furthermore, they did not reduce biofilm formation or planktonic growth of P. aeruginosa. In S. aureus, they did not reduce planktonic growth, and only one compound had minimal antibiofilm effects. The anthocyanidin delphinidin and anthocyanin keracyanin were found to promote bacterial swimming, whereas anthocyanidin cyanidin and flavonoid myricetin did not. No compounds that were tested inhibited bacterial swarming.
Conclusion:
Results of this study indicated that, although anthocyanidins may elicited an innate immune NO response from human cells, they do not cause an increase in ciliary beating and they may also cause a pathogenicity-enhancing effect in P. aeruginosa. Additional studies are necessary to understand how this would affect the use of anthocyanidins as therapeutics. This study emphasized the usefulness of in vitro screening of candidate compounds against multiple parameters of both epithelial and bacterial physiologies to prioritize candidates for in vivo therapeutic testing.
Keywords: Mucociliary clearance, cilia, airway surface liquid, chronic rhinosinusitis, air liquid interface, innate immunity, phytochemicals, flavonoids, polyphenols, bacterial motility
Chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS)1,2 affects more than one in eight adults in the United States1,3 and accounts for >$8 billion in direct health care costs3–5 and >$20 billion dollars in total economic burden6 annually. CRS is a syndrome of complex etiologies that involve chronic infection and/or persistent inflammation of the paranasal sinuses, often linked to ineffective sinonasal mucociliary clearance7 and/or chronic bacterial infection and biofilm formation.8 Patients with CRS who require surgery report worse quality-of-life scores for physical pain and social functioning than those patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, congestive heart failure, or angina.9
CRS accounts for one in five adult antibiotic prescriptions in the United States,10,11 a modality that is becoming less effective with the emergence of antibiotic-resistant microorganisms. Nonantibiotic topical CRS therapeutics are needed. Bitter taste receptors (T2Rs) are emerging potential therapeutic targets.12–16 Originally identified on the tongue, T2Rs are also located throughout the sinonasal cavity,12–16 where they stimulate nitric oxide (NO) production17–19 or antimicrobial peptide secretion.20 Moreover, a nonfunctional (“nontaster”) polymorphism in the TAS2R38 gene encoding T2R38 is an independent risk factor for CRS17,18,21 and predicts surgical outcome in nonpolypoid CRS.22 Because T2Rs regulate important host defense responses in the sinonasal cavity, bitter compounds may be useful as topical therapeutics to stimulate endogenous immune responses.
Anthocyanidins are a class of naturally occurring plant flavonoids found in red berries and other fruits, with antioxidant activity in vitro.23 Moreover, anthocyanidins can activate some T2R receptors24,25 and have been linked to endothelial NO production.26 Because NO is an important component of sinonasal innate immunity,19,27,28 we hypothesized that anthocyanidins may activate sinonasal T2Rs to generate NO. In addition, anthocyanidin-rich plant extracts have antibacterial properties against Staphylococcus aureus,29,30 Escherichia coli,29,31 Corynebacterium diphtheria,32 Moraxella catarrhalis,32 Bacillus cereus,33 and Pseudomonas aeruginosa.34 However, other studies have indicated that anthocyanidins do not have antibacterial effects against B. cereus,34 E. coli,34,35 or P. aeruginosa,30 or that anthocyanidins only reduce inflammation.36 The interactions between anthocyanidins and bacteria are complex,37–39 but interest in anthocyanidins has increased with the correlation between consumption of grapes and grape products (e.g., wine) with lower incidences of cancers and inflammatory diseases.40
We hypothesized that anthocyanidins may be potential natural topical therapeutics for CRS, either as T2R agonists or direct antimicrobials. Because plant compounds can have multiple effects on airway epithelial cells,41 we sought to investigate the effects of various representative anthocyanidins on primary human epithelial cells and common sinonasal pathogens, P. aeruginosa and S. aureus. In addition to microbiologic assays, we used optical imaging of air-liquid interface (ALI) cultures of primary human sinonasal cells isolated from residual surgical material, a state-of-the-art in vitro model for testing epithelial cell responses to novel compounds. Analysis of the results of this study emphasizes the importance of testing multiple parameters of epithelial cell responses when screening candidate compounds in vitro, which may help to identify and prioritize the best compounds for subsequent in vivo testing.
METHODS
Solutions and Reagents
Anthocyanidins (Fig. 1) were obtained from Cayman Chemical (Ann Arbor, MI). Stock solutions of chemicals were dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide before dissolving in Dulbecco's phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), with the highest working concentrations reflecting no more than 0.1% dimethyl sulfoxide, a level that does not affect sinonasal ALIs.19,20,42,43 In the experiments, PBS was primarily used on the apical side and Hank's Balanced Salt Solution (which contained 10 mM HEPES and Minimal Essential Medium amino acids) basolaterally, as described elsewhere.19,20,42–44 4-Amino-5-methylamino-2′,7′-difluroescein (DAF-FM) was from Life Technologies, Inc. (Carlsbad, CA). All other reagents were from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO).
Figure 1.
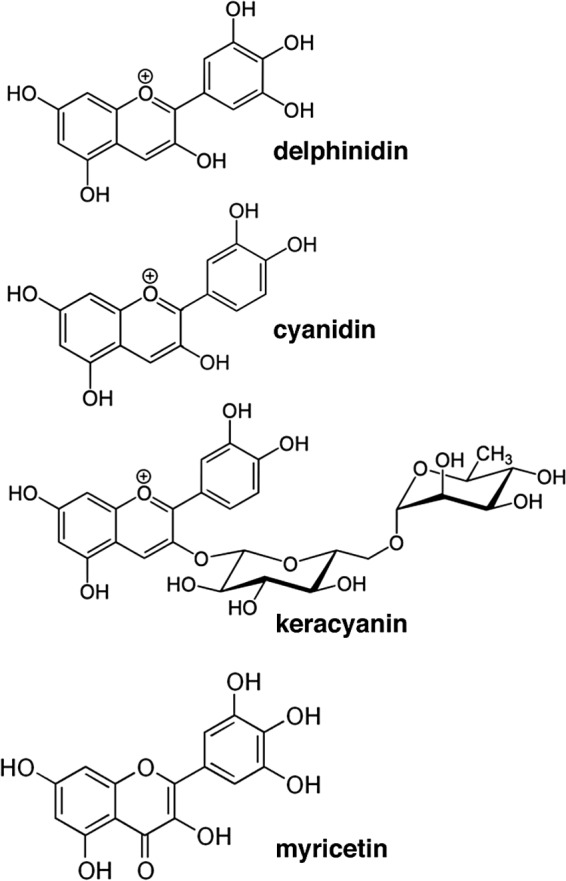
Compounds tested in this study. Two anthocyanidins, delphinidin and cyanidin, were tested. Keracyanin, the glycosylated anthocyanin derivative of cyanidin, also was examined. The non–anthocyanidin flavonoid myricetin was used as a control.
Sinonasal ALI Cultures
ALIs were prepared as described elsewhere.19,20,43–46 Patients were recruited from the Department of Otorhinolaryngology—Head and Neck Surgery, University of Pennsylvania, with full institutional review board approval (protocol 800614, “Pathogenesis of Chronic Rhinosinusitis”). Informed consent was obtained during the preoperative clinic visit or in the preoperative waiting room. The criterion for patient selection was those patients undergoing sinonasal surgery. Criteria for exclusion were a history of systemic diseases (Wegener's granulomatosis, cystic fibrosis, sarcoid, immunodeficiencies) and the use of antibiotics, oral corticosteroids, or antibiologics (e.g., omalizumab) within 1 month of surgery.
ALIs were established from sinonasal epithelial cells enzymically dissociated from residual surgical material and grown in proliferation medium that consisted of Dulbecco's Modified Eagle's Medium (Invitrogen/Life Technologies, Inc.)/Nutrient Mixture F-12 Ham and bronchial epithelial basal medium (Lonza Group, Basel, Switzerland) for 7 days. Cells were then trypsinized and seeded on Transwell cell culture inserts (6–7 × 104 cells per membrane; Corning Inc., Corning, NY) coated with bovine serum albumin, bovine collagen, and fibronectin. Five days later, the culture medium was removed from the upper compartment and the epithelium was allowed to differentiate in medium that consisted of 1:1 Dulbecco's Modified Eagle's Medium and bronchial epithelial basal medium (Lonza Group) with human epidermal growth factor, epinephrine, bovine pituitary extract, hydrocortisone, insulin, triiodothyronine, and transferrin, with penicillin, streptomycin, retinoic acid, and fetal bovine serum in the basal compartment.
Low-Light–Level Live-Cell Fluorescence Imaging of Intracellular NO Production
Cells were loaded with DAF-FM as described elsewhere19,20,43,44,47 by incubation in 10 μM DAF-FM diacetate and 5 μM 2-(4-carboxyphenyl)-4,4,5,5-tetramethylimidazoline-1-oxyl-3-oxide, a cell-permeant NO scavenger to prevent NO production during loading. After 30 minutes, cultures were washed with PBS to remove 2-(4-carboxyphenyl)-4,4,5,5-tetramethylimidazoline-1-oxyl-3-oxide and unloaded DAF-FM, followed by 15 minutes of incubation to allow for dye retention. Images were acquired on an IX-81 microscope (×10, 0.3 NA UPlanFLN objective; Olympus, Tokyo, Japan) at 5-second intervals by using a 488 laser and FluoView confocal system (Olympus). Because magnitudes of fluorescence changes were used to approximate NO production, care was taken to follow the loading protocol strictly to normalize dye loading, and microscope and/or software settings were identical for each experiment. No gain, offset, or gamma alterations were used.
High-Speed Digital Imaging of Ciliary Beat Frequency
Ciliary beat frequency (CBF) was performed as described elsewhere.19,20,43,44,46,48 Images of beating cilia from mature cultures were visualized by using a ×20 objective on an inverted microscope (DM IL; Leica Microsystems, Inc., Wetzlar, Germany) with a model A602f Basler area scan high-speed monochromatic digital video camera (Basler, AG, Ahrensburg, Germany) at 100 frames/s. Video images were analyzed with the Sisson-Ammons Video Analysis (SAVA) system version 2.1 (Ammons Engineering, Clio, MI). Experiments were performed at ∼28°C. Whole-field analysis was performed, with each measured point representing a single cilium. The reported frequencies represent the arithmetic means of these values.
Biofilm Formation Assays
Crystal violet biofilm assays were carried out as described elsewhere.49–51 Briefly, 100 μL of 0.5 McFarland P. aeruginosa (PAO1 or ATCC 27853) or S. aureus (methicillin-resistant strain M252) cultures in 50% lysogeny broth (LB) were added to a 96-well plate and grown for 48 hours statically at 37°C. Media were changed after 24 hours. The plates were washed two to three times with water, then stained with 1% crystal violet for 30–60 minutes, followed by a second wash. Stained biofilms were solubilized in crystal violet with 30% acetic acid and read in a spectrophotometer plate reader at ∼550 nm. Variation was minimized by normalizing values to LB only (control) conditions grown on the same plate.
P. aeruginosa and S. aureus Planktonic Growth Assay
Briefly, 100 μL of anthocyanidin solution was added to at least three wells of a 96-well plate, followed by 100 μL of an overnight culture diluted to the optical density of a 0.5 McFarland standard in LB, and subsequent incubation for 2 hours at 37°C, with periodic shaking at 30-minute intervals. Before spotting on the LB agar plates, dilutions were made at 1:10, 1:100, 1:1000, and 1:10,000 with LB. Colony-forming units (CFUs) were manually counted after overnight incubation.
Plate-based Assays for P. aeruginosa Motility
Plates were prepared as described elsewhere,53,54 with some slight modifications, by using M9 media, 0.5% casamino acids, 0.01% MgSO4, 0.2% glucose, and 0.4% (swimming) or 0.8% (swarming) agar. Agar solutions were allowed to cool to the touch while stirring to avoid any heat deactivation of the flavonoid compounds, added after autoclaving. The plates were inoculated with 5 μL of an overnight P. aeruginosa culture grown at 37°C in LB diluted with LB to an optical density of 0.5 and allowed to dry on the bench. Once dry, the plates were incubated at 37°C for 16–20 hours and subsequently imaged.
Data Analysis and Statistics
Data were analyzed in SAVA and/or Fiji.55 Statistical analyses were performed in Excel (Microsoft Corporation, Redmond, WA) and/or Prism (GraphPad Software, Inc., La Jolla, CA) with p < 0.05 considered statistically significant. For multiple comparisons with one-way analysis of variance, the Bonferroni posttest was used when preselected pairwise comparisons were performed, and the Dunnett posttest was used when values were compared with a control value. All data are presented as mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM).
RESULTS
Anthocyanidins Trigger Sinonasal Epithelial Cells to Produce NO
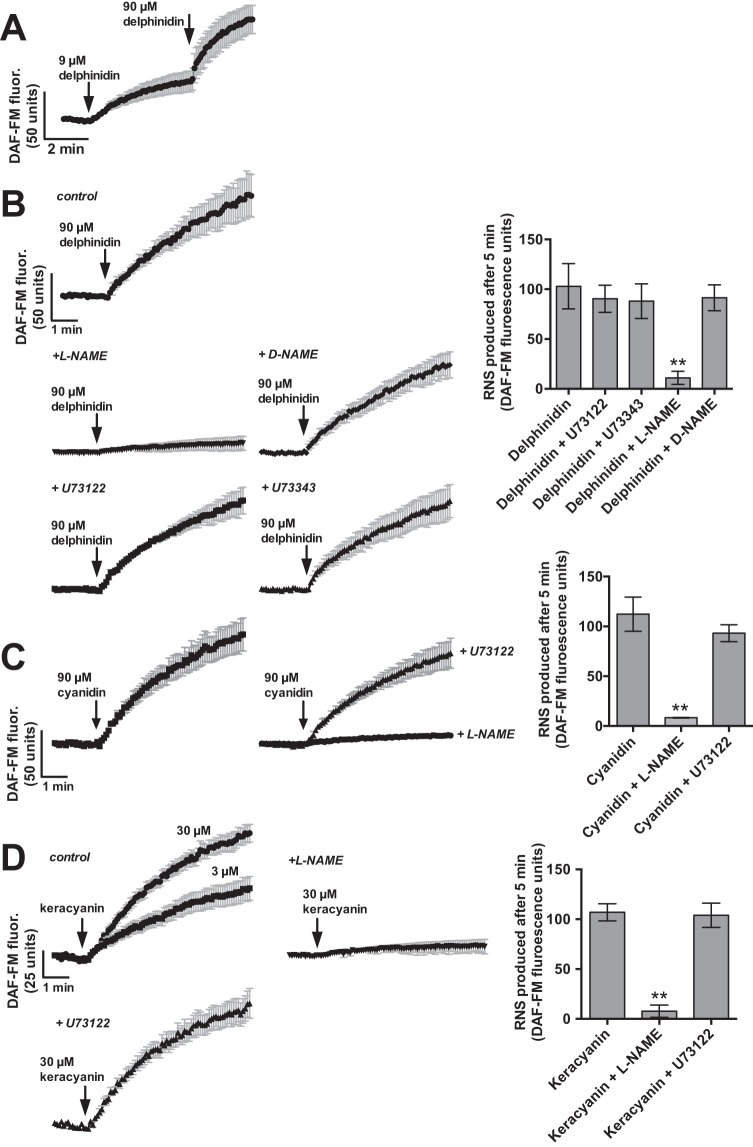
NO generation can be activated by receptor-driven changes in intracellular calcium concentrations that stimulate NO synthase activation.19,42,56 Cellular NO production was imaged in real time by using DAF-FM, which reacts with NO-derived reactive nitrogen species to form a fluorescent benzotriazole.19 Treating the apical side of ALIs with delphinidin, a representative anthocyanidin found in Cabernet Sauvignon grapes,57,58 elicited DAF-FM fluorescence increases over ∼5 minutes, which signaled production of NO (Fig. 2 A). This was confirmed by using the NO synthase inhibitor L-NG-nitroarginine methyl ester (L-NAME) and inactive stereoisomer D-NG-nitroarginine methyl ester. L-NAME, but not D-NG-nitroarginine methyl ester, blocked DAF-FM fluorescence increases in response to delphinidin (Fig. 2 B), which demonstrated that this indeed reflected NO production. However, the DAF-FM fluorescence responses were not blocked by phospholipase C inhibitor U73122 (Fig. 2 B). The inactive analog of U73122, U73343, also showed no effect (Fig. 2 B). The structurally similar cyanidin activated similar NO responses that were inhibited by L-NAME but not U73122 (Fig. 2 C).
Figure 2.
Anthocyanins and anthocyanidins can stimulate sinonasal epithelial nitric oxide (NO) production. (A) Average traces of 4-amino-5-methylamino-2′,7′-difluroescein (DAF-FM) fluorescence (n = 6 ALI cultures from three patients), showing increases in reactive nitrogen species (RNS) production in response to 9 and 90 μM delphinidin, an anthocyanidin. (B) Pharmacology of the delphinidin-induced response. DAF-FM fluorescence increases in response to 90 μM delphinidin (103 ± 23 units; n = 3 cultures from three patients) were inhibited in the presence of L-NG-nitroarginine methyl ester (L-NAME) (11 ± 7; n = 5 cultures from three patients; p < 0.01) but not D-NG-nitroarginine methyl ester (91 ± 13; n = 4 cultures from three patients; p = not significant [n.s.]), U73122 (90 ± 14; n = 3 cultures from three patients; p =n.s), or U73343 (88 ± 17; n = 4 cultures from three patients; p = n.s.). (C) DAF-FM fluorescence increases in response to another anthocyanidin, cyanidin (90 μM; 112 ± 17; n = 5 cultures from three patients), were likewise inhibited by L-NAME (8 ± 1; n = 3 cultures from three patients; p < 0.01) but not U73122 (93 ± 9; n = 3 cultures from three patients; p = n.s.). (D) The anthocyanin keracyanin similarly caused an increase in RNS production at 3 μM (58 ± 10; n = 5 cultures from four patients) and 30 μM (107 ± 8; n = 7 cultures from four patients). Response to 30 μM was inhibited by L-NAME (8 ± 6; n = 3 cultures from three patients; p < 0.01) but not U73122 (104 ± 12; n = 7 cultures from four patients; p =n.s.). For all bar graphs, **p < 0.01 compared with control (first bar) by one-way analysis of variance with the Dunnett posttest.
Anthocyanidins are often found as glycosylated anthocyanins (Fig. 1). Keracyanin is the anthocyanin derivative of cyanidin, found in black currants and raspberries.59 To determine if anthocyanins have similar effects, we tested keracyanin on sinonasal ALIs. Keracyanin similarly stimulated NO production that was inhibited by L-NAME but not by U73122 (Fig. 2 D). In addition, delphinidin- and keracyanin-induced DAF-FM fluorescence responses were not dependent on the TAS2R38 gene, which encodes T2R38.60,61 There was no significant difference between cultures homozygous for the functional TAS2R38 PAV “taster” allele and those homozygous for the nonfunctional AVI “nontaster” allele (Fig. 3), which confirmed the lack of involvement of this taste receptor in these responses.
Figure 3.
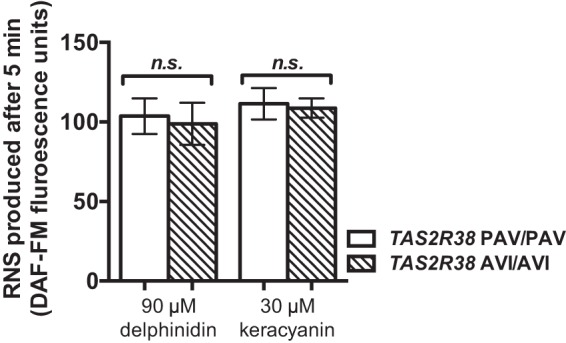
T2R38 is not involved in anthocyanin- and/or anthocyanidin-stimulated nitric oxide (NO) production. 4-Amino-5-methylamino-2′,7′-difluroescein (DAF-FM) measured NO production in human sinonasal epithelial cells in response to delphinidin or keracyanin stimulation did not differ between patient cultures homozygous for the functional “taster” TAS2R38 haplotype (PAV) or the nonfunctional “nontaster” haplotype (AVI). DAF-FM fluorescence increases were 104 ± 11 units (90 μM delphinidin, PAV/PAV; n = 6 cultures from three patients), 99 ± 13 units (90 μM delphinidin, AVI/AVI; n = 6 cultures from three patients), 111 ± 10 units (30 μM keracyanin; PAV/PAV; n = 6 cultures from three patients), and 109 ± 6 units (30 μM keracyanin; AVI/AVI; n = 6 cultures from three patients). Significance determined by one-way analysis of variance with the Bonferroni posttest comparing bracket-indicated conditions.
Anthocyanidins and Anthocyanins Do Not Impact Ciliary Beat Frequency
To determine if anthocyanin- and/or anthocyanidin-stimulated NO production results in increased ciliary beating, we imaged CBF in vitro by using high-speed digital imaging. Changes in CBF were reported as a ratio of stimulated basal frequencies. No significant differences were observed when ALIs were stimulated with delphinidin (Fig. 4 A) or keracyanin (Fig. 4 B). Application of adenosine 5′-trisphosphate (ATP), a purinergic agonist and a positive control to assess responsiveness, induced a robust 40–50% CBF increase.
Figure 4.
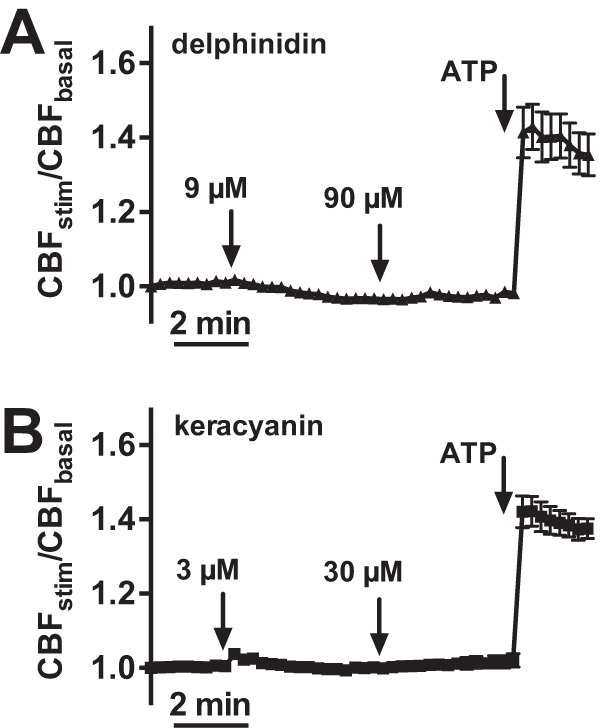
Delphinidin and keracyanin did not stimulate significant increases in ciliary beat frequency (CBF). Mean traces of normalized CBF are shown for delphinidin (A) (n = 6 cultures from three patients) and keracyanin (B) (n = 6 cultures from three patients). Responses to ATP, added at the end, confirmed the responsiveness and viability of cultures. ATP = adenosine 5′-trisphosphate.
Anthocyanidins and Anthocyanins Have Minimal Effects on P. aeruginosa and S. aureus Growth
We sought to determine if anthocyanidins or anthocyanins affect biofilm or planktonic growth of P. aeruginosa or S. aureus, common sinonasal pathogens sensitive to sinonasal NO production.14 We tested two wild-type P. aeruginosa strains, ATCC 27853 and PAO1. Although biofilm mass appeared to be slightly reduced in the presence of both keracyanin and delphinidin, the results were not statistically significant (Fig. 5 A), which indicated that these compounds had minimal or no antibiofilm effects. We also tested these compounds on P. aeruginosa planktonic growth. No significant reduction of CFUs was observed with either delphinidin or keracyanin (Fig. 5 B). As a control, the potent gram-negative antibiotic colistin sulfate reduced CFUs by ∼1000-fold (Fig. 5 B). Similarly, we tested biofilm and planktonic growth in methicillin-resistant S. aureus strain M2. There was no significant difference in biofilm mass in the presence of cyanidin or delphinidin, although there seemed to be a slight reduction in the latter. A small but statistically significant reduction was observed in the presence of keracyanin (Fig. 5 C). There was no significant difference in the percentage of S. aureus CFUs that remained in the presence of cyanidin, delphinidin, or keracyanin relative to an LB-only control (Fig. 5 D).
Figure 5.
Anthocyanidins had minimal effects on Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus planktonic and biofilm growth. (A) Bar graph showing P. aeruginosa normalized biofilm mass (PAO1) grown in the presence of LB-only (control) or LB that contained delphinidin or keracyanin at indicated concentrations. Although biofilm mass seemed to be slightly reduced, the values were not significant when compared with LB-only by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with the Dunnett posttest. Each biofilm mass measurement represents the average of five experiments, with each experiment being the average of at least eight wells grown in a single 96-well plate. Normalized biofilm masses were 100 ± 6 (LB-only), 72 ± 7 (0.9 μM delphinidin), 71 ± 5 (9 μM delphinidin), 75 ± 5 (90 μM delphinidin), 88 ± 14 (0.3 μM keracyanin), 70 ± 6 (3 μM keracyanin), and 66 ± 4 (30 μM keracyanin). (B) Bar graph, showing planktonic growth, measured by a colony-forming unit (CFU) spotting and counting assay of two P. aeruginosa wild-type strains, PAO1 and ATCC 27853. CFUs were not significantly reduced in the presence of delphinidin or keracyanin at indicated concentrations (ANOVA with the Dunnett posttest). The potent gram-negative antibiotic colistin sulfate was included as a control; **p < 0.01. CFUs recovered for PAO1 were 15,571 ± 2119 (LB), 10,417 ± 1031 (0.9 μM delphinidin), 15,333 ± 1312 (9 μM delphinidin), 8722 ± 1370 (90 μM delphinidin), 5667 ± 623 (0.3 μM keracyanin), 9000 ± 816 (3 μM keracyanin), 11,000 ± 3391 (30 μM keracyanin), and 5 ± 3 (10 μg/mL colistin). CFUs recovered for ATCC 27853 were 22,000 ± 3536 (LB), 17,667 ± 4327 (0.9 μM delphinidin), 27,667 ± 4249 (9 μM delphinidin), 12,667 ± 4784 (90 μM delphinidin), 35,000 ± 3342 (0.3 μM keracyanin), 16,333 ± 1546 (3 μM keracyanin), 27,667 ± 5573 (30 μM keracyanin), and 6 ± 2 (10 μg/mL colistin). (C) Bar graph, showing S. aureus normalized biofilm mass grown in the presence of LB-only (control) or LB that contained cyanidin, delphinidin, or keracyanin at indicated concentrations. Normalized S. aureus biofilm masses were 100 ± 4% (LB), 97 ± 6% (9 μM cyanidin), 106 ± 5% (90 μM cyanidin), 81 ± 5% (9 μM delphinidin), 94 ± 5% (90 μM delphinidin), 59.7 ± 8% (9 μM keracyanin), and 68 ± 9% (90 μM keracyanin). (D) Normalized S. aureus CFUs remaining were 100 ± 7% (LB), 108 ± 11% (0.9 μM cyanidin), 75 ± 22% (9 μM cyanidin), 105 ± 12% (90 μM cyanidin), 88 ± 11% (0.9 μM delphinidin), 128 ± 6% (9 μM delphinidin), 93 ± 4% (90 μM delphinidin), 116 ± 8% (0.9 μM keracyanin), 95 ± 4% (9 μM keracyanin), 111 ± 10% (90 μM keracyanin); *p < 0.05 by ANOVA with Dunnett post-test. LB = lysogeny broth.
Delphinidin, Cyanidin, and Keracyanin Do Not Inhibit Bacterial Swarming Motility
Swarming motility, evidenced by a characteristic uneven radiance of colonies from a spot on semisolid high-agar plates that mimics gelatinous viscous surfaces, e.g., a mucosal membrane,54 plays a pivotal role in bacteria spreading and the onset of biofilm formation.54 Swarming requires intact flagellar function and the production of rhamnolipids,54,62 linked to airway infection,63,64 as well as 3-hydroxyalkanoic acids.54 However, a plate-based swarming assay54 revealed that neither delphinidin, cyanidin, nor keracyanin caused reductions in bacterial swarming (Fig. 6A).
Figure 6.
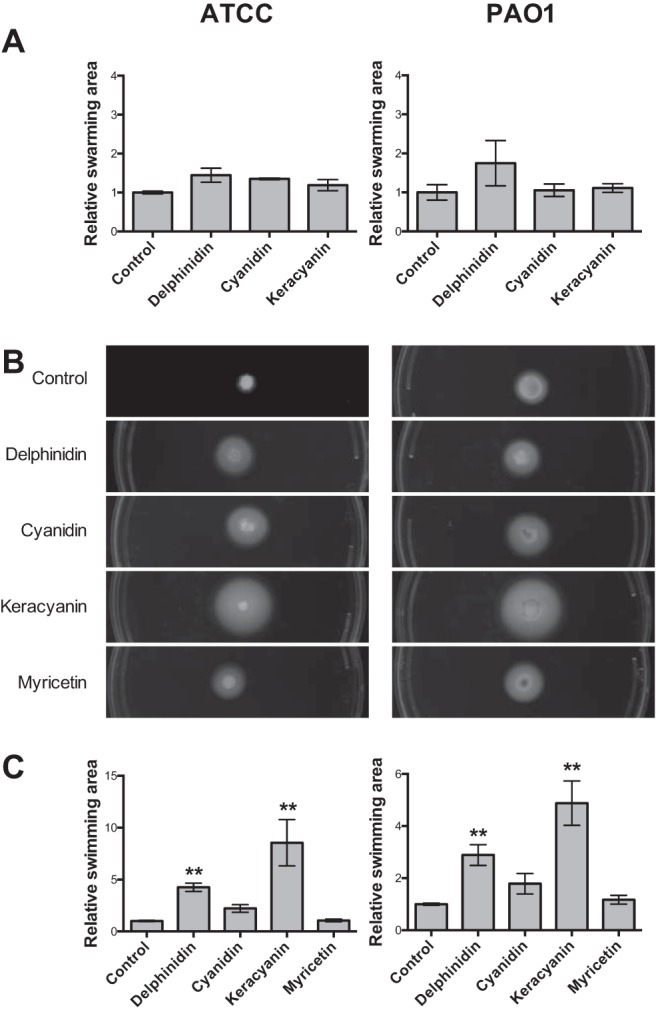
Effects of flavonoid compounds on swarming and swimming motility of two Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains. (A) Summary of bacterial swarming results for each condition. For both strains, ATCC 27853 (left) and PAO1 (right), delphinidin, cyanidin, and keracyanin did not have a statistically significant effect on relative swarming area. Relative bacterial swarming area for ATCC 27853 was 1.00 ± 0.03 (control), 1.45 ± 0.18 (delphinidin), 1.35 ± 0.02 (cyanidin), and 1.19 ± 0.14 (keracyanin). Relative bacterial swarming area for PAO1 was 1.00 ± 0.20 (control), 1.75 ± 0.58 (delphinidin), 1.06 ± 0.16 (cyanidin), and 1.11 ± 0.11 (keracyanin); n = 3–4 experiments each, 4–6 plates per experiment. (B) Representative images of bacterial swimming results for each condition. (C) Summary of bacterial swimming results. For both strains, the anthocyanidin delphinidin and the anthocyanin keracyanin demonstrated statistically significant increases in the relative bacterial swimming area (**p < 0.01). Cyanidin and myricetin did not produce statistically significant differences in the relative swimming area. The relative bacterial swimming area for ATCC 27853 was 1.00 ± 0.06 (control), 4.23 ± 0.41 (delphinidin), 2.21 ± 0.37 (cyanidin), 8.55 ± 2.23 (keracyanin), and 1.06 ± 0.13 (myricetin). The relative bacterial swimming area for PAO1 was 1.00 ± 0.04 (control), 2.89 ± 0.40 (delphinidin), 1.79 ± 0.39 (cyanidin), 4.88 ± 0.85 (keracyanin), and 1.17 ± 0.17 (myricetin).
Delphinidin and Keracyanin Promote Bacterial Swimming Mobility
Swimming is a method of Pseudomonas motility that occurs near surfaces,65,66 is involved in chemotaxis,67 requires twitching68 and flagellar motility, and is implicated in pathogenesis69,70 and biofilm formation.71,72 Swimming is evidenced by an even colony spread, characteristic of uncooperative motion, on lower-agar plates.53 Delphinidin and keracyanin caused a statistically significant increase in swimming of both P. aeruginosa strains (p < 0.01) (Fig. 6, B and C). However, this was not statistically significant with cyanidin and the non–anthocyanidin flavonoid myricetin, which indicated that variation exists in terms of flavonoid stimulation of bacterial swimming.
DISCUSSION
Our results indicated that anthocyanidins stimulated sinonasal NO production, previously shown to have antibacterial effects,19,73,74 but not through bitter taste receptor stimulation. Although cyanidin can activate both T2R39 (effective concentration [EC], 32 μM; EC50, 187 μM24) and T2R14 (EC, 250 μM24), the lower EC observed in this study (90 μM) combined with the lack of inhibition by U73122 indicated that these effects of anthocyanidins are not mediated through T2Rs. Moreover, cells from patients who were homozygous for both functional (PAV) T2R38 and nonfunctional (AVI) T2R38 responded equally to delphinidin and keracyanin, which indicated that T2R38, a major T2R isoform in sinonasal cilia, was not involved. Phospholipase Cβ2 is an essential downstream component of taste signal transduction,12,13,15,16,19,20 and the lack of an effect of U73122 here indicated that the anthocyanidin-stimulated production of NO observed is likely not due to a taste receptor response. We previously demonstrated that U73122 inhibits NO downstream of the T2R38 taste receptor expressed in sinonasal cilia.19,42 The mechanism of this NO production remains unknown. We recently reported on a secreted S. aureus compound that likewise stimulated acute taste receptor–independent NO production.47 It remains to be determined if anthocyanidins activate this same pathway.
Mucociliary clearance, driven by ciliary beating, removes foreign debris, including bacteria, from the respiratory tract.7 NO can elevate CBF through activation of protein kinase G. It remains unclear why anthocyanidin-driven NO increases do not increase CBF. Possibilities include off-target effects, including changes in intracellular pH or protein kinase C activity75 to “cancel out” stimulatory effects of protein kinase G, or, perhaps the NO response is somehow uncoupled from downstream protein kinase G signaling. The lack of CBF increases, lack of inhibition of biofilm or planktonic growth or swarming, and promotion of bacterial swimming indicated that anthocyanidins may have less therapeutic benefit than compounds that stimulate both NO and CBF together (e.g., agonists that activate sinonasal T2R isoforms19). Analysis of these data also indicated that anthocyanidins alone had minimal antibacterial effects against Pseudomonas and Staphylococcus biofilm or planktonic growth. Although a statistically significant reduction in S. aureus biofilm growth was seen with keracyanin, it is unclear whether this small decrease (<1 log) in vitro would result in clinically significant biofilm reduction in vivo. Cranberry proanthocyanidins, another flavonoid class, were previously shown to have antibiofilm properties76 and block P. aeruginosa swarming,77 which indicates that they may be more useful as therapeutics than anthocyanidins.
Analysis of these results indicates that in vitro screening of compounds under investigation for topical application in CRS, including naturally occurring compounds, e.g., anthocyanidins, against both human sinonasal cells in vitro and sinonasal bacteria can be useful for identification and prioritization of which compounds may have the most therapeutic benefit. Although a lack of effect in vitro (e.g., as with the lack of effects on ciliary beating observed in this study) does not necessarily mean a lack of benefit in vivo, the in vitro testing of two of the most common natural CRS therapeutics, Sinupret (Bionorica SE, Neumarkt in der Oberpfalz, Germany)78,79 and GeloMyrtol (G. Pohl-Boskamp GmbH & Co. KG, Hohenlockstedt, Germany),80 demonstrated significant in vitro enhancement of components of sinonasal innate immunity. In vitro screening may also be useful to identify compounds with off-target effects that may increase bacterial virulence.
CONCLUSION
Although analysis of our data indicates that some anthocyanin or anthocyanidin compounds activate a potentially beneficial NO response from sinonasal cells, the same compounds can stimulate activation of a possibly pathogenicity-enhancing response in P. aeruginosa. Further study is required to determine (1) whether this bacterial response would offset the potential beneficial responses of anthocyanins and/or anthocyanidins in vivo and (2) which specific anthocyanidin isoforms might stimulate the most efficacious host NO production without modulating bacterial physiology. However, therapeutic effects of anthocyanins and/or anthocyanidins nonetheless may be reduced by their lack of a net effect on cilia. Analysis of these data indicated that in vitro screening of compounds against multiple parameters of epithelial and bacterial physiology may allow prioritization of classes of compounds for in vivo testing by identifying which compound isoforms activate the most beneficial responses.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors thank Danielle R. Reed and the Monell Chemical Senses Center Genotyping Core, supported by National Institutes of Health grant P30DC011735.
Footnotes
This study was supported by National Institutes of Health grant 1R03DC013862 to R.J. Lee as well as a grant from the Department of Otorhinolaryngology at the University of Pennsylvania to R.J. Lee
N.D. Adappa and J.N. Palmer are consultants for Acclarent. The remaining authors have no conflicts of interest pertaining to this article
REFERENCES
- 1. Settipane RA, Peters AT, Chandra R. Chapter 4: Chronic rhinosinusitis. Am J Rhinol Allergy 27(suppl. 1):S11–S15, 2013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Gudis D, Zhao KQ, Cohen NA. Acquired cilia dysfunction in chronic rhinosinusitis. Am J Rhinol Allergy 26:1–6, 2012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Fokkens WJ, Lund VJ, Mullol J, et al. European Position Paper on Rhinosinusitis and Nasal Polyps 2012. Rhinol Suppl (23):3 p preceding table of contents, 1–298, 2012. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Bhattacharyya N. Incremental health care utilization and expenditures for chronic rhinosinusitis in the United States. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 120:423–427, 2011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Bhattacharyya N, Grebner J, Martinson NG. Recurrent acute rhinosinusitis: Epidemiology and health care cost burden. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 146:307–312, 2012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Smith KA, Orlandi RR, Rudmik L. Cost of adult chronic rhinosinusitis: A systematic review. Laryngoscope 125:1547–1556, 2015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Antunes MB, Gudis DA, Cohen NA. Epithelium, cilia, and mucus: Their importance in chronic rhinosinusitis. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am 29:631–643, 2009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Al-Mutairi D, Kilty SJ. Bacterial biofilms and the pathophysiology of chronic rhinosinusitis. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol 11:18–23, 2011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Toledano A, Rodriguez G, Martin AM, et al. Quality of life in patients with smell loss due to upper respiratory tract infections. Am J Otolaryngol 32:504–510, 2011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Manes RP, Batra PS. Bacteriology and antibiotic resistance in chronic rhinosinusitis. Facial Plast Surg Clin North Am 20:87–91, 2012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Kennedy JL, Borish L. Chronic rhinosinusitis and antibiotics: The good, the bad, and the ugly. Am J Rhinol Allergy 27:467–472, 2013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Lee RJ, Cohen NA. Bitter and sweet taste receptors in the respiratory epithelium in health and disease. J Mol Med 92:1235–1244, 2014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Lee RJ, Cohen NA. Taste receptors in innate immunity. Cell Mol Life Sci 72:217–236, 2015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Lee RJ, Cohen NA. Role of the bitter taste receptor T2R38 in upper respiratory infection and chronic rhinosinusitis. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol 15:14–20, 2015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Lee RJ, Cohen NA. Sinonasal solitary chemosensory cells “taste” the upper respiratory environment to regulate innate immunity. Am J Rhinol Allergy 28:366–373, 2014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Lee RJ, Cohen NA. The emerging role of the bitter taste receptor T2R38 in upper respiratory infection and chronic rhinosinusitis. Am J Rhinol Allergy 27:283–286, 2013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Adappa ND, Howland TJ, Palmer JN, et al. Genetics of the taste receptor T2R38 correlates with chronic rhinosinusitis necessitating surgical intervention. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol 3:184–187, 2013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Adappa ND, Zhang Z, Palmer JN, et al. The bitter taste receptor T2R38 is an independent risk factor for chronic rhinosinusitis requiring sinus surgery. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol 4:3–7, 2014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Lee RJ, Xiong G, Kofonow JM, et al. T2R38 taste receptor polymorphisms underlie susceptibility to upper respiratory infection. J Clin Invest 122:4145–4159, 2012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Lee RJ, Kofonow JM, Rosen PL, et al. Bitter and sweet taste receptors regulate human upper respiratory innate immunity. J Clin Invest 124:1393–1405, 2014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Mfuna Endam L, Filali-Mouhim A, Boisvert P, et al. Genetic variations in taste receptors are associated with chronic rhinosinusitis: A replication study. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol 4:200–206, 2014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Adappa ND, Farquhar D, Palmer JN, et al. TAS2R38 genotype predicts surgical outcome in nonpolypoid chronic rhinosinusitis. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol 6:25–33, 2016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Ksonzekova P, Mariychuk R, Eliasova A, et al. In vitro study of biological activities of anthocyanin-rich berry extracts on porcine intestinal epithelial cells. J Sci Food Agric 96:1093–1100, 2016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Roland WS, van Buren L, Gruppen H, et al. Bitter taste receptor activation by flavonoids and isoflavonoids: Modeled structural requirements for activation of hTAS2R14 and hTAS2R39. J Agric Food Chem 61:10454–10466, 2013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Narukawa M, Noga C, Ueno Y, et al. Evaluation of the bitterness of green tea catechins by a cell-based assay with the human bitter taste receptor hTAS2R39. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 405:620–625, 2011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Edwards M, Czank C, Woodward GM, et al. Phenolic metabolites of anthocyanins modulate mechanisms of endothelial function. J Agric Food Chem 63:2423–2431, 2015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Jeong JH, Yoo HS, Lee SH, et al. Nasal and exhaled nitric oxide in chronic rhinosinusitis with polyps. Am J Rhinol Allergy 28:e11–e16, 2014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Phillips PS, Sacks R, Marcells GN, et al. Nasal nitric oxide and sinonasal disease: A systematic review of published evidence. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 144:159–169, 2011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Pala CU, Zorba NN, Ozcan G. Microbial inactivation and physicochemical properties of ultrasound processed pomegranate juice. J Food Prot 78:531–539, 2015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Leitao DP, Polizello AC, Ito IY, Spadaro AC. Antibacterial screening of anthocyanic and proanthocyanic fractions from cranberry juice. J Med Food 8:36–40, 2005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Junqueira-Goncalves MP, Yanez L, Morales C, et al. Isolation and characterization of phenolic compounds and anthocyanins from Murta (Ugni molinae Turcz.) fruits. Assessment of antioxidant and antibacterial activity. Molecules 20:5698–5713, 2015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Krauze-Baranowska M, Majdan M, Halasa R, et al. The antimicrobial activity of fruits from some cultivar varieties of Rubus idaeus and Rubus occidentalis. Food Funct 5:2536–2541, 2014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Viskelis P, Rubinskiene M, Jasutiene I, et al. Anthocyanins, antioxidative, and antimicrobial properties of American cranberry (Vaccinium macrocarpon Ait.) and their press cakes. J Food Sci 74:C157–C161, 2009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Ombra MN, Fratianni F, Granese T, et al. In vitro antioxidant, antimicrobial and anti-proliferative activities of purple potato extracts (Solanum tuberosum cv Vitelotte noire) following simulated gastro-intestinal digestion. Nat Prod Res 29:1087–1091, 2015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Lacombe A, Wu VC, Tyler S, et al. Antimicrobial action of the American cranberry constituents; Phenolics, anthocyanins, and organic acids, against E. coli O157:H7. Int J Food Microbiol 139:102–107, 2010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Kim JM, Kim KM, Park EH, et al. Anthocyanins from black soybean inhibit Helicobacter pylori-induced inflammation in human gastric epithelial AGS cells. Microbiol Immunol 57:366–373, 2013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Faria A, Fernandes I, Norberto S, et al. Interplay between anthocyanins and gut microbiota. J Agric Food Chem 62:6898–6902, 2014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Cisowska A, Wojnicz D, Hendrich AB. Anthocyanins as antimicrobial agents of natural plant origin. Nat Prod Commun 6:149–156, 2011. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Aura AM, Martin-Lopez P, O'Leary KA, et al. In vitro metabolism of anthocyanins by human gut microflora. Eur J Nutr 44:133–142, 2005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Xia EQ, Deng GF, Guo YJ, LI HB. Biological activities of polyphenols from grapes. Int J Mol Sci 11:622–646, 2010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Chang JH, Song KJ, Kim HJ, et al. Dietary polyphenols affect MUC5AC expression and ciliary movement in respiratory cells and nasal mucosa. Am J Rhinol Allergy 24:e59–e62, 2010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Lee RJ, Chen B, Redding KM, et al. Mouse nasal epithelial innate immune responses to Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum-sensing molecules require taste signaling components. Innate Immun 20:606–617, 2014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Zhao KQ, Cowan AT, Lee RJ, et al. Molecular modulation of airway epithelial ciliary response to sneezing. FASEB J 26:3178–3187, 2012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Lee RJ, Chen B, Doghramji L, et al. Vasoactive intestinal peptide regulates sinonasal mucociliary clearance and synergizes with histamine in stimulating sinonasal fluid secretion. FASEB J 27:5094–5103, 2013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Abad A, Fernandez-Molina JV, Bikandi J, et al. What makes Aspergillus fumigatus a successful pathogen? Genes and molecules involved in invasive aspergillosis. Rev Iberoam Micol 27:155–182, 2010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Lai Y, Chen B, Shi J, et al. Inflammation-mediated upregulation of centrosomal protein 110, a negative modulator of ciliogenesis, in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol 128:1207–1215.e1, 2011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Carey RM, Workman AD, Chen B, et al. Staphylococcus aureus triggers nitric oxide production in human upper airway epithelium. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol 5:808–813, 2015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Zhao KQ, Goldstein N, Yang H, et al. Inherent differences in nasal and tracheal ciliary function in response to Pseudomonas aeruginosa challenge. Am J Rhinol Allergy 25:209–213, 2011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. O'Toole GA. Microtiter dish biofilm formation assay. J Vis Exp (47): pii: 2437, 2011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50. Antunes MB, Chi JJ, Liu Z, et al. Molecular basis of tobacco-induced bacterial biofilms: An in vitro study. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 147:876–884, 2012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51. Goldstein-Daruech N, Cope EK, Zhao KQ, et al. Tobacco smoke mediated induction of sinonasal microbial biofilms. PloS One 6:e15700, 2011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52. Harro JM, Daugherty S, Bruno VM, et al. Draft genome sequence of the methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolate MRSA-M2. Genome Announc (1): pii: e00037–12. 2013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53. Ha DG, Kuchma SL, O'Toole GA. Plate-based assay for swimming motility in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Methods Mol Biol 1149:59–65, 2014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54. Ha DG, Kuchma SL, O'Toole GA. Plate-based assay for swarming motility in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Methods Mol Biol 1149:67–72, 2014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55. Schindelin J, Arganda-Carreras I, Frise E, et al. Fiji: An open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat Methods 9:676–682, 2012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56. Forstermann U, Sessa WC. Nitric oxide synthases: Regulation and function. Eur Heart J 33:829–837, 837a–837d, 2012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57. Nyman NA, Kumpulainen JT. Determination of anthocyanidins in berries and red wine by high-performance liquid chromatography. J Agric Food Chem 49:4183–4187, 2001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58. Ryan JM, Revilla E. Anthocyanin composition of Cabernet Sauvignon and Tempranillo grapes at different stages of ripening. J Agric Food Chem 51:3372–3378, 2003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59. Tulio AZ, Jr, Reese RN, Wyzgoski FJ, et al. Cyanidin 3-rutinoside and cyanidin 3-xylosylrutinoside as primary phenolic antioxidants in black raspberry. J Agric Food Chem 56:1880–1888, 2008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60. Lipchock SV, Mennella JA, Spielman AI, Reed DR. Human bitter perception correlates with bitter receptor messenger RNA expression in taste cells. Am J Clin Nutr 98:1136–1143, 2013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61. Bufe B, Breslin PA, Kuhn C, et al. The molecular basis of individual differences in phenylthiocarbamide and propylthiouracil bitterness perception. Curr Biol 15:322–327, 2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62. Caiazza NC, Shanks RM, O'Toole GA. Rhamnolipids modulate swarming motility patterns of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol 187:7351–7361, 2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63. Read RC, Roberts P, Munro N, et al. Effect of Pseudomonas aeruginosa rhamnolipids on mucociliary transport and ciliary beating. J Appl Physiol 72:2271–2277, 1992. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64. Zulianello L, Canard C, Kohler T, et al. Rhamnolipids are virulence factors that promote early infiltration of primary human airway epithelia by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun 74:3134–3147, 2006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65. Conrad JC, Gibiansky ML, Jin F, et al. Flagella and pili-mediated near-surface single-cell motility mechanisms in P. aeruginosa. Biophys J 100:1608–1616, 2011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66. Keller JB. Effect of viscosity on swimming velocity of bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 71:3253–3254, 1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67. Sampedro I, Parales RE, Krell T, Hill JE. Pseudomonas chemotaxis. FEMS Microbiol Rev 39:17–46, 2015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68. Mattick JS. Type IV pili and twitching motility. Annu Rev Microbiol 56:289–314, 2002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69. Shi W, Sun H. Type IV pilus-dependent motility and its possible role in bacterial pathogenesis. Infect Immun 70:1–4, 2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70. Kazmierczak BI, Schniederberend M, Jain R. Cross-regulation of Pseudomonas motility systems: The intimate relationship between flagella, pili and virulence. Curr Opin Microbiol 28:78–82, 2015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71. Li Y, Xia H, Bai F, et al. Identification of a new gene PA5017 involved in flagella-mediated motility, chemotaxis and biofilm formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. FEMS Microbiol Lett 272:188–195, 2007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72. Adams H, Horrevoets WM, Adema SM, et al. Inhibition of biofilm formation by Camelid single-domain antibodies against the flagellum of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Biotechnol 186:66–73, 2014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73. Marcinkiewicz J. Nitric oxide and antimicrobial activity of reactive oxygen intermediates. Immunopharmacology 37:35–41, 1997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74. Fang FC. Perspectives series: Host/pathogen interactions. Mechanisms of nitric oxide-related antimicrobial activity. J Clin Invest 99:2818–2825, 1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75. Salathe M. Regulation of mammalian ciliary beating. Annu Rev Physiol 69:401–422, 2007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76. Ulrey RK, Barksdale SM, Zhou W, van Hoek ML. Cranberry proanthocyanidins have anti-biofilm properties against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. BMC Complement Altern Med 14:499, 2014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77. O'May C, Tufenkji N. The swarming motility of Pseudomonas aeruginosa is blocked by cranberry proanthocyanidins and other tannin-containing materials. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:3061–3067, 2011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78. Virgin F, Zhang S, Schuster D, et al. The bioflavonoid compound, sinupret, stimulates transepithelial chloride transport in vitro and in vivo. Laryngoscope 120:1051–1056, 2010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79. Zhang S, Skinner D, Hicks SB, et al. Sinupret activates CFTR and TMEM16A-dependent transepithelial chloride transport and improves indicators of mucociliary clearance. PloS One 9:e104090, 2014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80. Lai Y, Dilidaer D, Chen B, et al. In vitro studies of a distillate of rectified essential oils on sinonasal components of mucociliary clearance. Am J Rhinol Allergy 28:244–248, 2014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]