TRP channels are remarkable in their functional diversity. The Melastatin group representative TRPM3 is no exception. TRPM3 has been implicated in diverse physiological processes, ranging from inflammatory hyperalgesia in somatosensory neurons to glucose-induced insulin release in pancreatic β-cells. In addition to the expression of TRPM3 in the indicated tissues, the variety of its functional contributions is modulated by the diverse stimuli that regulate TRPM3 channel activity. Indeed, in native and heterologous cellular systems, TRPM3 activity is driven by various endogenous and exogenous factors, including temperature and number of chemical compounds.
To determine agonist-specific TRPM3 channel functions we aimed to reconstitute TRPM3 in the planar lipid bilayers in our recent work.1 The extensive biophysical analysis of TRPM3 in the bilayer system allowed defining the channel characteristics and its direct regulators.
Intriguingly, after the incorporation, TRPM3 demonstrated distinctive and well-organized basal channel activity. For comparison, other TRP channels characterized in such a reconstituted system did no yield a similar activity. We suggested that the basal channel openings resemble the constitutive TRPM3 activity detected in cellular recordings. Another TRP representative that possesses similar constitutive activity in cells is TRPV6. However in the planar lipid bilayer system TRPV6 was readily stimulated with only an addition of phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2), which was required for its activity.2 Interestingly, for obtaining TRPM3 basal currents in the bilayers addition of PIP2 was not required. Even more surprising was the fact that the basal TRPM3 activity lasted only for a limited period, but was observed more often in the complete absence of Mg2+. These results indicated that channel activity is finely tuned by cations. In agreement with this, earlier studies by Oberwinkler et al. demonstrated that TRPM3 activity is tightly controlled by both monovalent and divalent cations, as evidenced by whole-cell patch clamp recordings.3 Therefore, the inactivation of the constitutive activity in the bilayers could be causative of the certain inhibitory effects exerted by cations.
Recent studies indicated that one of the prominent endogenous agonists of TRPM3 channels is a neurosteroid, pregnenolone sulfate (PS).4 Appreciating its physiological significance, we evaluated the effects PS exerts on TRPM3 in the bilayer system. These experiments supported a direct agonistic PS action on TRPM3 gating, although PS alone was insufficient and required a co-factor for its activity. Hence, PS evoked TRPM3 openings occurred only in the presence of PIP2 or clotrimazole. TRPM3 regulation by phosphoinositides was similarly observed in patch clamp recordings,5,6 indicating their physiological role in channel activity. However, in comparison to other PIP2-regulated TRP channels, TRPM3 dependence was much less. The critical part of this analogy is that TRPM3 needed PIP2 only under some conditions, while for the other PIP2-dependent TRP channels its presence was essential at all times. For instance, previously characterized TRP channels in our lab, including TRPM8, TRPV6, and TRPV1, absolutely required the presence of PIP2 in the bilayers to induce their channel activity with all the stimuli.2,7,8
Another agonist that has been previously detected for TRPM3 is nifedipine.4 Nifedipine is a pharmacological compound and an inhibitor of L-type voltage-gated Ca2+ channels. Unlike PS, nifedipine activated TRPM3 with a different gating mode and did not require any additives. These results indicate that PS and nifedipine act on the channel differently, which is in agreement with the allosteric activation of TRPM3 by these compounds observed in cells.
One of the important TRPM3 activities was linked to temperature sensation. To establish the role of TRPM3 in heat-induced activity, we evaluated its temperature sensitivity in bilayers. In contrast to cell recordings, we could not potentiate TRPM3 opening by exposing it to heat alone or in the presence of PS. Taking into consideration that temperature-induced activation of the cold receptor, TRPM8, and the heat receptor, TRPV1, is effectively achieved in bilayers in the presence of their permanent gating factor – PIP2,8 we wondered whether PIP2 could also contribute to temperature-induced gating of TRPM3. Testing the addition of PIP2 to bilayers upon heat-induced activation of TRPM3 indeed was more efficient, yet it could not stimulate sufficient conformational changes of the protein to extend it to the fully open channel and only exhibited a low open probability mode. Furthermore, the thermodynamic analysis indicated that intrinsically TRPM3 is only slightly temperature dependent, in comparison to highly temperature sensitive TRPM8 and TRPV1.
In conclusion, in our recent work, we provided insights into the mechanism of TRPM3 channel gating. In parallel with the earlier reports obtained from cell recordings, in planar lipid bilayers TRPM3 was directly activated by PS and depended on the presence of PIP2 (Fig. 1). On the other hand, we did not observe previously reported temperature sensitivity of TRPM3. Despite its strong heat-induced activity and current potentiation in cells, in the artificial system TRPM3 is only slightly temperature sensitive and could not transition into the fully open conformation when exposed to heat. These channel characteristics along with the basal activity indicated an existence of other endogenous factors that regulate TRPM3 in cells.
Figure 1.
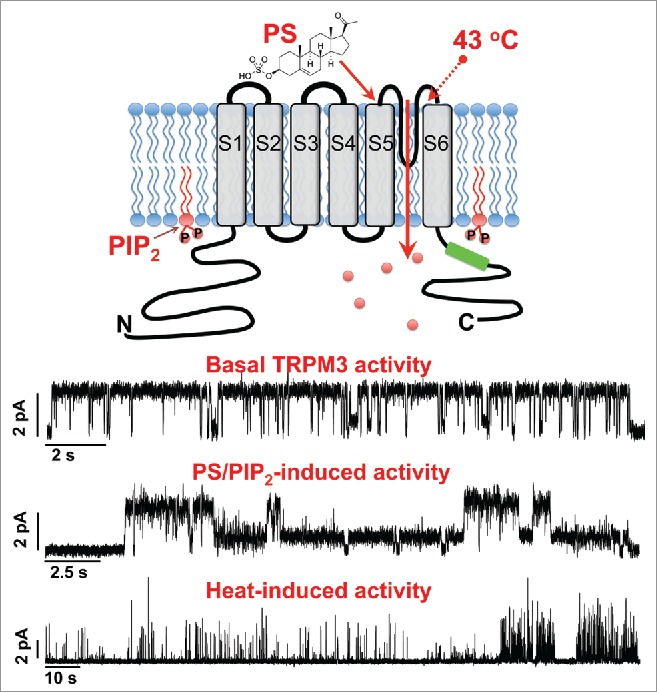
The activity of the TRPM3 channel reconstituted in planar lipid bilayers. The model and recordings of TRPM3 in the bilayers: Top traces: Basal TRPM3 activity, regularly obtained and characterized by its complete inactivation within ˜10 min. Middle traces: TRPM3 activity induced by 5 μM pregnenolone sulfate (PS) in the presence of 5 μM phosphatidylinositol-4, 5-bisphosphate (PIP2). Lower traces: Heat-induced TRPM3 exhibits low open probability in the presence of PIP2. All recording were obtained at 100 mV.
Disclosure of potential conflicts of interest
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
References
- [1].Uchida K, Demirkhanyan L, Asuthkar S, Cohen A, Tominaga M, Zakharian E. Stimulation-dependent gating of TRPM3 channel in planar lipid bilayers. FASEB J 2016; 3:1306-16; PMID:26655382; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1096/fj.15-281576 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [2].Zakharian E, Cao C, Rohacs T. Intracellular ATP supports TRPV6 activity via lipid kinases and the generation of PtdIns(4, 5) P. FASEB J 2011; 25:3915-28; PMID:21810903; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1096/fj.11-184630 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [3].Oberwinkler J, Lis A, Giehl KM, Flockerzi V, Philipp SE. Alternative splicing switches the divalent cation selectivity of TRPM3 channels. J Biol Chem 2005; 280:22540-8; PMID:15824111; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1074/jbc.M503092200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [4].Wagner TF, Loch S, Lambert S, Straub I, Mannebach S, Mathar I, Düfer M, Lis A, Flockerzi V, Philipp SE, Oberwinkler J. Transient receptor potential M3 channels are ionotropic steroid receptors in pancreatic β cells. Nat Cell Biol 2008; 10:1421-30; PMID:18978782; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1038/ncb1801 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [5].Badheka D, Borbiro I, Rohacs T. Transient receptor potential melastatin 3 is a phosphoinositide-dependent ion channel. J Gen Physiol 2015; 146:65-77; PMID:26123195; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1085/jgp.201411336 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [6].Toth BI, Konrad M, Ghosh D, Mohr F, Halaszovich CR, Leitner MG, Vriens J, Oberwinkler J. Regulation of the transient receptor potential channel TRPM3 by phosphoinositides. J Gen Physiol 2015; 146:51-63; PMID:26123194; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1085/jgp.201411339 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [7].Zakharian E, Thyagarajan B, French RJ, Pavlov E, Rohacs T. Inorganic polyphosphate modulates TRPM8 channels. Plos One 2009; 4:e5404; PMID:19404398; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1371/journal.pone.0005404 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [8].Sun X, Zakharian E. Regulation of the temperature-dependent activation of transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 (TRPV1) by phospholipids in planar lipid bilayers. J Biol Chem 2015; 290:4741-7; PMID:25561742; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1074/jbc.M114.611459 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


