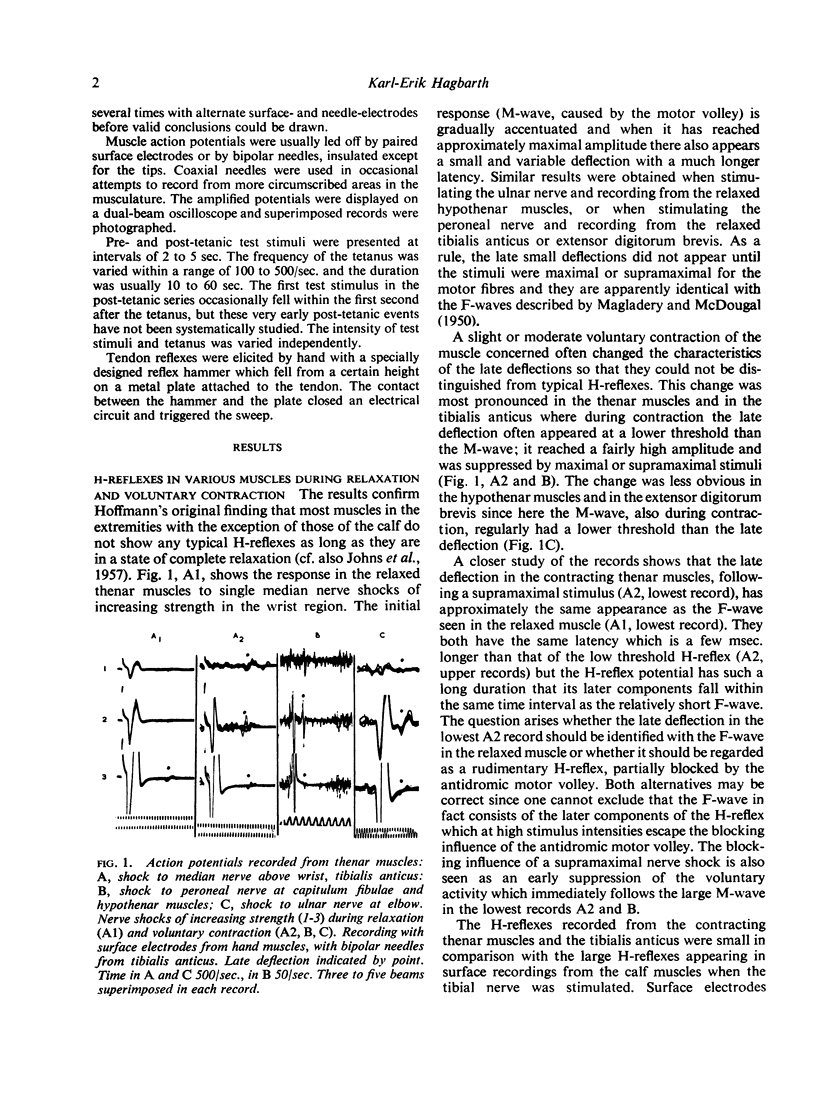
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOTELHO S. Y. Alterations in muscle tension without similar changes in electrical activity in patients with myasthenia gravis. J Clin Invest. 1955 Sep;34(9):1403–1409. doi: 10.1172/JCI103189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOTELHO S. Y., CANDER L. Post-tetanic potentiation before and during ischemia intact human skeletal muscle. J Appl Physiol. 1953 Oct;6(4):221–228. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1953.6.4.221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown G. L., von Euler U. S. The after effects of a tetanus on mammalian muscle. J Physiol. 1938 Jun 14;93(1):39–60. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1938.sp003623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C., ECCLES R. M., LUNDBERG A. The convergence of monosynaptic excitatory afferents on to many different species of alpha motoneurones. J Physiol. 1957 Jun 18;137(1):22–50. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C., RALL W. Effects induced in a monosynaptic reflex path by its activation. J Neurophysiol. 1951 Sep;14(5):353–376. doi: 10.1152/jn.1951.14.5.353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRANIT R., PHILLIPS C. G., SKOGLUND S., STEG G. Differentiation of tonic from phasic alpha ventral horn cells by stretch, pinna and crossed extensor reflexes. J Neurophysiol. 1957 Sep;20(5):470–481. doi: 10.1152/jn.1957.20.5.470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUGHES J. R. Post-tetanic potentiation. Physiol Rev. 1958 Jan;38(1):91–113. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1958.38.1.91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOHNS R. J., GROB D., HARVEY A. M. An electromyographic study of a spinal cord reflex in the normal human arm. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1957 Oct;101(4):232–239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOHNS R. J., GROB D., HARVEY A. M. Electromyographic changes in myasthenia gravis. Am J Med. 1955 Nov;19(5):679–683. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(55)80007-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAGLADERY J. W., McDOUGAL D. B., Jr Electrophysiological studies of nerve and reflex activity in normal man. I. Identification of certain reflexes in the electromyogram and the conduction velocity of peripheral nerve fibers. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1950 May;86(5):265–290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAGLADERY J. W., TEASDALL R. D. Stretch reflexes in patients with spinal cord lesions. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1958 Nov;103(5):236–241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAILLARD J. Analyse électrophysiologique et comparaison, chez l'homme, du réflexe de Hoffmann et du réflexe myotatique. Pflugers Arch. 1955;260(6):448–479. doi: 10.1007/BF00363666. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARK A. M., TEASDALL R. D., MAGLADERY J. W. Electrophysiological studies of nerve and reflex activity in normal man. VII. Certain effects of brief stretch. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1951 Jun;88(6):549–561. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TEASDALL R. D., PARK A. M., LANGUTH H. W., MAGLADERY J. W. Electrophysiological studies of reflex activity in patients with lesions of the nervous system. II. Disclosure of normally suppressed monosynaptic reflex discharge of spinal motoneurones by lesions of lower brain-stem and spinal cord. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1952 Oct;91(4):245–256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



