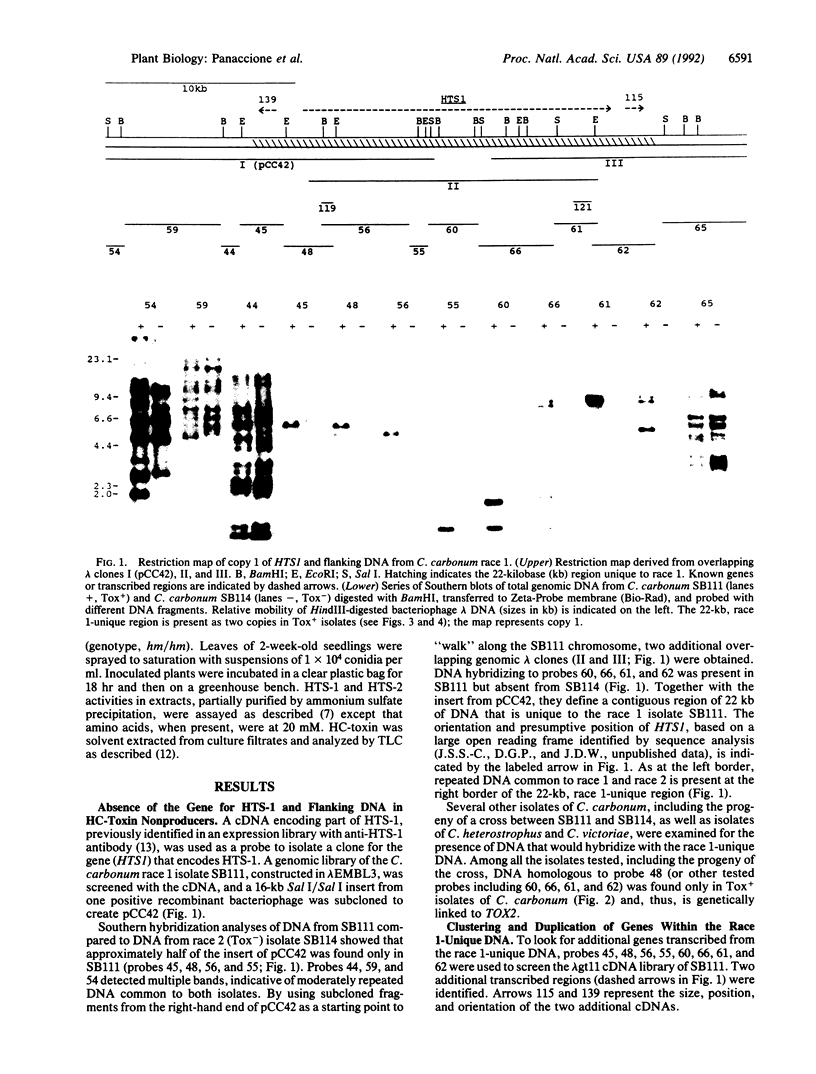
Abstract
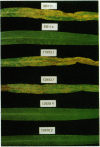
Specificity in many plant-pathogen interactions is determined by single genes in pathogen and host. The single locus for host-selective pathogenicity (TOX2) in the fungus Cochliobolus carbonum governs production of a cyclic tetrapeptide named HC-toxin. We have isolated a chromosomal region, 22 kilobases (kb) long, that contains a 15.7-kb open reading frame (HTS1) encoding a multifunctional cyclic peptide synthetase. The 22-kb chromosomal region is duplicated in toxin-producing isolates of the fungus but is completely absent from the genomes of toxin-nonproducing isolates. Mutants of the fungus with disruptions in both copies of HTS1, at either of two different sites within HTS1, were engineered by DNA-mediated transformation. Disruption of both copies at either site resulted in loss of ability to produce HC-toxin and loss of host-selective pathogenicity, but the mutants displayed different biochemical phenotypes depending on the site of disruption. The results demonstrate that TOX2 encodes, at least in part, a large, multifunctional biosynthetic enzyme and that the evolution of host range in C. carbonum involved the insertion or deletion of a large piece of chromosomal DNA.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Hynes M. J., Corrick C. M., King J. A. Isolation of genomic clones containing the amdS gene of Aspergillus nidulans and their use in the analysis of structural and regulatory mutations. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Aug;3(8):1430–1439. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.8.1430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai M., Rich D. H., Walton J. D. The structure and conformation of HC-toxin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Mar 16;111(2):398–403. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)90319-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohmoto K., Otani H. Host recognition by toxigenic plant pathogens. Experientia. 1991 Aug 15;47(8):755–764. doi: 10.1007/BF01922454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen J. B., Scheffer R. P. Isolation and Biological Activities of Four Selective Toxins from Helminthosporium carbonum. Plant Physiol. 1988 Jan;86(1):187–191. doi: 10.1104/pp.86.1.187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schäfer W., Straney D., Ciuffetti L., VAN Etten H. D., Yoder O. C. One enzyme makes a fungal pathogen, but not a saprophyte, virulent on a new host plant. Science. 1989 Oct 13;246(4927):247–249. doi: 10.1126/science.246.4927.247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott-Craig J. S., Panaccione D. G., Cervone F., Walton J. D. Endopolygalacturonase is not required for pathogenicity of Cochliobolus carbonum on maize. Plant Cell. 1990 Dec;2(12):1191–1200. doi: 10.1105/tpc.2.12.1191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walton J. D., Earle E. D., Gibson B. W. Purification and structure of the host-specific toxin from Helminthosporium carbonum race 1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Aug;107(3):785–794. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)90592-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walton J. D. Two enzymes involved in biosynthesis of the host-selective phytotoxin HC-toxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8444–8447. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]