Abstract
Pluripotent stem cells offer great therapeutic promise for personalized treatment platforms for numerous injuries, disorders, and diseases. Octamer-binding transcription factor 4 (OCT4) is a key regulatory gene maintaining pluripotency and self-renewal of mammalian cells. With site-specific integration for gene correction in cellular therapeutics, use of the OCT4 promoter may have advantages when expressing a suicide gene if pluripotency remains. However, the human OCT4 promoter region is 4 kb in size, limiting the capacity of therapeutic genes and other regulatory components for viral vectors, and decreasing the efficiency of homologous recombination. The purpose of this investigation was to characterize the functionality of a novel 967bp OCT4-short response element during pluripotency and to examine the OCT4 titer-dependent response during differentiation to human derivatives not expressing OCT4. Our findings demonstrate that the OCT4-short response element is active in pluripotency and this activity is in high correlation with transgene expression in vitro, and the OCT4-short response element is inactivated when pluripotent cells differentiate. These studies demonstrate that this shortened OCT4 regulatory element is functional and may be useful as part of an optimized safety component in a site-specific gene transferring system that could be used as an efficient and clinically applicable safety platform for gene transfer in cellular therapeutics.
Introduction
Octamer-binding transcription factor 4 (OCT4) is a nuclear transcription factor of the POU-homeodomain family. The role of OCT4 in mammalian cells is critical in several aspects of embryonic stem cell maintenance including self-renewal and sustainment of totipotency or pluripotency, and for regulation of gene expression networks.1–4 Changes in its expression are involved in multiple developmental programs such as lineage commitment to primitive endoderm and mesoderm by its transient increase, and to trophectoderm differentiation with its repression.5–8 The OCT4 promoter consists of both a (i) distal promoter, which mediates the molecular response for transcription via a putative OCT4-SOX2 binding site, and (ii) a proximal promoter, containing a retinoic acid, NANOG, estrogen and steroid-thyroid response element located within a region 3.1 kb upstream of the OCT4 gene. These are present as four conserved regions which can be methylated during embryogenesis and cell fate specialization9–12 (Figure 1a).
Figure 1.
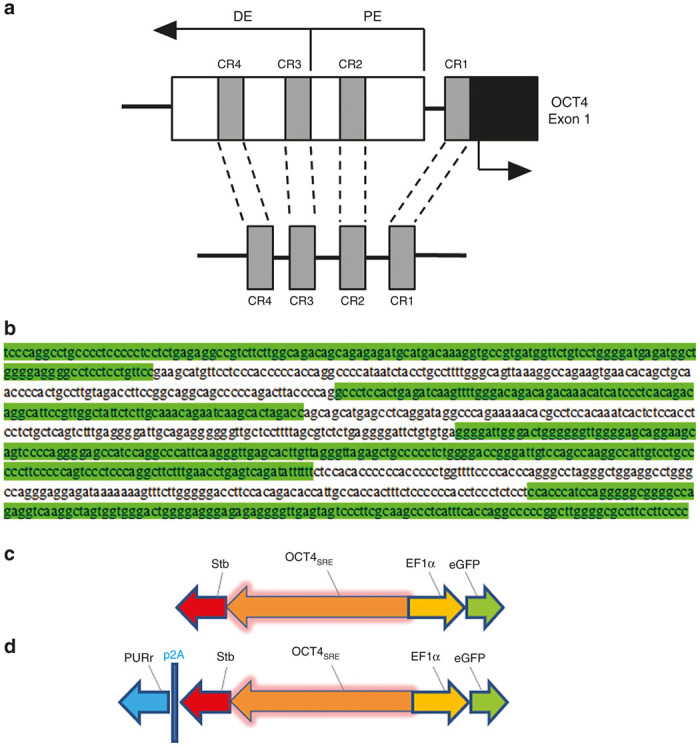
Schematic of OCTS4SRE and vector constructs. (a) OCT4 expression is regulated by an upstream proximal enhancer (PE) and distal enhancer (DE). Comparison of human, bovine, and murine OCT4 5′ upstream sequences revealed four conserved regions (CR1–CR4) and these were combined with linkers to create the OCT4SRE. (b) Sequence of OCT4SRE with conserved regions are highlighted in green with CR4 → CR1 from top to bottom. Linkers between regions are unhighlighted. (c) Constructs were developed to test the OCT4-short response element (OCT4SRE) expressing strawberry fluorescent protein (Stb) in the reverse orientation while the constitutive elongation factor 1α promoter (EF1α) directed eGFP expression. (d) A second construct was developed that also provided coexpression of puromycin resistance (PURr) to the OCT4SRE by a porcine teschovirus-1 (p2A) linker. OCT4, Octamer-binding transcription factor 4; eGFP, enhanced green fluorescent protein.
The mechanism of reprograming adult dermal fibroblasts modifies the epigenetic landscape by transient addition or genomic incorporation of four essential reprogramming factors (OCT4, SOX2, KLF4, and MYC13). As one of the OSKM factors, OCT4 initiates chromatin rearrangement, gene transactivation, and pluripotency development.14–16 Additionally, OCT4 is used in part to maintain the pluripotent phenotype and for self-renewal.17 As mammalian cells undergo differentiation into somatic tissues, there is a loss in OCT4 expression.18,19 This regulation of OCT4 is essential in tissue development and is orchestrated by feed-forward transcription, autoregulatory-promoting mechanisms, and by methylation-susceptible sequences20 that determine the timing of differentiation.21
Human induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSCs) are a promising source of cells for autologous tissue engineering and therapeutic application; however, potential compromise of genomic integrity by genomic remodeling during cellular reprogramming and tumorigenic potential attributed to avid OCT4 activity represent safety concerns for their eventual clinical application.22–24 Specifically, OCT4 may act to promote malignancy,3 as its ectopic expression in somatic cells can cause epithelial dysplasia.25 Additionally, as OCT4 protein expression gradually increases in different types of malignant cells, it can promote tumorigenesis and inhibit cancer cell apoptosis26,27 and has been detected in both germ cell28–30 and various human somatic tumors, including hepatocellular carcinoma,31 breast cancer,32,33 and bladder cancer,34,35 suggesting that OCT4 has a role in both the embryo and in adult malignancies.
The purpose of this study was to characterize the functionality of a 967 bp OCT4-short response element (OCT4SRE) (Figure 1b) during pluripotency and differentiation; a shortened promoter would be useful in genomic modification vectors, providing additional space for therapeutic or other regulatory components. In addition, both viral vector titer and homologous recombination can be improved by smaller constructs and utilizing a shortened but functional promoter will reduce the overall size. Finally, if pluripotency remains in a delivered therapeutic cell product, utilizing the OCT4SRE to drive a suicide gene as part of a therapeutic construct would allow for the removal of these cells and decrease the potential risk of unintended implantation of cells with pluripotency.
Results
Construct delivery, OCT4 activation, and positive selection
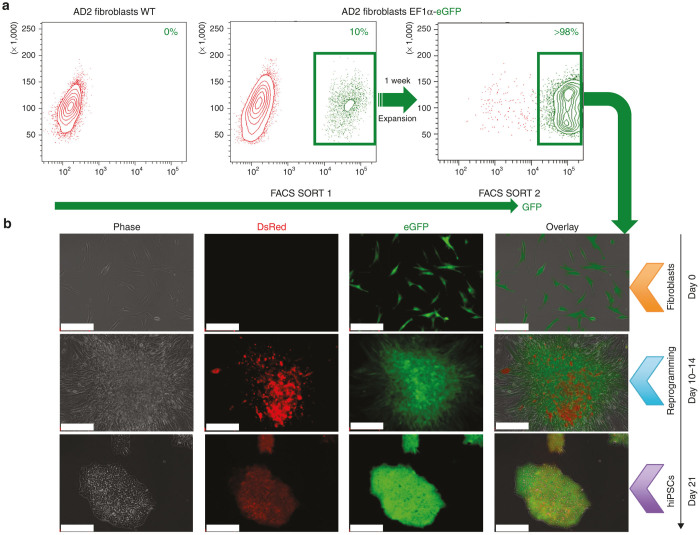
AD2 fibroblasts were transduced with the OCT4SRE vector at 10 multiplicity of infection (MOI) and the High10% eGFP-expressing cells (mean fluorescence intensity ≥ 1 × 104) were collected by fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) purification. The purified fraction was expanded for 1 week and FACS-purified for eGFP, for a second time. The eGFP-expressing cells with a mean fluorescence intensity of ~1 × 105 (>98%) were allowed to recover for 48 hours before beginning lentivirus-based reprogramming to hiPSC (Figure 2a). These genetically modified cells, that constitutively expressed eGFP, were transduced for reprogramming at 10 MOI with stem cell cassette (STEMCCA). The cells were then seeded over a mouse embryonic fibroblast layer at day 7 and were inspected regularly prior to harvesting the Stb-expressing putative hiPSC candidate clones at 21 days.
Figure 2.
FACS-based purification plots of fibroblasts and OCT4SRE activity with reprogramming. (a) FACSAria cell sorter was pre-adjusted and calibrated to very high purity for all purifications. eGFP-positive fraction post-2x FACS SORT was collected for OCT4 activation by reprogramming adult somatic cells to hiPSC. (b) Live imaging of AD2 cells with genetic modification where DsRed = Stb expression driven by OCT4SRE and eGFP = EF1α-eGFP. Orange arrow = AD2 fibroblasts (eGFP-positive fraction post-2x FACS SORT); blue arrow = day 10–14 high Stb-expressing reprogramming cell aggregates; and purple arrow = eGFP/Stb-double positive putative AD2 hiPSC on CGPM at day 21. (Bar = 200 μm). CGPM, clinical grade pluripotent media; eGFP, enhanced green fluorescent protein; EF1α, elongation factor 1α; FACS, fluorescence-activated cell sorting; hiPSC, human induced pluripotent stem cell; OCT4, octamer-binding transcription factor 4; OCT4SRE, OCT4-short response element.
At day 10–14 after initiation of reprogramming, the Stb expression peaked, allowing visualization of the Stb-positive cell aggregates by fluorescence microscopy at low exposure time (<300 ms, second row) (Figure 2b). However, Stb fluorescence intensity decreased for the remaining days of the culture until reaching a consistent basal level at approximately day 21 (800–1,200 ms) (Figure 2b, third row). This decline of Stb fluorescence intensity is consistent with previous observations of OCT4 expression fluctuation during cellular reprogramming where OCT4 expression peaks to commence pluripotency development then returns to a substantially lower basal level in hiPSCs to maintain pluripotency.19 The putative hiPSC clones (now referred as C1) were then selected by examining for pluripotent-like cell morphology and eGFP/Stb-double positive expression; they were then converted to clinical grade (by growing in clinical grade pluripotent media and conditions).
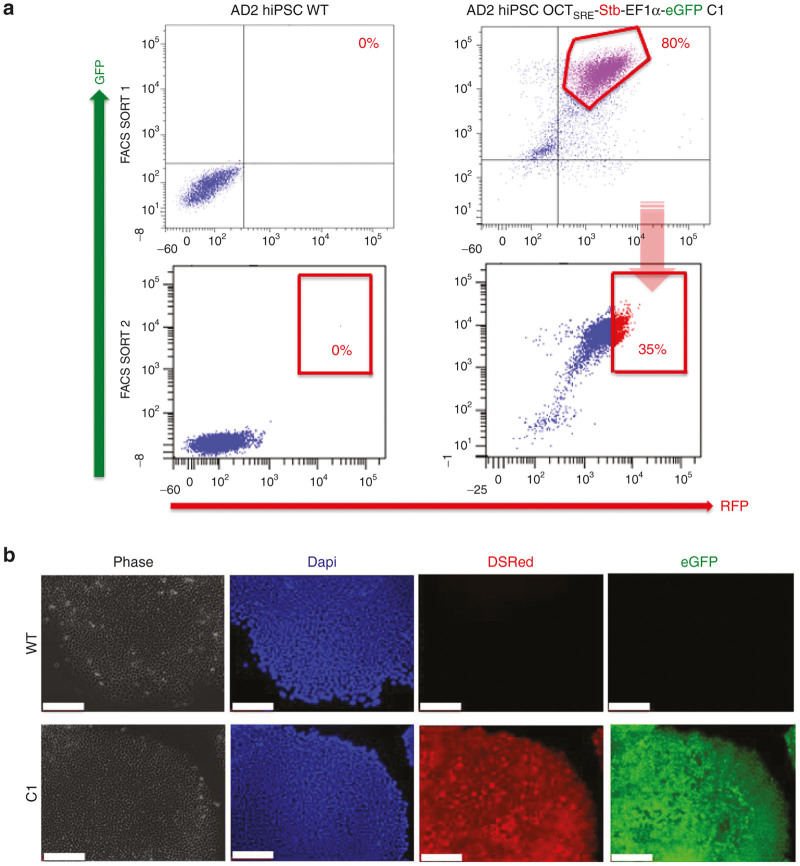
After establishing the clinical grade pluripotent cultures, FACS purification of Stb/eGFP-double positive cells was performed for C1 and the Stb/eGFP-expressing subset was collected (Figure 3a), followed by 1 week recovery and FACS purification for Stb/eGFP a second time. The High35% Stb/eGFP-expressing cells, with a MFI ≥ 5 × 103 for both colors, were collected for further investigations. Stb expression in the pluripotent state was further confirmed by immunocytochemistry (ICC) against RFP (Figure 3b).
Figure 3.
FACS-based purification plots of human induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSCs) and OCT4SRE activity. (a) The High35% Stb/eGFP-double positive fraction post-2x FACS SORT was collected. (b) Indirect OCT4SRE-mediated Stb expression assessment was performed after OCT4 activation by reprogramming to hiPSC by ICC staining for RFP where blue = DAPI, RFP = Stb expression driven by OCT4SRE, eGFP = EF1α-eGFP. (Bar = 200 μm). eGFP, enhanced green fluorescent protein; EF1α, elongation factor 1α; FACS, fluorescence-activated cell sorting; hiPSC, human induced pluripotent stem cell; OCT4, octamer-binding transcription factor 4; OCT4SRE, OCT4-short response element.
Evaluation of pluripotency
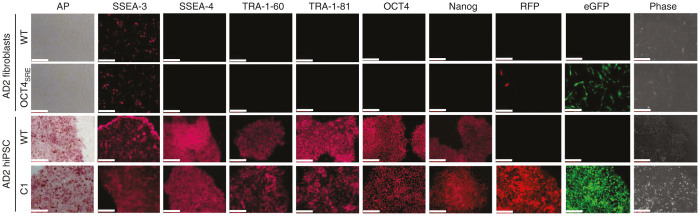
The putative AD2 hiPSC Stb/eGFP-double positive C1, AD2 hiPSC WT, and the nonpluripotent counterparts (AD2 fibroblasts OCT4SRE and AD2 fibroblasts WT) were examined by ICC for markers of canonical stemness for pluripotency, expecting these to have been activated through STEMCCA-based reprogramming (Figure 4).36 Both of the putative hiPSCs tested positive for the pluripotent immunophenotype. Both of the hiPSCs were positive for Nanog37 and OCT4,17,37 having distinct functionality in initiating and maintaining the pluripotent state. In addition, the putative hiPSCs highly expressed alkaline phosphatase (alkaline phosphatase is markedly increased in undifferentiated PSCs).38 Although the surface glycosphingolipids stage-specific embryonic antigen 3 (SSEA-3) and stage-specific embryonic antigen 4 (SSEA-4) may not play critical functional roles in maintaining pluripotency, they are highly expressed on PSCs, have discrete multipotent abilities, and may potentiate reprograming efficiency,37,39 and therefore, were also examined and found to be positive on the hiPSCs. Finally, the transmembrane proteins TRA-1–60 and TRA-1–81 are avidly expressed by undifferentiated human PSCs, and while these are without an attributed pluripotent function, their expression is lost during differentiation40; both were positive on AD2 hiPSC C1. The fibroblasts tested negative for all the markers except SSEA-3 which was weakly positive; this has been previously reported elsewhere.39
Figure 4.
Immunophenotyping of hiPSCs confirms pluripotency as cells can be differentiated into the three germ layers. AD2 hiPSC where alkaline phosphatase (AP), stage-specific embryonic antigens 3 (SSEA-3) and 4 (SSEA-4), tumor-related antigen 1–60 (TRA 1–60) and 1–81 (TRA 1–81) octamer-binding transcription factor 4 (OCT4), and transcription of homeobox protein Nanog were tested. Stb (RFP), eGFP and phase images were collected for each cell type to demonstrate construct expression. Cell types of images from top to bottom are: AD2 fibroblasts wild type (WT), AD2 fibroblasts post-2x FACS-purified for eGFP (OCT4SRE), AD2 hiPSC wild type (WT), AD2 hiPSC Clone 1 expressing Stb/eGFP (C1). FACS, fluorescence-activated cell sorting; hiPSC, human induced pluripotent stem cell; eGFP, enhanced green fluorescent protein; OCT4SRE, OCT4-short response element.
We did detect a small number of fibroblasts as being RFP positive, suggesting that there was some off-target activity of the OCT4SRE (Figure 4). To further examine the sensitivity and off-target activity of the OCT4SRE in OCT4-negative cells, we performed flow cytometry comparing the number of eGFP/Stb-double positive AD2 fibroblasts with Stb driven by the OCT4SRE and the full-length OCT4 promoter. We found that off-target expression by the full-length OCT4 promoter and OCT4SRE occurred in approximately 0.4% and 3.2% of cells, respectively (see Supplementary Figure S1).
The ability of these hiPSCs to differentiate into the three germ layers was evaluated in vitro utilizing the d-Stem Tri-lineage differentiation kit. The lineage-specific differentiation was assessed with validated antibodies (listed in Table 1) to: (i) Brachyury, a protein encoded by the T gene and initiates early cellular differentiation into mesoderm and axis differentiation; (ii) SOX17, a transcriptional regulator promoting endoderm formation, allowing for cellular differentiation by indirectly antagonizing self-renewal; and (iii) SOX1 which regulates neural plate delineation, ectoderm and neural determination41,42 (see Supplementary Figure S2). The lines demonstrated their ability to differentiate into all three germ layers confirming pluripotency.
Table 1. Primary and secondary antibodies.
|
Primary antibody |
Secondary antibody | Reference | Dilution | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reference | Dilution | Isotype | |||
| Nanog | Abcam, ab21603 | 1:100 | Goat anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) Alexa Fluor 647 | Life Technologies, A-21244 | 1:200 |
| OCT4 | SCBT, SC-5279 | 1:200 | Goat anti-Mouse IgG2b Alexa Fluor 647 | Life Technologies, A-21242 | 1:200 |
| RFP | Rockland, 600-401-379 | 1:250 | Goat anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L)Alexa Fluor 555 | Life Technologies, A-21428 | 1:200 |
| SSEA-3 | Millipore, mab4303 | 1:200 | Goat anti-Rat IgM, µ Chain DyLight 649 | Jackson Laboratories, 112-496-075 | 1:200 |
| SSEA-4 | Millipore, mab4304 | 1:200 | Goat anti-Mouse IgG2b Alexa Fluor 647 | Life Technologies, A-21242 | 1:200 |
| TRA 1–60 | Millipore, mab4360 | 1:200 | Goat anti-Mouse IgM (H+L) Alexa Fluor 647 | Life Technologies, A-21238 | 1:200 |
| TRA 1–81 | Millipore, mab4381 | 1:200 | Goat anti-Mouse IgM (H+L) Alexa Fluor 647 | Life Technologies, A-21238 | 1:200 |
| Brachury | MicroStem, MS052013 | 1:10 | Goat anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) Alexa Fluor 647 | Life Technologies, A-21244 | 1:200 |
| Sox17 | MicroStem, MS052013 | 1:10 | Goat anti-Mouse IgM (H+L) Alexa Fluor 647 | Life Technologies, A-21238 | 1:200 |
| Sox1 | MicroStem, MS052013 | 1:10 | Donkey anti-Goat IgG (H+L) DyLight594 | Abcam, ab96937 | 1:200 |
OCT4, octamer-binding transcription factor 4; OCT4SRE, OCT4-short response element; SSEA-3, stage-specific embryonic antigen 3; SSEA-4, stage-specific embryonic antigen.4; TRA (1–60), tumor-related antigen 1–60; TRA (1–81), tumor-related antigen (1–81).
In vitro functional response and OCT4SRE inactivation
After 1 week of dermal culture media (DCM) conditioning, AD2 hiPSC C1 demonstrated robust eGFP expression and a very low OCT4SRE-mediated Stb expression by ICC (see Supplementary Figure S3, RFP column for C1). The morphologic appearance of the pluripotent cells in the cultures drastically changed during the first 48 hours in DCM, acquiring a flattened fibroblast-like appearance with a noticeable reduction in their self-renewability.
To investigate the in vitro functional response of the OCT4SRE, AD2 hiPSC WT were transduced with lenti-pRRL-sin-cPPT-rPAC-rp2A-rStb-rOCT4SRE-EF1α-eGFP (now referred as C1P) and were puromycin-selected. AD2 hiPSC C1P were then FACS-purified for Stb/eGFP-double positive cells, puromycin-selected, and FACS-purified a second time to collect the High35%-Stb/eGFP-double positive cells before DCM conditioning. Puromycin (1 μg/ml) was then added to the AD2 hiPSC C1P-derived DCM-treated cultures for 96 hours. Puromycin selection permits the pluripotent cells (that is, those cells expressing OCT4 to drive OCT4SRE-mediated puromycin resistance (see Figure 1c)) to proliferate under puromycin treatment. Thus, high OCT4-expressing hiPSCs will have high OCT4SRE-mediated puromycin resistance, whereas the differentiated derivatives will have low or no OCT4 expression and thus, no puromycin resistance resulting in negative selection (i.e., cell death). Addition of puromycin was toxic to the AD2 hiPSC WT and C1P-derived DCM derivatives (DCM-d) causing complete cell death after 96 hours of exposure, demonstrating the efficacy of the serum-based treatment to promote spontaneous differentiation and, thus, OCT4SRE inactivation (with loss of puromycin resistance).
To further confirm this result, replicate cultures of (i) fibroblasts, (ii) High35% Stb/eGFP-expressing hiPSCs, and (iii) DCM-d (i.e., spontaneously differentiated cells) were analyzed by flow cytometry for quantitative protein detection (Figure 5) and by quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) to assess the transcript level (Figure 6). AD2 fibroblasts post-2x FACS purification expressed eGFP in 96% of cells; <3% were Stb/eGFP-double positive. With STEMCAA reprogramming to pluripotency, the post-2x FACS purification for Stb demonstrated AD2 hiPSCs with Stb/eGFP-double positive expression in ≥ 90% of cells. Thus, the hiPSCs developed OCT4SRE activity during pluripotency as detected by the substantial increase in Stb/eGFP-double positive cells. After 1 week the media was changed to DCM with fetal bovine serum (FBS) (i.e., inducing cellular differentiation), the AD2 DCM-derivatives (DCM-d) revealed a statistically significant (P = 0.0001) decrease of the Stb/eGFP-double positive cells from the pluripotent state; this decrease was from ≥ 90% in hiPSCs to < 1% in the differentiated DCM-d.
Figure 5.
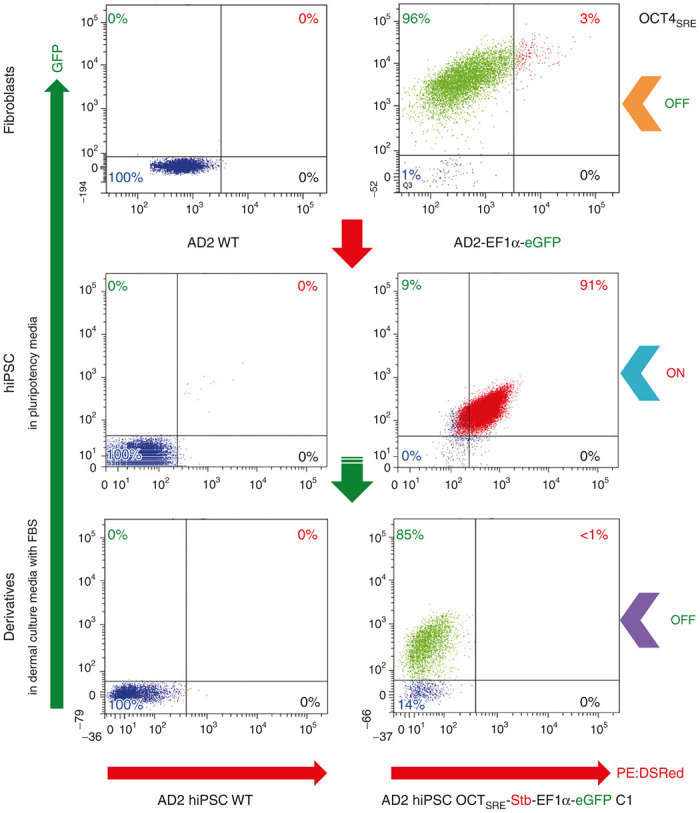
OCT4SRE shows an off-on-off pattern with fibroblast reprogramming to hiPSC to differentiation to dermal derivatives. FACS analysis plots of AD2 cells with genomic modification: Orange arrow = AD2 fibroblasts eGFP-positive fraction post-2x FACS SORT demonstrating that OCT4SRE-transcriptional regulatory activity is off. Blue arrow = High35% Stb/eGFP-expressing AD2 hiPSC clone C1 OCT4SRE activity on. Purple arrow = DCM (differentiated) derivatives clones C1 with OCT4SRE activity off. WT = Wild Type. OCT4SRE = OCT4-short response element. eGFP = enhanced green fluorescent protein. PE:TexasRed = Stb. Percentages on the quadrant-corners of the FACS plots represent the average of triplicate measurements where green = eGFP only, blue = Stb/eGFP-double negative, red = Stb/eGFP-double positive, black = Stb only. FACS, fluorescence-activated cell sorting; hiPSC, human induced pluripotent stem cell; OCT4, octamer-binding transcription factor 4; DCM, dermal culture media.
Figure 6.
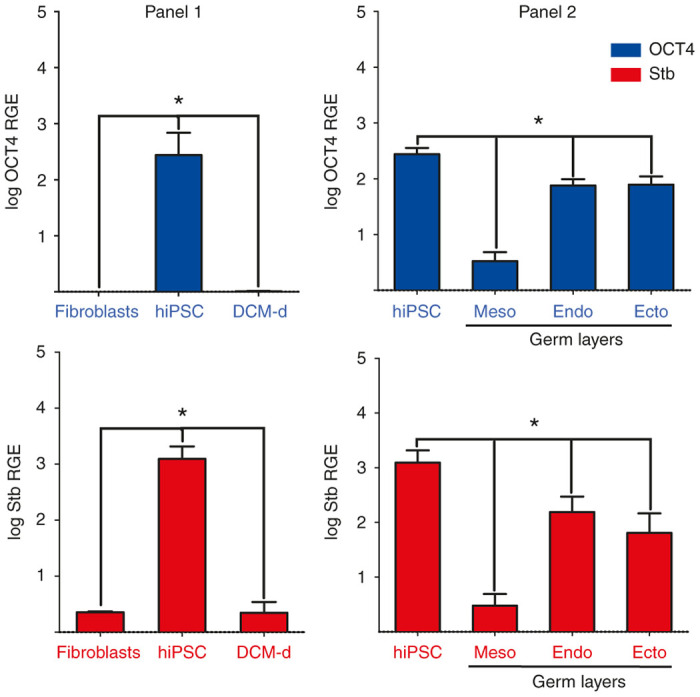
Quantitative real time PCR data analysis of OCT4SRE activity. Quantitative PCR for blue = OCT4 and red = Stb of AD2 fibroblasts, hiPSC and DCM-derivatives (DCM-d) where meso = mesoderm, endo = endoderm, ecto = ectoderm. Log Relative Gene Expression (RGE) is on the y-axis. Error bars represent mean ± SD (n = 9). Black * indicates significance P < 0.05 between experimental groups. hiPSC, human induced pluripotent stem cell; OCT4, octamer-binding transcription factor 4; DCM, dermal culture media; OCT4SRE, OCT4-short response element; PCR, polymerase chain reaction.
We measured the target transcript levels of OCT4SRE-mediated Stb expression. This demonstrated significantly higher Stb (P = 0.008) and OCT4 (P = 0.006) RNA expression during pluripotency (hiPSC) (Figure 6, panel 1, center bars) versus the parental genetically modified fibroblasts and the differentiated DCM-d (Figure 6, panel 1, outer bars); OCT4 and Stb transcript RNA expression was 2–3 logs higher than fibroblasts and DCM-d while maintained with pluripotency. Transcript levels of OCT4SRE and Stb fluctuate in equal degree during reprogramming and differentiation, indicating a direct correlation between OCT4 and Stb mRNA levels. We would expect OCT4 not to be active in these latter two conditions, and there were no statistical difference for the expression of these genes in these cell states (P = 0.235). The OCT4SRE-Stb transcript content of the parental hiPSCs and the hiPSC-derived mesoderm-, endoderm-, and ectoderm-like cells displayed RNA transcript levels for both OCT4 and Stb in ectoderm and endoderm, while mesoderm showed the lowest RNA expression among the derivatives (Figure 6, panel 2). The Pearson correlation analysis with a coefficient r2 = 0.965 (n = 15) confirms a direct statistically significant correlation of OCT4/Stb mRNA across the clones and culture conditions.
OCT4SRE-mediated cellular toxicity with thymidine kinase and ganciclovir
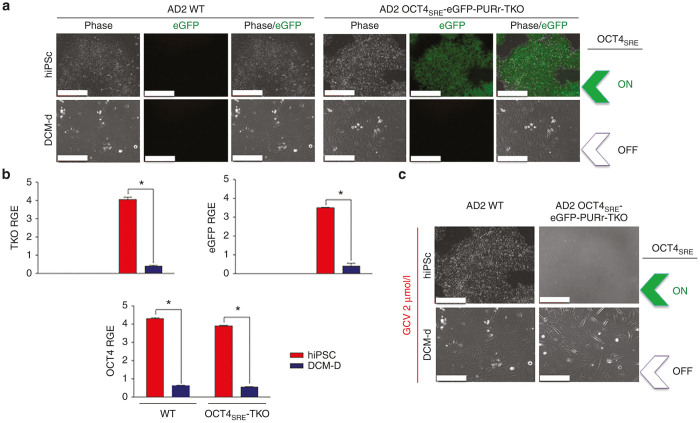
As previously described, high OCT4 expression during pluripotency promotes OCT4SRE-mediated transgene expression. While the OCT4SRE-driven RFP expression as measured by fluorescence microscopy was relatively low in AD2 hiPSC C1P, OCT4SRE demonstrated functional and specific OCT4SRE-driven antibiotic resistance (puromycin). In order to eventually apply such technology for treatment of urea cycle disorder (arginase deficiency), we developed a preclinical bidirectional third generation lentivirus. This vector is pRRL-sin-cPPT-rArgO-rEF1α-OCT4SRE-eGFP-F2A-PAC-P2A-TKO (ArgO, arginase 1 codon optimized) for single-vector gene transfer of OCT4SRE-driven expression of a relevant suicide gene (human codon optimized Herpes simplex virus 1 SR39 thymidine kinase (TKO)) and a urea cycle enzyme needed for metabolism of nitrogen. (Functional recovery of arginase in arginase-deficient hiPSCs is not further examined as part of the scope of this manuscript.) Here, we demonstrate that transduction of AD2 hiPSC WT cells with this preclinical vector conferred OCT4SRE-driven expression of eGFP and puromycin resistance as well as TKO-mediated cell death) (Figure 7). Under live fluorescence microscopy, OCT4SRE-expressing AD2 hiPSC-TKO drove eGFP expression, but eGFP was not visible after conversion to DCM-d (AD2 DCM-d-TKO) (Figure 7a). OCT4SRE-expressing AD2 hiPSC-TKO promoted expression of TKO and eGFP (and conferred puromycin resistance) while conversion to DCM-d resulted in significant decline of OCT4 expression level (P < 0.0001) (n = 3) and significant loss of TKO (P < 0.0001) (n = 3) and eGFP (P < 0.0013) (n = 3) RNA expression measured via quantitative reverse-transcriptase PCR (Figure 7b). Pearson correlation analysis between OCT4SRE-TKO (n = 3) and OCT4SRE-eGFP (n = 3) showed coefficients of r2 = 0.998 and r2 = 0.971, respectively, confirming direct statistically significant correlation between OCT4 expression levels and the transgenes regulated by OCT4SRE.
Figure 7.
Examining the functionality of the OCT4SRE promoter in ganciclovir-mediated cell killing. (a) AD2 hiPSCs transduced with vector encoding OCT4SRE-eGFP-PURr-TKO (AD2 hiPSC-TKO) and AD2 hiPSC-TKO-derived nonpluripotent DCM-d (DCM-d-TKO). OCT4SRE-driven eGFP and puromycin resistance (PURr) were only expressed in OCT4-expressing hiPSC-TKO. (TKO = Thymidine Kinase codon optimized. (Bar = 200 µm). (b) Quantitative real time PCR data analysis of OCT4SRE activity. Quantitative PCR for red = AD2 hiPSC and blue = AD2 DCM-d for wild type (WT) and OCT4SRE-TKO-eGFP-expressing cells. Log Relative Gene Expression (RGE) is on the y- axis. Error bars represent mean ± SD (n = 3). * indicates significance P < 0.05 between experimental groups. (c) Live microscopy demonstrated complete OCT4SRE-driven TKO-mediated cell death after 72-hours of 2 µm ganciclovir (GCV) administration to hiPSC-TKO, but not DCM-d-TKO determined via visual assessment. After OCT4SRE inactivation, DCM-d-TKO was viable and replicative during GCV treatment. (Bar = 200 µm). eGFP, enhanced green fluorescent protein; hiPSC, human induced pluripotent stem cell; OCT4, octamer-binding transcription factor 4; DCM, dermal culture media; OCT4SRE, OCT4-short response element; PCR, polymerase chain reaction.
We then performed an in vitro TKO functional assay to determine the applicability and relevance of TKO as a suicide gene transfer modulator for induced cell death under the control of OCT4SRE. OCT4SRE-expressing AD2 hiPSC-TKO and DCM-d-TKO and their WT counterparts were evaluated for their OCT4SRE-mediated TKO functional response to ganciclovir (GCV) administration. After 72hours of 2 μmol/l GCV supplementation, we attained 100% GCV-mediated cell death in only OCT4SRE-expressing AD2 hiPSC-TKO cells and no visible cell death in AD2 DCM-d-TKO, WT counterparts, and vehicle control cells (Figure 7c). These results demonstrate OCT4SRE-driven TKO expression conferring induced cell death after GCV treatment only during an OCT4-expressing cell state.
Discussion
During embryonic development, OCT4 is expressed in the early zygote and morula and initially in all blastomeres, with subsequent restricted expression to the inner cell mass. OCT4 expression is then downregulated in the trophectoderm and the primitive endoderm and, at maturity, expression becomes confined exclusively to the developing germ cells, being negative in differentiated lineages.43,44 Targeted disruption of OCT4 in mice has produced embryos devoid of a pluripotent inner cell mass,7 suggesting that OCT is essential for maintaining pluripotency and is a key regulator of stem cell differentiation; its activity must be tightly regulated to ensure the proper differentiation of various tissues and organs.1
In this investigation, we have demonstrated the functional in vitro competence of a 967 bp reduced OCT4 promoter as a functional dynamic response element during pluripotency. As OCT4 levels are reduced with cellular differentiation, OCT4SRE inactivation occurs. These findings show that in this culture system and with the given experimental parameters, OCT4SRE promotes transcription directly modulated by OCT4 expression switching on when pluripotency is initiated and off when cells differentiate. In these studies, OCT4SRE-Stb/EF1α-eGFP transduced fibroblasts demonstrated very low OCT4SRE activity as shown by Stb expression in only 3% of transduced fibroblasts, while at the same time the vast majority of cells (96%) demonstrated GFP expression by the constitutive promoter. In contrast, OCT4 overexpression during early stages of reprogramming (day 10–14) was visually detected by a Stb expression peak and decline, which corresponds to OCT4 activity during reprogramming.45,46
Moreover, when these cells completed reprogramming to pluripotency, the vast majority (91%) demonstrate OCT4-mediated activity of the short response element. When these hiPSCs underwent differentiation through the conversion from clinical grade pluripotent media (CGPM) to FBS-containing DCM, activity of the OCT4SRE turned off as <1% of cells showed Stb expression; this demonstrated a quantifiable reduction of Stb expression from 91% at OCT4-high titers during pluripotency while the majority of the remaining population continued to express GFP (85%). In addition, further OCT4SRE inactivation in DCM conditions was illustrated by loss of puromycin resistance and complete cell death after 96 hours of puromycin treatment. Furthermore, we were able to demonstrate that this reduced size promoter was sufficiently effective in driving thymidine kinase activity such that when supplemented with the prodrug GCV, death of only pluripotent cells occurs (while differentiated DCM-d cells remain viable).
Overall, these findings in human cells demonstrate the regulation of pluripotency by OCT4 expression described in vivo in mice, and at the same time show that a reduced OCT4 construct size of 967 bp (from 4 kb) remains functional during pluripotency and remains regulatable with differentiation (whether as dermal fibroblasts or as FBS-mediated differentiated derivatives). To our knowledge this functional OCT4 activity has only previously been shown with murine cells and is the first functional description of this phenomenon in a human in vitro model and with a shortened response element.
The ability to condense the OCT4 responsive elements potentially allows greater use of the limited genome size in vector development. This would not only allow the use of therapeutic genes but also safety elements in a vector construct. It is generally accepted that retroviral and adeno-associated viral particles are capable of packaging vector genomes that are shorter or approximately the same length and, in some cases, slightly above the wild-type proviral genome (9.7 kb in the case of lentivirus and 4.7 kb in the case of adeno-associated viral), and that there is a sharply demarcated upper limit on the length of genomic material capable of being encapsidated.47 This packaging limit partially determines the utility of the vector for gene delivery purposes48 as generally titer decreases as insert size and proviral genome length increase. Multigenic and regulatable vectors and vectors with extensive promoter, enhancer, or other noncoding sequences (such as homologous arms) will likely be useful in a variety of experimental and therapeutic settings48; these may be of greater length than standard vector constructs and thus, finding areas where elements may be decreased in size are important in vector development.
hiPSCs hold immense potential for the future of personalized cellular therapeutics in the treatment of a wide range of human conditions. However, to achieve their full therapeutic capabilities, transgenic safety elements should be considered and efficient and broadly applicable approaches will assist in their future adoption. We have demonstrated that the OCT4SRE, a 967 bp short response element, could potentially serve a functional role to remove unwanted pluripotent stem cell derivatives in vitro and after in vivo post-transplantation in site-specific targeting delivery in genomic modification for single gene disorders. In these in vitro studies, we have shown the OCT4SRE as a promising modulator of puromycin-induced cell death for in vitro hiPSC purification and as a driver for GCV-mediated cell death promoting the expression a codon optimized HSV1-SR39 TKO sequence for suicide gene transfer-induced cell death.
Advances in site-specific gene transferring have been achieved by CRISPR/Cas9-based genomic editing and is being applied to PSCs. We believe that a construct that incorporates the OCT4SRE and a suicide gene can provide both an efficient platform for single gene transfer into a genomic safe harbor while at the same time providing a suicide element in the case of remaining pluripotency. This reduced construct may provide a broadly applicable safety element for clinical application.
Materials and Methods
OCT4SRE synthesis
The OCT4 gene minimal promoter element demonstrates functionality in murine cells by the regulatory action of distal and proximal enhancers upstream to a 380 bp minimal OCT4-promoter region (Figure 1a).11,12 The OCT4 (3.9 kb) promoter was obtained from Addgene (www.addgene.org, plasmid #38776) and was used to develop the full-length construct. The upstream elements, proximal enhancers and distal enhancers display four conserved regions of 563 bp (CR1-to-CR4) (Figure 1a) critical for regulation of OCT4 promoter with a sequence homology of 69–96% between murine, bovine, and human orthologs.9 However, the mapping of these four regions is not exact in their detail. Consequently, we decided to include additional sequences upstream or downstream of these four CRs to avoid omitting important surrounding regulatory sequences and also to provide space to prevent functional interference between the regulatory domains. Thus, this OCT4 SRE construct consists of 5' (CR4 = 648–779 plus 780–893), fused to (1227–1248 plus CR3 = 1249–1353 plus 1354–1397) fused to (1620–1694 plus CR2 = 1695–1890 plus 1891–1957) fused to (2999–3074 plus CR1 3075–3204) as a 967 bp construct (Figure 1b) and was cloned into a standard pUC57 provided with HindIII and NcoI restriction sites (Genewiz, South Plainfield, NJ). The OCT4 sequence number is based on the OCT4 sequence Genbank Ref AJ297527.1.
Vector design and construction
The pRRL-sin-cPPT-rStb-rOCT4SRE-EF1α-eGFP (Stb = strawberry fluorescent protein) lentiviral vector (Figure 1c) was constructed by PCR cloning of plasmid EF1α-eGFP (provided by UCLA Vector Core) with primers 5′-EF1α-ClaI (5′-CGT AAT CGA TCG TGA GGC TCC GGT GCC-3′) and 3′-GFP-SalI (5′-GCT AGT CGA CTT ACT TGT ACA GCT CGT CCA TG CC-3′), then digested and ligated into the plasmid pRRL-sin-cPPT-MCS (provided by UCLA Vector Core). The strawberry fluorescent protein (Stb) lacking a start codon was cloned into the 5′ end EF1α-eGFP in reverse orientation using primers 5′-rStb(-ATG)-PmlI-EcoRI (5′-GCA TGA ATT CCA CGT GAG CAA GGG CGA GGA GAA TAA-3′) and 3′-rStb-XbaI (5′-GCA TTC TAG ATT ACT TGT ACA GCT CGT CCAT GCC-3′). The OCT4SRE promoter was subcloned by digesting phOCT4SRE plasmid-eGFP with HindIII and NcoI, blunting, and ligating into the previous construct digested with PmlI. The resulting plasmid provided a start codon to Stb driven by OCT4 and in an opposite orientation of the EF1α-eGFP. Similarly the full-length OCT4 promoter was removed from plasmid #38776 by restriction enzyme digestion and subcloned into the construct.
The pRRL-rPAC-rp2A-rStb-rOCT4SRE-EF1α-eGFP (Figure 1d) was cloned by PCR of puromycin N-acetyl-transferase (PAC) with primers 5′-PAC-P (5′-ATG ACC GAG TAC AAG CCC ACG GTG CGC-3′) and 3′-PAC-SalI (5′-GCT AGT CGA CTC AGG CAC CGG GCT TG CG-3′) from a PAC-containing plasmid (provided by the UCLA Vector Core), then digested and ligated with pRRL-EF1α-Stb-p2A digested with SmaI and SalI. PCR was then performed on the resulting construct with primers 5′-mid-rStb-SbfI (5′-CTC CTC CCT GCA GGA CGG CGA GTT-3′) and 3′-PAC-XbaI (5′-GCA TTC TAG ATC AGG CAC CGG GCT TGC GG-3′), followed by digestion and ligation into vector pRRL-sin-cPPT-rStb-rOCT4SRE-EF1α-eGFP.
The pRRL-sin-cPPT-rArgO-rEF1α-OCT4SRE-eGFP-F2A-PAC-P2A-TKO was cloned by a two-step process of introducing the transgenes to a previously constructed plasmid, pRRL-sin-cPPT-MCS-rEF1α-OCT4SRE-MCS. The multiple cloning site (MCS) downstream of OCT4SRE was cut with PacI 5′ and SalI 3′. Transgene eGFP-F2A-PAC-P2A-TKO was isolated from plasmid pRRL-sin-cPPT-CMV-eGFP-F2A-PAC-P2A-TKO by PCR using primers 5-GFP-PacI (GCTATTAATTAAACCATGGCCAGCAAGGGCG) and 3-TKO-SalI (GCATGTCGACTCAGTTGGCTTCGCCCATTTCC) to create 5′ PacI and 3′ SalI sequences flanking the transgene. PCR product was then digested with both restriction enzymes and ligated downstream of OCT4SRE. Construct pRRL-sin-cPPT-MCS-rEF1α-OCT4SRE-eGFP-F2A-PAC-P2A-TKO was then cut upstream of the reverse EF1α promoter using restriction enzymes SpeI 5′ and KpnI 3′. Transgene ArgO was produced from plasmid pRRL-sin-cPPT-HPRT-Exon1-LHA-EF1α-ArgO-IRES-PAC-HPRT-Exon1-RHA by PCR with 5-ArgO-KpnI (GCTAGGTACCATGAGCGCAAAGTCACGCACCAT) and 3-ArgO-SpeI (GCATACTAGTTTATTTAGGAGGGTTCAGGTAATCGATAGGC) and digested with the respective restriction enzymes. ArgO was then ligated into digested pRRL-sin-cPPT-MCS-rEF1α-OCT4SRE-eGFP-F2A-PAC-P2A-TKO in reverse orientation to coincide with the EF1α promoter to produce the final vector product.
The lentiviral vectors (rStb-rOCT4SRE-EF1α-eGFP, rPAC-rp2A-rStb-rOCT4SRE-EF1α-eGFP, rStb-rOCT4-EF1α-eGFP, and rArgO-rEF1α-OCT4SRE-eGFP-F2A-PAC-P2A-TKO) were generated by transient transfection of 293T cells with a three packaging plasmid combination, as described previously,49 and with the specific pRRL plasmid for each lentiviral vector: pMD.G was used for the production of the VSV-G viral envelope in combination with the packaging constructs pMDLg/pRRE and pRSV–REV. Briefly, 100 mm dishes of nonconfluent 293T cells were transfected with 6.5 μg of pMDLg/pRRE, 3.5 μg of pMDG, 2.5 μg of pRSV–REV (all three provided by Luigi Naldini, University of Torino, Italy) and 10 μg of pRRL-rStb-rOCT4SRE-EF1α-eGFP, pRRL-rPAC-rp2A-rStb-rOCT4SRE-EF1α-eGFP, rStb-rOCT4-EF1α-eGFP, or rArgO-rEF1α-OCT4SRE-eGFP-F2A-PAC-P2A-TKO by calcium phosphate precipitation.50,51 The next day, the cells were washed with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and were incubated with media containing 10 mmol/l sodium butyrate for 8 hours to obtain high-titer virus as previously described.52 After 8 hours, cells were washed with PBS and incubated in fresh media without sodium butyrate. Media was harvested 16 hours later and passed through a 0.45 µm filter. Viral titer was determined by assessing viral p24 antigen concentration by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (Alliance HIV-I p24 ELISA Kit, Perkin Elmer, Waltham, MA) and hereafter expressed as μg of p24 equivalent units per ml.53
For transduction of 293T cells, cells were seeded at 2 × 105 cells per well and incubated at 37°C overnight in their regular media. Transductions were carried out in 1 ml of Dulbecco’s modified Eagle media, including serial dilutions of lentiviral vector supernatant. The cells were then washed with PBS 24 hours post-transduction and incubated in regular media for 48 hours.
Cellular reprogramming
The humanized single excisable lentiviral STEMCCA as lentiviral vectors were used to reprogram fibroblasts to pluripotency and were kindly provided by Dr Donald Kohn (UCLA) and produced as described elsewhere.54
In vitro culture of primary human skin cells
All procedures were approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB#13-001469-AM-00002) at the University of California, Los Angeles and informed consent was obtained from all individuals. The deidentified human fibroblast cell line AD2 utilized in this study was obtained from a 4 mm skin punch biopsy. Plastic-adherent cells proliferated in DCM consisting of Dulbecco’s modified Eagle media nutrient mixture (DMEM/F-12, Life Technologies, Carlsbad, CA catalog number 11320-082) supplemented with 10% FBS (Atlanta Biologicals, Flowery Branch, GA, catalog number S10650), 1% MEM nonessential amino acids (Life Technologies, catalog number 11140-076), 2 mmol/l GlutaMAX (Life Technologies, catalog number 35050–061), and 100 μg/ml Primocin (Invivogen, San Diego, CA; catalog number ant-pm-1). The culture media was changed every 2 days. The cells were allowed to expand to >90% confluency before passaging with 0.05% trypsin- ethylene diamine tetra acetate (Gemini Bio-Products, West Sacramento, CA, catalog number 400-150) and seeded at 4,400 cells/cm2.36,55
Genetic modification of adherent human dermal cells
1 × 105 AD2 fibroblasts were transduced with lenti-pRRL-sin-cPPT-rStb-rOCT4SRE-EF1α-eGFP, a bidirectional third generation lentivirus encoding 5′→3′ eGFP driven by human EF1α promoter and 3′→5′ Stb driven by the OCT4SRE. This was performed with 4 µg/ml polybrene (Millipore, Billerica, MA, catalog number TR-1003-G) at an MOI of 10.39,56 Cells were allowed to recover and then reseeded as described above. At 1 week post-lentiviral transduction, ~2.5 × 106 cells were trypsinized and washed twice with ice-cold PBS, passed through a 40 µm filter to remove clumps, and then resuspended in 1 ml of ice-cold PBS and immediately analyzed and FACS-purified for eGFP on a FACSAria cell sorter (BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA). All FACS analyses were performed in triplicate. 4’,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI)-stained (Life Technologies, D1306), dead-cell exclusion and doublet-exclusion gating was performed, and viable single-cell subpopulations were sorted using BD FACSDiva Software version 6.1.3 (BD Biosciences).39 eGFP-positive purified fractions were allowed to recover and then expanded for 1 week before a second round of FACS purification.
OCT4-mediated activation and positive selection
OCT4 activation of AD2 fibroblasts was achieved by hiPSC generation using STEMCCA.54 The reprogramming cultures were scrutinized weekly and candidate Stb-expressing hiPSC clones were selected 28 days post-STEMCCA transduction and allowed to expand in CGPM consisting of a 50:50 blend of mTeSRII (StemCell Technologies, Vancouver, BC, catalog number 5860) and Nutristem (Stemgent, Cambridge, MA, catalog number 01-0005) with Primocin on Vitronectin XF-(StemCell Technologies, catalog number 7180) coated plates following the manufacturer’s recommendations.56,57 Once each Stb-expressing putative hiPSC clone reached >80% confluency with ~5 × 106 cells, the cells were incubated at 37°C with Y-27632 (ROCK inhibitor) (BioPioneer, San Diego, CA, catalog number SM-008) at 1.61 µg/ml in CGPM. After 1 hour, cells were gently rinsed with PBS and then incubated at 37°C for ~7 minutes with Stempro Accutase (Life Technologies, catalog number A1110501).57 The single cell suspensions were passed twice through a 40 µm filter to remove clumps and then resuspended in 1 ml of ice-cold CGPM with 2X Rock inhibitor. FACS purification was performed as described. PE-TexasRed-expressing cells (i.e., Stb) were collected and seeded at 1–1.5 × 106 cells/cm2. Stb-expressing PSCs were allowed to recover and expand for 1 week before a second round of FACS purification.58
OCT4SRE-mediated hiPSC cell killing with GCV in vitro
The in vitro functionality of OCT4SRE-driven TKO was examined by transducing AD2 hiPSC WT with lenti-pRRL-sin-cPPT-rArgO-rEF1α-OCT4SRE-eGFP-F2A-PAC-P2A-TKO at 20 MOI conferring eGFP, puromycin resistance, and TKO expression under OCT4SRE. The cells were allowed to recover and were puromycin-selected for 72 hours before being twice FACS-purified for High35%-eGFP-positive cells as described. The purified cells (AD2 hiPSC-TKO) were collected and converted to DCM conditions (AD2 DCM-d-TKO) as described.
For the in vitro GCV (Gemini Bio-Products, catalog number 400-143P)-mediated cell death assay, AD2 hiPSC-TKO, AD2 DCM-d-TKO, and their WT counterparts were treated for 72 hours with either 2 μmol/l GCV or vehicle controls the day after passage for hiPSCs or immediately after day 7 of DCM-d conversion. Cell death was determined by visual assessment under live microscopy.
Pluripotent state characterization and in vitro three germ layer differentiation
The OCT4-driven pluripotent state of the putative hiPSC-Stb candidate clones and parental AD2 fibroblasts (no OCT4 expression) were demonstrated by immunophenotyping for common stemness markers.38 Alkaline phosphatase staining (AP) was performed according to the manufacturer’s recommendations (Stemgent, catalog number 00-0055). Light microscopy-based imaging was performed with an AxioCam HR Color Camera using AxioVision Digital Image Processing Software version 4.7.2.0 (Axio Observer Inverted Microscope, Carl Zeiss, Oberkochen, Germany).42 ICC of cultured cells was performed by 20 minutes fixation in 4% paraformaldehyde, then washed once with PBS (supplemented with 100 mmol/l glycine) for 10 minutes, followed by washing twice with PBS for 5 minutes each. Samples to be examined for intracellular markers were permeabilized with 1% Triton-X100 for 1 hour. Blocking was performed with 4% goat serum in casein-PBS for 1 hour at room temperature. Primary antibodies were applied overnight at 4°C (Table 1). The pluripotent nature of the reprogrammed cells was examined in vitro by enabled tri-lineage differentiation into early mesoderm, endoderm and ectoderm (d-Stem-MicroStem, catalog number MS52013) under validated xeno-free and chemically defined conditions.
OCT4SRE inactivation
The construct response to a reduction in the OCT4 levels was examined by the conversion from CGPM to DCM containing 10% FBS (as previously described, this redirects the PSCs toward spontaneous FBS-mediated differentiation with progressive and consistent reduction in the OCT4 levels within 1 week19,59) The functionality of the OCT4SRE in CGPM and DCM was assessed by flow cytometry, ICC, and qPCR for Stb expression linked to the OCT4SRE.
The in vitro construct functionality was additionally tested by transducing AD2 hiPSC WT with lenti-pRRL-rPAC-rp2A-rStb-rOCT4SRE-EF1α-eGFP at 20 MOI conferring puromycin resistance. The cells were allowed to recover and were puromycin-selected for 72 hours before being twice FACS-purified for Stb/eGFP-double positive cells as described. The High35% Stb/eGFP-expressing cells (AD2 hiPSC C1P) were collected and converted to DCM conditions. This was performed for the demonstration of OCT4SRE-mediated puromycin resistance activation during pluripotent and puromycin resistance inactivation in response to DCM treatment.
Quantitative reverse transcription PCR
Total RNA was isolated from cultures with Roche High Pure RNA Isolation Kit (Roche Applied Sciences, Penzberg, Germany, catalog number 011828665001) and 10 ng-1 µg was reverse transcribed to cDNA utilizing Transcriptor First Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit (Roche Applied Sciences, catalog number 04379012001) following the manufacturer’s instructions. Primers and probes were designed from Roche’s Universal Probe Library. Primers for the genes were synthetized at Valuegene (San Diego, CA) and are listed in Table 2. Quantitative PCR relative expression experiments were performed on a LightCycler 480 Real-Time PCR System (Roche) and data was analyzed with LightCycler 480 Software (release 1.5.0.) with 1–10 ng of sample in a 20 µl total reaction mix (10 μmol/l UPL probe, 20 μmol/l each forward and reverse primer, and 20 μmol/l 2X LightCycler 480 Probes master mix). Triplicate experimental samples were paired using the all-to-mean pairing rule ΔCt value calculation with glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase for advanced relative quantification.36,60
Table 2. PCR primer sequences.
| Gene | Genbank ID | Length | Primer sequence | Probe | Amplicon |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| eGFP1a | 723 | F: 5′TCGTGACCACCCTGACCTAC3 ′; R: 5′GAAGTCGTGCTGCTTCATGT 3′ | 41 | 71 | |
| eGFP2a | 723 | F: 5′GAAGCGCGATCACATGGT3 ′; R: 5′CCATGCCGAGAGTGATCC3 ′ | 67 | 62 | |
| GAPDH | ENST00000229239.5 | 1,875 | F: 5′GCTCTCTGCTCCTCCTGTTC3 ′; R: 5′ACGACCAAATCCGTTGACTC3 ′ | 60 | 115 |
| OCT4 | ENSG00000206454 | 1,086 | F: 5′CTTCGGATTTCGTCTTCTCG3 ′; R: 5′CTTAGCCAGGTCCGAGGAT3 ′ | 77 | 94 |
| Stb | 711 | F: 5′TTGACCTCAGCGTCGTAGTG3 ′; R: 5′CTGAAGGGCGAGATCAAGA 3′ | 41 | 65 | |
| TKO | 1,131 | F: 5′CTGCGGGTCTATATCGATGG3 ′; R: 5′AGTGCCACCAGGAGTTGTGT3 ′ | 60 | 68 |
Statistical analysis
All collected data was analyzed with the SPSS (Armonk, NY) statistical package (Version 21.0). Results are expressed as mean and SD with a confidence interval of 95%. The Levene test for equality of variances was used to analyze the normal distribution of the variables (P < 0.05). Quantitative data without a normal distribution was analyzed with nonparametric tests (Mann–Whitney U and Kolmogorov-Smirnov), whereas data with a normal distribution was analyzed with parametric tests as for independent sample t-test and two-way analysis of variance. Bonferroni and Dunnet T3 tests were performed for post-hoc analyses. P-values <0.05 were considered statistically significant. Correlation was established with a two-tailed Pearson correlation for variables with normal distribution. r2 values< 0.01 were considered a significant correlation. All graphs were generated utilizing GraphPad Prism 6 (La Jolla, CA).
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the grant CIRM TR4-06831 from the California Institute of Regenerative Medicine (to G.S.L.), and the Eli and Edythe Broad Center of Regenerative Medicine and Stem Cell Research (to J.A.B.). The authors thank Donald Kohn (UCLA) and Noriyuki Kasahara (UCLA) for kindly providing the elements necessary for lentivirus preparation. J.A.B. and A.V.C. receive research funding support from Fibrocell Science, Inc. J.A.B. is a scientific consultant for Fibrocell Science. No other authors have competing financial interests to report.
The last two authors are the co-senior authors.
References
- Pan, GJ, Chang, ZY, Schöler, HR and Pei, D (2002). Stem cell pluripotency and transcription factor Oct4. Cell Res 12: 321–329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babaie, Y, Herwig, R, Greber, B, Brink, TC, Wruck, W, Groth, D et al. (2007). Analysis of Oct4-dependent transcriptional networks regulating self-renewal and pluripotency in human embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells 25: 500–510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang, YD, Cai, N, Wu, XL, Cao, HZ, Xie, LL and Zheng, PS (2013). OCT4 promotes tumorigenesis and inhibits apoptosis of cervical cancer cells by miR-125b/BAK1 pathway. Cell Death Dis 4: e760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koo, BS, Lee, SH, Kim, JM, Huang, S, Kim, SH, Rho, YS et al. (2015). Oct4 is a critical regulator of stemness in head and neck squamous carcinoma cells. Oncogene 34: 2317–2324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers, I, Colby, D, Robertson, M, Nichols, J, Lee, S, Tweedie, S et al. (2003). Functional expression cloning of Nanog, a pluripotency sustaining factor in embryonic stem cells. Cell 113: 643–655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsui, K, Tokuzawa, Y, Itoh, H, Segawa, K, Murakami, M, Takahashi, K et al. (2003). The homeoprotein Nanog is required for maintenance of pluripotency in mouse epiblast and ES cells. Cell 113: 631–642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols, J, Zevnik, B, Anastassiadis, K, Niwa, H, Klewe-Nebenius, D, Chambers, I et al. (1998). Formation of pluripotent stem cells in the mammalian embryo depends on the POU transcription factor Oct4. Cell 95: 379–391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strumpf, D, Mao, CA, Yamanaka, Y, Ralston, A, Chawengsaksophak, K, Beck, F et al. (2005). Cdx2 is required for correct cell fate specification and differentiation of trophectoderm in the mouse blastocyst. Development 132: 2093–2102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordhoff, V, Hübner, K, Bauer, A, Orlova, I, Malapetsa, A and Schöler, HR (2001). Comparative analysis of human, bovine, and murine Oct-4 upstream promoter sequences. Mamm Genome 12: 309–317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He, H, McHaney, M, Hong, J and Weiss, ML (2009). Cloning and characterization of 3.1kb promoter region of the Oct4 gene from the Fischer 344 rat. Open Stem Cell J 1: 30–39. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghorbani, R, Emamzadeh, A, Khazaie, Y, Dormiani, K, Ghaedi, K, Rabbani, M et al. (2013). Constructing a mouse Oct4 promoter/EGFP vector, as a whole-cellular reporter to monitor the pluripotent state of cells. Avicenna J Med Biotechnol 5: 2–9. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang, HM, Do, HJ, Oh, JH, Kim, JH, Choi, SY, Cha, KY et al. (2005). Characterization of putative cis-regulatory elements that control the transcriptional activity of the human Oct4 promoter. J Cell Biochem 96: 821–830. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buganim, Y, Faddah, DA and Jaenisch, R (2013). Mechanisms and models of somatic cell reprogramming. Nat Rev Genet 14: 427–439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee, E, Lee, SH, Kim, S, Jeong, YW, Kim, JH, Koo, OJ et al. (2006). Analysis of nuclear reprogramming in cloned miniature pig embryos by expression of Oct-4 and Oct-4 related genes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 348: 1419–1428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chuang, YS, Huang, WH, Park, SW, Persaud, SD, Hung, CH, Ho, PC et al. (2011). Promyelocytic leukemia protein in retinoic acid-induced chromatin remodeling of Oct4 gene promoter. Stem Cells 29: 660–669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrne, JA, Simonsson, S, Western, PS and Gurdon, JB (2003). Nuclei of adult mammalian somatic cells are directly reprogrammed to oct-4 stem cell gene expression by amphibian oocytes. Curr Biol 13: 1206–1213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radzisheuskaya, A and Silva, JC (2014). Do all roads lead to Oct4? The emerging concepts of induced pluripotency. Trends Cell Biol 24: 275–284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, ZN, Chung, SK, Xu, Z and Xu, Y (2014). Oct4 maintains the pluripotency of human embryonic stem cells by inactivating p53 through Sirt1-mediated deacetylation. Stem Cells 32: 157–165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radzisheuskaya, A, Chia, Gle B, dos Santos, RL, Theunissen, TW, Castro, LF, Nichols, J et al. (2013). A defined Oct4 level governs cell state transitions of pluripotency entry and differentiation into all embryonic lineages. Nat Cell Biol 15: 579–590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman, N, Gerson, A, Fang, J, Li, E, Zhang, Y, Shinkai, Y et al. (2006). G9a-mediated irreversible epigenetic inactivation of Oct-3/4 during early embryogenesis. Nat Cell Biol 8: 188–194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellner, S and Kikyo, N (2010). Transcriptional regulation of the Oct4 gene, a master gene for pluripotency. Histol Histopathol 25: 405–412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, L, Sung, MT, Cossu-Rocca, P, Jones, TD, MacLennan, GT, De Jong, J et al. (2007). OCT4: biological functions and clinical applications as a marker of germ cell neoplasia. J Pathol 211: 1–9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serra, M, Brito, C, Correia, C and Alves, PM (2012). Process engineering of human pluripotent stem cells for clinical application. Trends Biotechnol 30: 350–359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medvedev, SP, Shevchenko, AI and Zakian, SM (2010). Molecular basis of Mammalian embryonic stem cell pluripotency and self-renewal. Acta Naturae 2: 30–46. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochedlinger, K, Yamada, Y, Beard, C and Jaenisch, R (2005). Ectopic expression of Oct-4 blocks progenitor-cell differentiation and causes dysplasia in epithelial tissues. Cell 121: 465–477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tai, MH, Chang, CC, Kiupel, M, Webster, JD, Olson, LK and Trosko, JE (2005). Oct4 expression in adult human stem cells: evidence in support of the stem cell theory of carcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis 26: 495–502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan, CT, Guzman, ML and Noble, M (2006). Cancer stem cells. N Engl J Med 355: 1253–1261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, L (2004). Establishing a germ cell origin for metastatic tumors using OCT4 immunohistochemistry. Cancer 101: 2006–2010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones, TD, Ulbright, TM, Eble, JN, Baldridge, LA and Cheng, L (2004). OCT4 staining in testicular tumors: a sensitive and specific marker for seminoma and embryonal carcinoma. Am J Surg Pathol 28: 935–940. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Looijenga, LH, Stoop, H, de Leeuw, HP, de Gouveia Brazao, CA, Gillis, AJ, van Roozendaal, KE et al. (2003). POU5F1 (OCT3/4) identifies cells with pluripotent potential in human germ cell tumors. Cancer Res 63: 2244–2250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amin, R and Mishra, L (2008). Liver stem cells and tgf-Beta in hepatic carcinogenesis. Gastrointest Cancer Res 2(4 Suppl): S27–S30. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ezeh, UI, Turek, PJ, Reijo, RA and Clark, AT (2005). Human embryonic stem cell genes OCT4, NANOG, STELLAR, and GDF3 are expressed in both seminoma and breast carcinoma. Cancer 104: 2255–2265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu, CG, Lu, Y, Wang, BB, Zhang, YJ, Zhang, RS, Lu, Y et al. (2011). Clinical implications of stem cell gene Oct-4 expression in breast cancer. Ann Surg 253: 1165–1171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatefi, N, Nouraee, N, Parvin, M, Ziaee, SA and Mowla, SJ (2012). Evaluating the expression of oct4 as a prognostic tumor marker in bladder cancer. Iran J Basic Med Sci 15: 1154–1161. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang, CC, Shieh, GS, Wu, P, Lin, CC, Shiau, AL and Wu, CL (2008). Oct-3/4 expression reflects tumor progression and regulates motility of bladder cancer cells. Cancer Res 68: 6281–6291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Awe, JP, Lee, PC, Ramathal, C, Vega-Crespo, A, Durruthy-Durruthy, J, Cooper, A et al. (2013). Generation and characterization of transgene-free human induced pluripotent stem cells and conversion to putative clinical-grade status. Stem Cell Res Ther 4: 87. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Apostolou, E and Hochedlinger, K (2013). Chromatin dynamics during cellular reprogramming. Nature 502: 462–471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson, JA, Itskovitz-Eldor, J, Shapiro, SS, Waknitz, MA, Swiergiel, JJ, Marshall, VS et al. (1998). Embryonic stem cell lines derived from human blastocysts. Science 282: 1145–1147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vega Crespo, A, Awe, JP, Reijo Pera, R and Byrne, JA (2012). Human skin cells that express stage-specific embryonic antigen 3 associate with dermal tissue regeneration. Biores Open Access 1: 25–33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Constantinescu, D, Gray, HL, Sammak, PJ, Schatten, GP and Csoka, AB (2006). Lamin A/C expression is a marker of mouse and human embryonic stem cell differentiation. Stem Cells 24: 177–185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Awe, JP, Gschweng, EH, Vega-Crespo, A, Voutila, J, Williamson, MH, Truong, B et al. (2015). Putative immunogenicity expression profiling using human pluripotent stem cells and derivatives. Stem Cells Transl Med 4: 136–145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D’Amour, KA, Agulnick, AD, Eliazer, S, Kelly, OG, Kroon, E and Baetge, EE (2005). Efficient differentiation of human embryonic stem cells to definitive endoderm. Nat Biotechnol 23: 1534–1541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pesce, M and Schöler, HR (2001). Oct-4: gatekeeper in the beginnings of mammalian development. Stem Cells 19: 271–278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pesce, M and Schöler, HR (2000). Oct-4: control of totipotency and germline determination. Mol Reprod Dev 55: 452–457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadtfeld, M and Hochedlinger, K (2010). Induced pluripotency: history, mechanisms, and applications. Genes Dev 24: 2239–2263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maherali, N, Sridharan, R, Xie, W, Utikal, J, Eminli, S, Arnold, K et al. (2007). Directly reprogrammed fibroblasts show global epigenetic remodeling and widespread tissue contribution. Cell Stem Cell 1: 55–70. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanstrom, R, and Wills, JW (1997). Synthesis, assembly and processing of viral proteins. Retroviruses. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor, NY. pp. 263–334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, M, Keller, B, Makalou, N and Sutton, RE (2001). Systematic determination of the packaging limit of lentiviral vectors. Hum Gene Ther 12: 1893–1905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naldini, L, Blömer, U, Gage, FH, Trono, D and Verma, IM (1996). Efficient transfer, integration, and sustained long-term expression of the transgene in adult rat brains injected with a lentiviral vector. Proc Nat Acad Sci 93: 11382–11388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C and Okayama, H (1987). High-efficiency transformation of mammalian cells by plasmid DNA. Mol Cell Biol 7: 2745–2752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakoda, T, Kaibuchi, K, Kishi, K, Kishida, S, Doi, K, Hoshino, M et al. (1992). smg/rap1/Krev-1 p21s inhibit the signal pathway to the c-fos promoter/enhancer from c-Ki-ras p21 but not from c-raf-1 kinase in NIH3T3 cells. Oncogene 7: 1705–1711. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakoda, T, Kasahara, N, Hamamori, Y and Kedes, L (1999). A high-titer lentiviral production system mediates efficient transduction of differentiated cells including beating cardiac myocytes. J Mol Cell Cardiol 31: 2037–2047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marozsan, AJ, Fraundorf, E, Abraha, A, Baird, H, Moore, D, Troyer, R et al. (2004). Relationships between infectious titer, capsid protein levels, and reverse transcriptase activities of diverse human immunodeficiency virus type 1 isolates. J Virol 78: 11130–11141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somers, A, Jean, JC, Sommer, CA, Omari, A, Ford, CC, Mills, JA et al. (2010). Generation of transgene-free lung disease-specific human induced pluripotent stem cells using a single excisable lentiviral stem cell cassette. Stem Cells 28: 1728–1740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadner, A, Hoerstrup, SP, Zund, G, Eid, K, Maurus, C, Melnitchouk, S et al. (2002). A new source for cardiovascular tissue engineering: human bone marrow stromal cells. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 21: 1055–1060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mei, Y, Saha, K, Bogatyrev, SR, Yang, J, Hook, AL, Kalcioglu, ZI et al. (2010). Combinatorial development of biomaterials for clonal growth of human pluripotent stem cells. Nat Mater 9: 768–778. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tieng, V, Stoppini, L, Villy, S, Fathi, M, Dubois-Dauphin, M and Krause, KH (2014). Engineering of midbrain organoids containing long-lived dopaminergic neurons. Stem Cells Dev 23: 1535–1547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emre, N, Vidal, JG, Elia, J, O’Connor, ED, Paramban, RI, Hefferan, MP, et al. (2010). The ROCK inhibitor Y-27632 improves recovery of human embryonic stem cells after fluorescence-activated cell sorting with multiple cell surface markers. PLoS One 5: e12148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mummery, CL, Zhang, J, Ng, ES, Elliott, DA, Elefanty, AG and Kamp, TJ (2012). Differentiation of human embryonic stem cells and induced pluripotent stem cells to cardiomyocytes: a methods overview. Circ Res 111: 344–358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livak, KJ and Schmittgen, TD (2001). Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 25: 402–408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.