Abstract
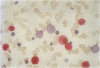
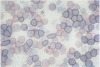
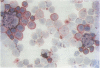
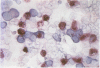
AIMS: To extend the alkaline phosphatase-antialkaline phosphatase (APAAP) immunoenzyme single stain method to a more generally applicable double stain technique. This will allow two primary antibodies of the same isotype of IgG and specifically the nuclear antigen bromodeoxyuridine (BRdU) to be evaluated with a cell surface antigen identifier. METHOD: Sequential applications of the APAAP method showed two antigen sites by different dye couplings to a common alkaline phosphatase substrate, producing blue and red reaction products on the same slide. Antigens on different cell populations as well as those in different compartments of the same cell were analysed. The method allowed a surface antigen monoclonal to be revealed first, using an optimal fixative, before alcohol/gluteraldehyde fixation was used to start the second (BRdU) staining sequence. RESULTS: An analysis of double staining of T lymphocyte subsets (CD4 and CD8) showed no significant difference in the order of application of the primaries (n = 10) and no significant difference from their corresponding single stain results (n = 50), confirming the validity of the technique where antigens are exclusively distributed. Other examples, including antigens distributed in different compartments of the same cell, displayed discrete staining which implied validity. CONCLUSION: Double staining by APAAP with this technique seems to be applicable to those cases where antigens are exclusively distributed and includes cases where different compartments of the same cell are stained. It is especially useful in revealing antigens that require different fixation and preparation--that is DNA incorporated BRdU with a surface antigen. But it does seem to have a limited ability to produce a dual colour at a common site.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Campana D., Coustan-Smith E., Janossy G. Double and triple staining methods for studying the proliferative activity of human B and T lymphoid cells. J Immunol Methods. 1988 Feb 24;107(1):79–88. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(88)90012-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campana D., Janossy G. Proliferation of normal and malignant human immature lymphoid cells. Blood. 1988 May;71(5):1201–1210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erber W. N., Pinching A. J., Mason D. Y. Immunocytochemical detection of T and B cell populations in routine blood smears. Lancet. 1984 May 12;1(8385):1042–1046. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)91451-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falini B., Abdulaziz Z., Gerdes J., Canino S., Ciani C., Cordell J. L., Knight P. M., Stein H., Grignani F., Martelli M. F. Description of a sequential staining procedure for double immunoenzymatic staining of pairs of antigens using monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol Methods. 1986 Nov 6;93(2):265–273. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(86)90199-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goff L. K., Habeshaw J. A., Rose M. L., Gracie J. A., Gregory W. Normal values for the different classes of venous blood mononuclear cells defined by monoclonal antibodies. J Clin Pathol. 1985 Jan;38(1):54–59. doi: 10.1136/jcp.38.1.54. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gratzner H. G. Monoclonal antibody to 5-bromo- and 5-iododeoxyuridine: A new reagent for detection of DNA replication. Science. 1982 Oct 29;218(4571):474–475. doi: 10.1126/science.7123245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gu J., de Mey J., Moeremans M., Polak J. M. Sequential use of the PAP and immunogold staining method for the light microscopical double staining of tissue antigens. Regul Pept. 1981 Mar;1(6):365–374. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(81)90040-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwatani Y., Amino N., Mori H., Asari S., Ina K., Ennyu K., Miyai K. Effects of various isolation methods for human peripheral lymphocytes on T cell subsets determined in a fluorescence activated cell sorter (FACS), and demonstration of a sex difference of suppressor/cytotoxic T cells. J Immunol Methods. 1982 Oct 15;54(1):31–42. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90110-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lokhorst H. M., Boom S. E., Bast B. J., Ballieux R. E. Determination of the plasma cell labelling index with bromodeoxyuridine in a double fluorescence technique. Br J Haematol. 1986 Oct;64(2):271–275. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1986.tb04119.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason D. Y., Sammons R. Alkaline phosphatase and peroxidase for double immunoenzymatic labelling of cellular constituents. J Clin Pathol. 1978 May;31(5):454–460. doi: 10.1136/jcp.31.5.454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason D. Y., Stein H., Naiem M., Abdulaziz Z. Immunohistological analysis of human lymphoid tissue by double immunoenzymatic labelling. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 1981;101(1):13–22. doi: 10.1007/BF00405059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason D. Y., Stein H. Reactive and neoplastic human lymphoid cells producing J chain in the absence of immunoglobulin: evidence for the existence of 'J chain disease'? Clin Exp Immunol. 1981 Nov;46(2):305–312. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moir D. J., Ghosh A. K., Abdulaziz Z., Knight P. M., Mason D. Y. Immunoenzymatic staining of haematological samples with monoclonal antibodies. Br J Haematol. 1983 Nov;55(3):395–410. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1983.tb02154.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakane P. K. Simultaneous localization of multiple tissue antigens using the peroxidase-labeled antibody method: a study on pituitary glands of the rat. J Histochem Cytochem. 1968 Sep;16(9):557–560. doi: 10.1177/16.9.557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Namikawa R., Ueda R., Suchi T., Itoh G., Ota K., Takahashi T. Double immunoenzymatic detection of surface phenotype of proliferating lymphocytes in situ with monoclonal antibodies against DNA polymerase alpha and lymphocyte membrane antigens. Am J Clin Pathol. 1987 Jun;87(6):725–731. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/87.6.725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neame P. B., Soamboonsrup P., Browman G., Barr R. D., Saeed N., Chan B., Pai M., Benger A., Wilson W. E., Walker I. R. Simultaneous or sequential expression of lymphoid and myeloid phenotypes in acute leukemia. Blood. 1985 Jan;65(1):142–148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staquet M. J., De Fraissinette A., Dezutter-Dambuyant C., Schmitt D., Thivolet J. A combined method for detection of cell surface marker expression and bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU) uptake by epidermal cells in suspension. J Immunol Methods. 1989 Jan 17;116(2):287–292. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(89)90215-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternberger L. A., Joseph S. A. The unlabeled antibody method. Contrasting color staining of paired pituitary hormones without antibody removal. J Histochem Cytochem. 1979 Nov;27(11):1424–1429. doi: 10.1177/27.11.92498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner L., Worman C. P. Color-contrast staining of two different lymphocyte subpopulations: a two-color modification of alkaline phosphatase monoclonal anti-alkaline phosphatase complex technique. Stain Technol. 1988 May;63(3):129–136. doi: 10.3109/10520298809107172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong G. K., Hui P. K., Ng W. L., Leong S. Enumerating T-cell subsets on blood smears. An evaluation of an indirect immunoalkaline phosphatase method. Am J Clin Pathol. 1986 Dec;86(6):756–759. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/86.6.756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Fraissinette A., Staquet M. J., Dezutter-Dambuyant C., Schmitt D., Thivolet J. Langerhans cells in S-phase in normal skin detected by simultaneous analysis of cell surface antigen and BrdU incorporation. J Invest Dermatol. 1988 Dec;91(6):603–605. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12477142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]