Abstract
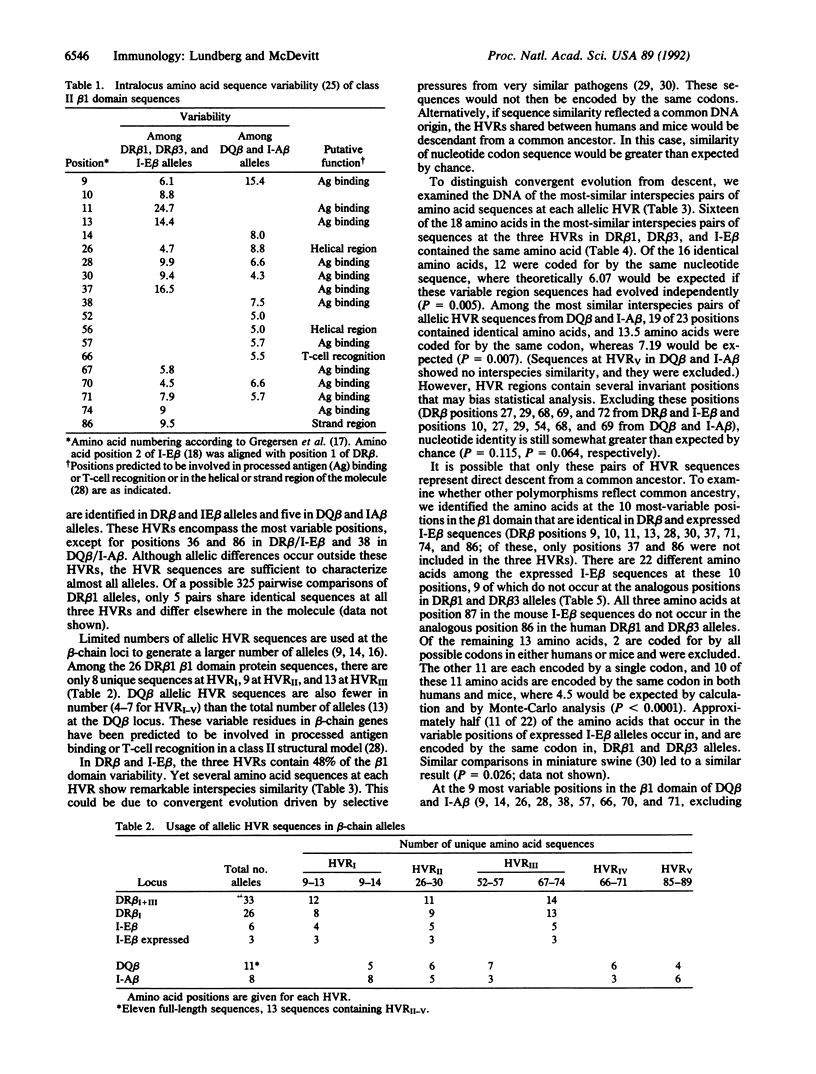
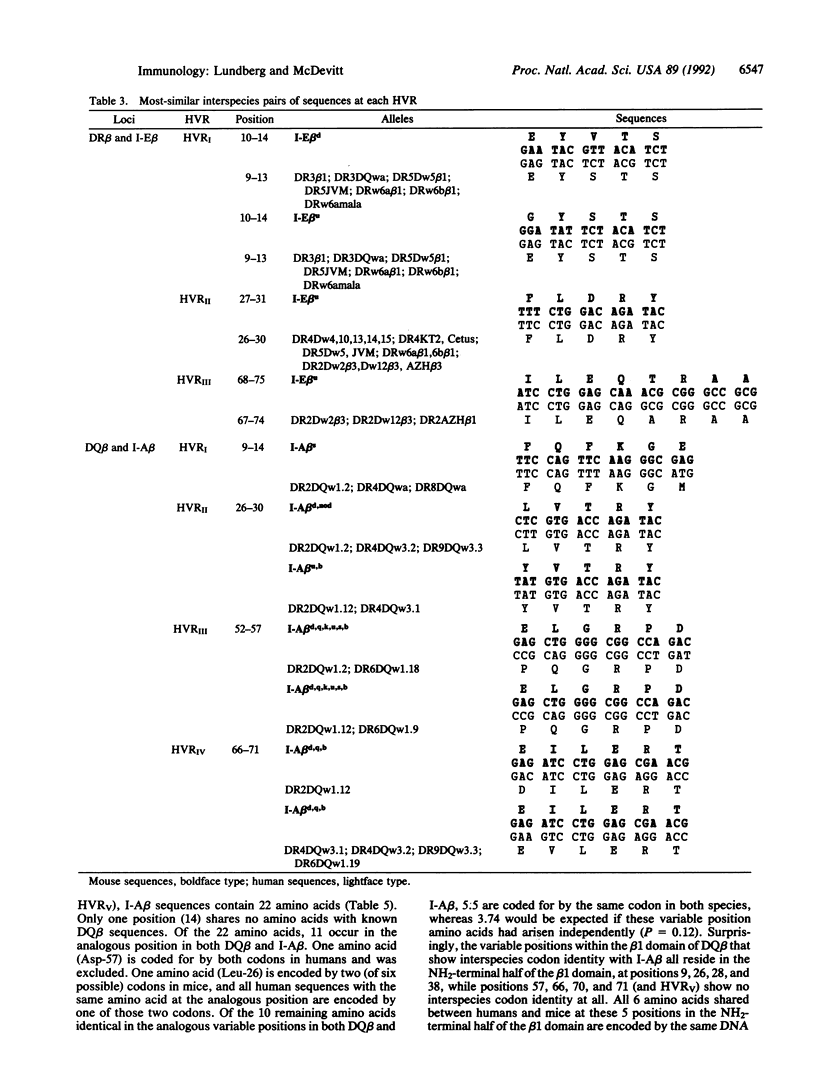
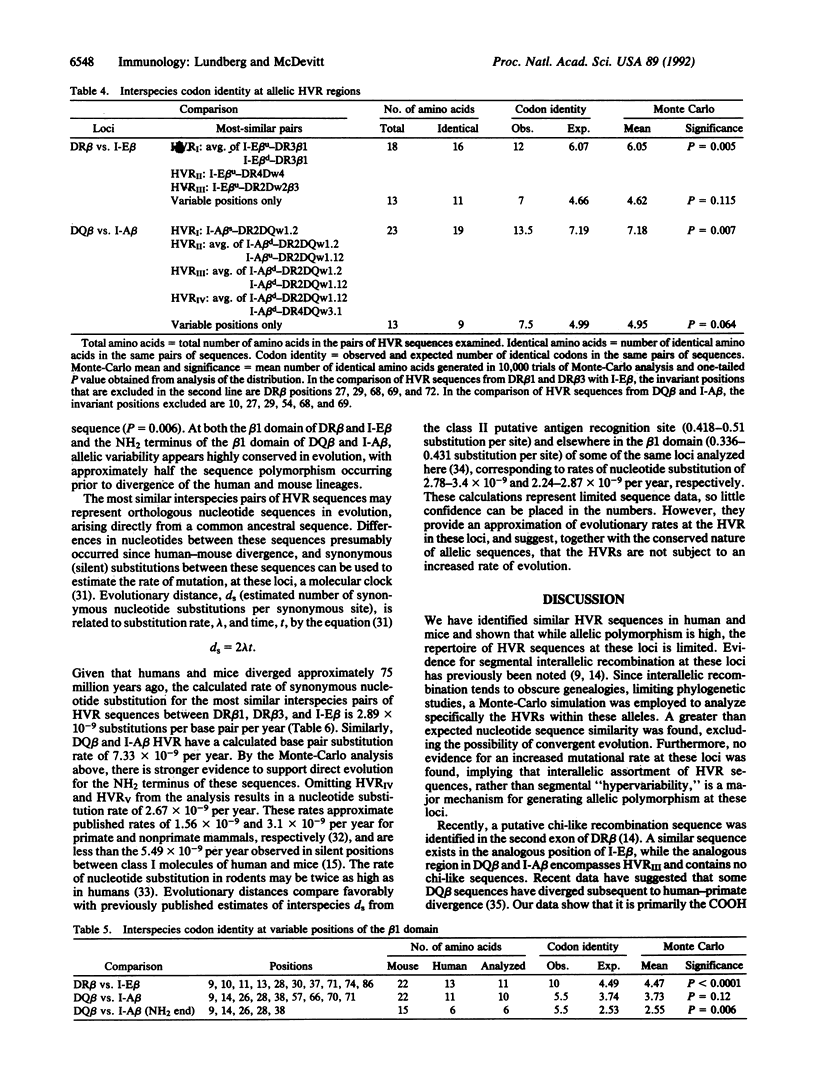
The high degree of polymorphism seen at major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II loci is a feature unique to the MHC. Most of the beta-chain polymorphism is localized in "hypervariable" regions (HVRs). HVR amino acid sequence similarity between distantly related species has recently been found. We have employed a Monte-Carlo statistic to show that shared HVR polymorphism between beta-chain genes of humans and mice represents direct descent of ancestral sequences rather than convergent evolution. Furthermore, half the sequence polymorphism seen in class II beta-chain genes of mice persists in evolution and is encoded by the same DNA sequence in humans. No evidence for increased mutation rate within the HVR was found. We postulate that the HVR can be considered the genetic unit of recombination, with selection for HVR sequences and combinations of HVRs constrained by functional considerations.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acha-Orbea H., McDevitt H. O. The first external domain of the nonobese diabetic mouse class II I-A beta chain is unique. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2435–2439. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell J. I., Denney D., Jr, Foster L., Belt T., Todd J. A., McDevitt H. O. Allelic variation in the DR subregion of the human major histocompatibility complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(17):6234–6238. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.17.6234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. H., Jardetzky T., Saper M. A., Samraoui B., Bjorkman P. J., Wiley D. C. A hypothetical model of the foreign antigen binding site of class II histocompatibility molecules. Nature. 1988 Apr 28;332(6167):845–850. doi: 10.1038/332845a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estess P., Begovich A. B., Koo M., Jones P. P., McDevitt H. O. Sequence analysis and structure-function correlations of murine q, k, u, s, and f haplotype I-A beta cDNA clones. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3594–3598. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan W. M., Kasahara M., Gutknecht J., Klein D., Mayer W. E., Jonker M., Klein J. Shared class II MHC polymorphisms between humans and chimpanzees. Hum Immunol. 1989 Oct;26(2):107–121. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(89)90096-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figueroa F., Günther E., Klein J. MHC polymorphism pre-dating speciation. Nature. 1988 Sep 15;335(6187):265–267. doi: 10.1038/335265a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorski J., Mach B. Polymorphism of human Ia antigens: gene conversion between two DR beta loci results in a new HLA-D/DR specificity. Nature. 1986 Jul 3;322(6074):67–70. doi: 10.1038/322067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafsson K., Germana S., Hirsch F., Pratt K., LeGuern C., Sachs D. H. Structure of miniature swine class II DRB genes: conservation of hypervariable amino acid residues between distantly related mammalian species. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9798–9802. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafsson K., Wiman K., Emmoth E., Larhammar D., Böhme J., Hyldig-Nielsen J. J., Ronne H., Peterson P. A., Rask L. Mutations and selection in the generation of class II histocompatibility antigen polymorphism. EMBO J. 1984 Jul;3(7):1655–1661. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02026.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyllensten U. B., Erlich H. A. Ancient roots for polymorphism at the HLA-DQ alpha locus in primates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):9986–9990. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.9986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyllensten U. B., Lashkari D., Erlich H. A. Allelic diversification at the class II DQB locus of the mammalian major histocompatibility complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(5):1835–1839. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.5.1835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyllensten U. B., Sundvall M., Erlich H. A. Allelic diversity is generated by intraexon sequence exchange at the DRB1 locus of primates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3686–3690. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashida H., Miyata T. Unusual evolutionary conservation and frequent DNA segment exchange in class I genes of the major histocompatibility complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2671–2675. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes A. L., Nei M. Nucleotide substitution at major histocompatibility complex class II loci: evidence for overdominant selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(3):958–962. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.3.958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes A. L., Nei M. Pattern of nucleotide substitution at major histocompatibility complex class I loci reveals overdominant selection. Nature. 1988 Sep 8;335(6186):167–170. doi: 10.1038/335167a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein J. Origin of major histocompatibility complex polymorphism: the trans-species hypothesis. Hum Immunol. 1987 Jul;19(3):155–162. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(87)90066-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larhammar D., Hammerling U., Denaro M., Lund T., Flavell R. A., Rask L., Peterson P. A. Structure of the murine immune response I-A beta locus: sequence of the I-A beta gene and an adjacent beta-chain second domain exon. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):179–188. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90148-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawlor D. A., Ward F. E., Ennis P. D., Jackson A. P., Parham P. HLA-A and B polymorphisms predate the divergence of humans and chimpanzees. Nature. 1988 Sep 15;335(6187):268–271. doi: 10.1038/335268a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee B. S., Bell J. I., Rust N. A., McDevitt H. O. Structural and functional variability among DQ beta alleles of DR2 subtypes. Immunogenetics. 1987;26(1-2):85–91. doi: 10.1007/BF00345459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malissen M., Hunkapiller T., Hood L. Nucleotide sequence of a light chain gene of the mouse I-A subregion: A beta d. Science. 1983 Aug 19;221(4612):750–754. doi: 10.1126/science.6410508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCaldon P., Argos P. Oligopeptide biases in protein sequences and their use in predicting protein coding regions in nucleotide sequences. Proteins. 1988;4(2):99–122. doi: 10.1002/prot.340040204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConnell T. J., Talbot W. S., McIndoe R. A., Wakeland E. K. The origin of MHC class II gene polymorphism within the genus Mus. Nature. 1988 Apr 14;332(6165):651–654. doi: 10.1038/332651a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDevitt H. O., Wraith D. C., Smilek D. E., Lundberg A. S., Steinman L. Evolution, function, and utilization of major histocompatibility complex polymorphism in autoimmune disease. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1989;54(Pt 2):853–857. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1989.054.01.099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mengle-Gaw L., McDevitt H. O. Genetics and expression of mouse Ia antigens. Annu Rev Immunol. 1985;3:367–396. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.03.040185.002055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mengle-Gaw L., McDevitt H. O. Isolation and characterization of a cDNA clone for the murine I-E beta polypeptide chain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7621–7625. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mengle-Gaw L., McDevitt H. O. Predicted protein sequence of the murine I-E-beta S-polypeptide chain from cDNA and genomic clones. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2910–2914. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito H., Maki R. A., Clayton L. K., Tonegawa S. Complete primary structures of the E beta chain and gene of the mouse major histocompatibility complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5520–5524. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakoyama Y., Hong K. J., Byun S. M., Hisajima H., Ueda S., Yaoita Y., Hayashida H., Miyata T., Honjo T. Nucleotide sequences of immunoglobulin epsilon genes of chimpanzee and orangutan: DNA molecular clock and hominoid evolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(4):1080–1084. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.4.1080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- She J. X., Boehme S. A., Wang T. W., Bonhomme F., Wakeland E. K. Amplification of major histocompatibility complex class II gene diversity by intraexonic recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 15;88(2):453–457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.2.453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart C. B., Schilling J. W., Wilson A. C. Adaptive evolution in the stomach lysozymes of foregut fermenters. 1987 Nov 26-Dec 2Nature. 330(6146):401–404. doi: 10.1038/330401a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. I., Li W. H. Evidence for higher rates of nucleotide substitution in rodents than in man. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1741–1745. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu S., Saunders T. L., Bach F. H. Polymorphism of human Ia antigens generated by reciprocal intergenic exchange between two DR beta loci. Nature. 1986 Dec 18;324(6098):676–679. doi: 10.1038/324676a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu T. T., Kabat E. A. An analysis of the sequences of the variable regions of Bence Jones proteins and myeloma light chains and their implications for antibody complementarity. J Exp Med. 1970 Aug 1;132(2):211–250. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.2.211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



