Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALVORD E. C., Jr, STEVENSON L. D., VOGEL F. S., ENGLE R. L., Jr Neuropathological findings in phenyl-pyruvic oligophrenia (phenyl-ketonuria). J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1950 Jul;9(3):298–310. doi: 10.1097/00005072-195007000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ARMSTRONG M. D., TYLER F. H. Studies on phenylketonuria. I. Restricted phenylalanine intake in phenylketonuria. J Clin Invest. 1955 Apr;34(4):565–580. doi: 10.1172/JCI103105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BICKEL H., GERRARD J., HICKMANS E. M. Influence of phenylalanine intake on phenylketonuria. Lancet. 1953 Oct 17;265(6790):812–813. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(53)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLAINEY J. D., GULLIFORD R. Phenylalanine-restricted diets in the treatment of phenylketonuria. Arch Dis Child. 1956 Dec;31(160):452–466. doi: 10.1136/adc.31.160.452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRIMBLECOMBE F. S., STONEMAN M. E., MALIPHANT R. Dietary treatment of an infant with phenylketonuria. Lancet. 1959 Mar 21;1(7073):609–611. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(59)92356-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
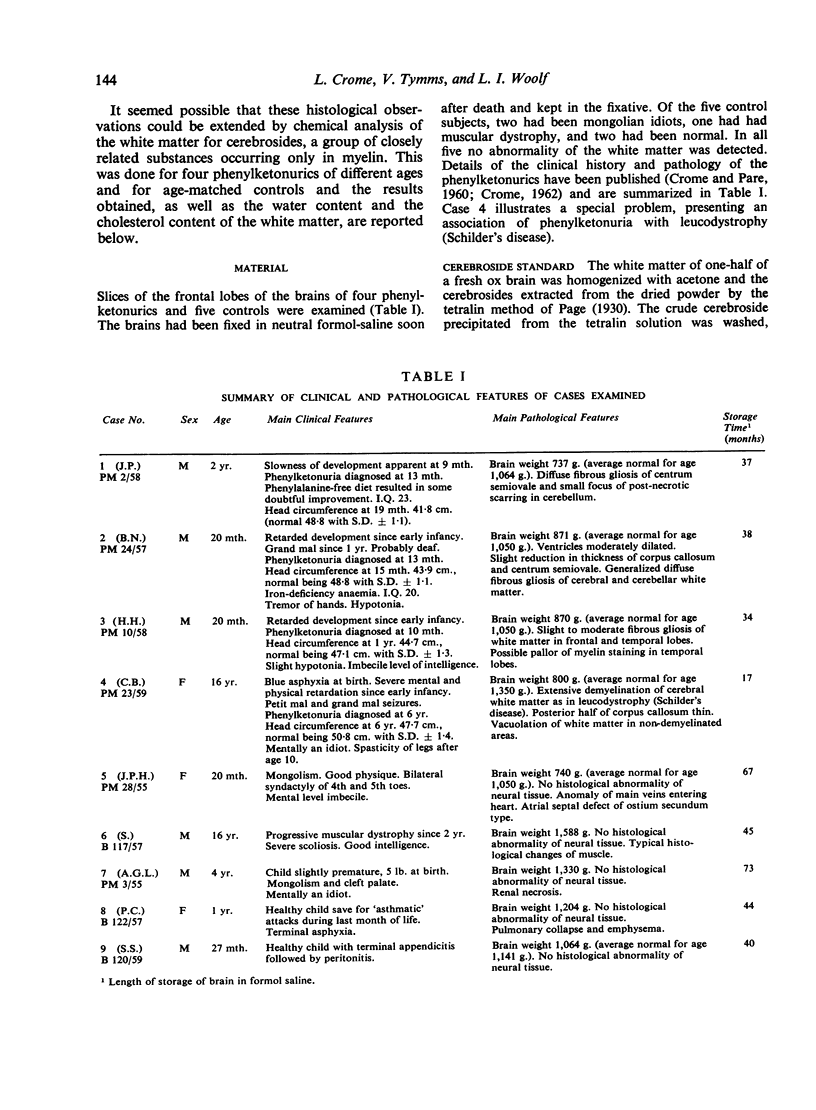
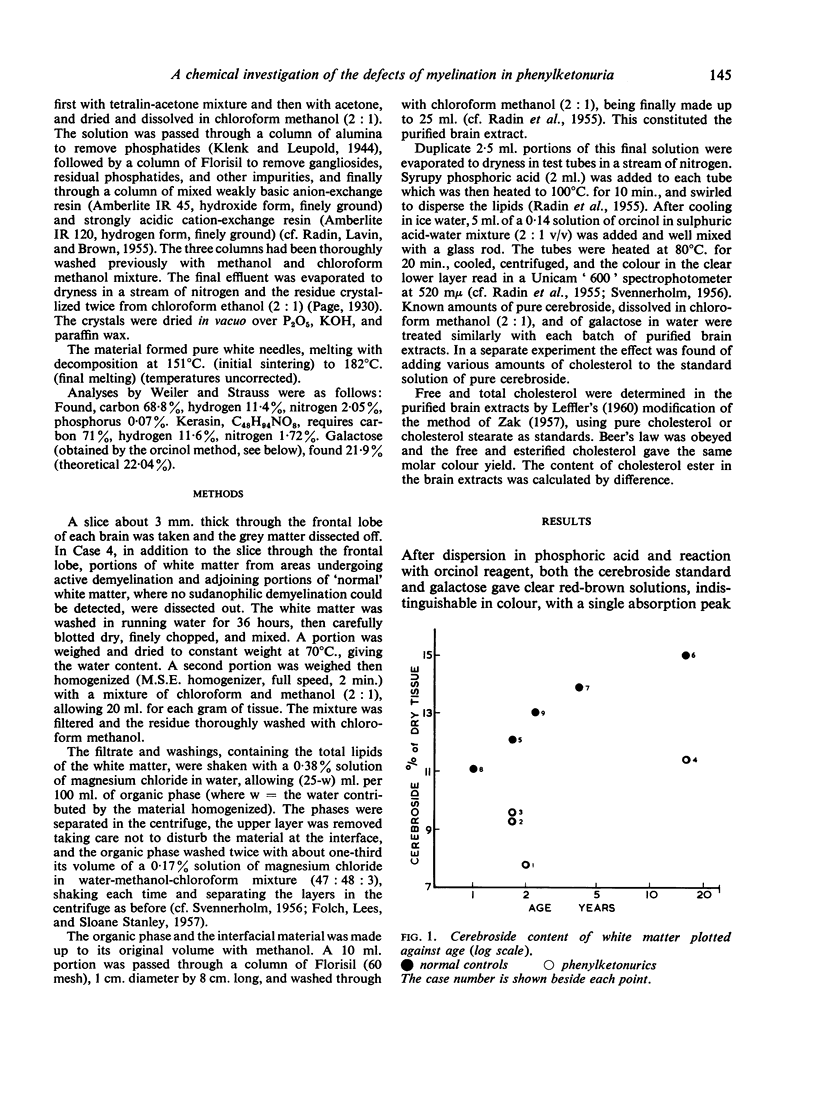
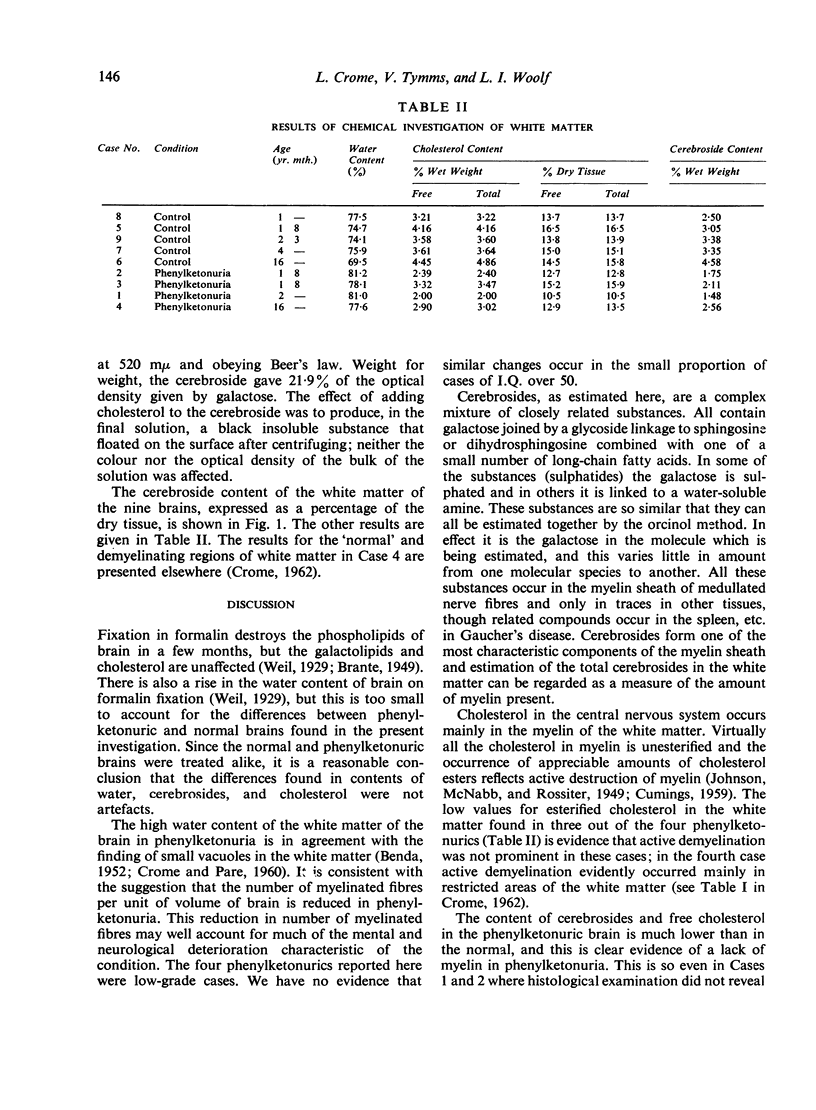
- CROME L. The association of phenylketonuria with leucodystrophy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1962 May;25:149–153. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.25.2.149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVISON A. N., SANDLER M. Inhibition of 5-hydroxytryptophan decarboxylase by phenylalanine metabolites. Nature. 1958 Jan 18;181(4603):186–187. doi: 10.1038/181186b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FELLMAN J. H. Inhibition of DOPA decarboxylase by aromatic acids associated with phenylpyruvic oligophrenia. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1956 Dec;93(3):413–414. doi: 10.3181/00379727-93-22773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JERVIS G. A. Phenylpyruvic oligophrenia (phenylketonuria). Res Publ Assoc Res Nerv Ment Dis. 1954;33:259–282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOHNSON A. C., McNABB A. R., ROSSITER R. J. Chemical studies of peripheral nerve during Wallerian degeneration; lipids. Biochem J. 1949;45(4):500–508. doi: 10.1042/bj0450500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOW N. L., BOSMA J. F., ARMSTRONG M. D. Studies on phenylketonuria. VI. EEG studies in phenylketonuria. AMA Arch Neurol Psychiatry. 1957 Apr;77(4):359–365. doi: 10.1001/archneurpsyc.1957.02330340035003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARE C. M., SANDLER M., STACEY R. S. 5-Hydroxytryptamine deficiency in phenylketonuria. Lancet. 1957 Mar 16;272(6968):551–553. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(57)90920-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POSER C. M., VAN BOGAERT L. Neuro-pathologic observations in phenylketonuria. Brain. 1959 Mar;82(1):1–9. doi: 10.1093/brain/82.1.1-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RADIN N. S., LAVIN F. B., BROWN J. R. Determination of cerebrosides. J Biol Chem. 1955 Dec;217(2):789–796. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SANDLER M., DAVIES A., RIMINGTON C. Effect of phenylacetic acid on the carcinoid syndrome. Lancet. 1959 Sep 12;2(7098):318–322. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(59)91359-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SVENNERHOLM L. The quantitative estimation of cerebrosides in nervous tissue. J Neurochem. 1956 May;1(1):42–53. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1956.tb12053.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TASHIAN R. E. Inhibition of brain glutamic acid decarboxylase by phenylalanine, valine, and leucine derivatives: a suggestion concerning the etiology of the neurological defect in phenylketonuria and branched-chain ketonuria. Metabolism. 1961 May;10:393–402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOOLF L. I., GRIFFITHS R., MONCRIEFF A., COATES S., DILLISTONE F. The dietary treatment of phenylketonuria. Arch Dis Child. 1958 Feb;33(167):31–45. doi: 10.1136/adc.33.167.31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOOLF L. I., GRIFFITHS R., MONCRIEFF A. Treatment of phenylketonuria with a diet low in phenylalanine. Br Med J. 1955 Jan 8;1(4905):57–64. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.4905.57. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOOLF L. I., VULLIAMY D. G. Phenylketonuria with a study of the effect upon it of glutamic acid. Arch Dis Child. 1951 Dec;26(130):487–494. doi: 10.1136/adc.26.130.487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZAK B. Simple rapid microtechnic for serum total cholesterol. Am J Clin Pathol. 1957 May;27(5):583–588. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/27.5_ts.583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


