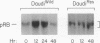Abstract
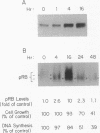
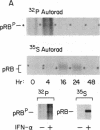
Interferon alpha (IFN-alpha) is a regulatory secretory protein with distinctive biological effects such as antiproliferative actions against many tumor cell lines, including human Burkitt lymphoma Daudi cells. The mechanism underlying growth inhibition by IFN-alpha is not well established. The growth of many mammalian cell types is also regulated by tumor suppressor retinoblastoma (RB) gene product, the RB protein. In the studies presented here, we explored the possible involvement of RB protein in the growth inhibitory action of IFN-alpha in the Daudi cell model system. We observed that IFN-alpha induces a 3- to 10-fold increased expression of RB protein in growth-sensitive Daudi cells but not in the growth-resistant variant of Daudi cells. IFN-alpha-mediated induction of RB protein was an early event that preceded the period of growth inhibition of Daudi cells. IFN-alpha-induced RB protein predominantly exists as the underphosphorylated form. Addition of antibody against IFN-alpha to Daudi cells resulted in the inhibition of constitutive expression of RB protein and stimulation of [3H]thymidine incorporation. These results demonstrate that the induction of RB protein expression in IFN-alpha-treated Daudi cells could constitute an important mechanism of IFN-alpha-mediated growth regulation.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ablashi D. V., Baron S., Armstrong G., Faggioni A., Viza D., Levine P. H., Pizza G. Spontaneous production of high levels of leukocyte (alpha) interferon by a human lymphoblastoid B-cell line (LDV/7). Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1982 Oct;171(1):114–119. doi: 10.3181/00379727-171-41486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bookstein R., Shew J. Y., Chen P. L., Scully P., Lee W. H. Suppression of tumorigenicity of human prostate carcinoma cells by replacing a mutated RB gene. Science. 1990 Feb 9;247(4943):712–715. doi: 10.1126/science.2300823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchkovich K., Duffy L. A., Harlow E. The retinoblastoma protein is phosphorylated during specific phases of the cell cycle. Cell. 1989 Sep 22;58(6):1097–1105. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90508-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen P. L., Scully P., Shew J. Y., Wang J. Y., Lee W. H. Phosphorylation of the retinoblastoma gene product is modulated during the cell cycle and cellular differentiation. Cell. 1989 Sep 22;58(6):1193–1198. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90517-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemens M. J., McNurlan M. A. Regulation of cell proliferation and differentiation by interferons. Biochem J. 1985 Mar 1;226(2):345–360. doi: 10.1042/bj2260345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemens M. Interferons and oncogenes. Nature. 1985 Feb 14;313(6003):531–532. doi: 10.1038/313531a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeCaprio J. A., Ludlow J. W., Lynch D., Furukawa Y., Griffin J., Piwnica-Worms H., Huang C. M., Livingston D. M. The product of the retinoblastoma susceptibility gene has properties of a cell cycle regulatory element. Cell. 1989 Sep 22;58(6):1085–1095. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90507-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz M. O., Ziemin S., Le Beau M. M., Pitha P., Smith S. D., Chilcote R. R., Rowley J. D. Homozygous deletion of the alpha- and beta 1-interferon genes in human leukemia and derived cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):5259–5263. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.5259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn J. M., Phillips R. A., Zhu X., Becker A., Gallie B. L. Mutations in the RB1 gene and their effects on transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):4596–4604. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.4596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einat M., Resnitzky D., Kimchi A. Close link between reduction of c-myc expression by interferon and, G0/G1 arrest. Nature. 1985 Feb 14;313(6003):597–600. doi: 10.1038/313597a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furukawa Y., DeCaprio J. A., Freedman A., Kanakura Y., Nakamura M., Ernst T. J., Livingston D. M., Griffin J. D. Expression and state of phosphorylation of the retinoblastoma susceptibility gene product in cycling and noncycling human hematopoietic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2770–2774. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Blanco M. A., Lengyel P., Morrison E., Brownlee C., Stiles C. D., Rutherford M., Hannigan G., Williams B. R. Regulation of 2',5'-oligoadenylate synthetase gene expression by interferons and platelet-derived growth factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;9(3):1060–1068. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.3.1060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang H. J., Yee J. K., Shew J. Y., Chen P. L., Bookstein R., Friedmann T., Lee E. Y., Lee W. H. Suppression of the neoplastic phenotype by replacement of the RB gene in human cancer cells. Science. 1988 Dec 16;242(4885):1563–1566. doi: 10.1126/science.3201247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar R., Choubey D., Lengyel P., Sen G. C. Studies on the role of the 2'-5'-oligoadenylate synthetase-RNase L pathway in beta interferon-mediated inhibition of encephalomyocarditis virus replication. J Virol. 1988 Sep;62(9):3175–3181. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.9.3175-3181.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar R., Mendelsohn J. Growth regulation of A431 cells. Modulation of expression of transforming growth factor-alpha mRNA and 2',5'-oligoadenylate synthetase activity. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 15;265(8):4578–4582. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar R., Mendelsohn J. Role of 2'-5'-oligoadenylate synthetase in gamma-interferon-mediated growth inhibition of A431 cells. Cancer Res. 1989 Sep 15;49(18):5180–5184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar R., Shepard H. M., Mendelsohn J. Regulation of phosphorylation of the c-erbB-2/HER2 gene product by a monoclonal antibody and serum growth factor(s) in human mammary carcinoma cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;11(2):979–986. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.2.979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar R., Tiwari R. K., Kusari J., Sen G. C. Clonal derivatives of the RD-114 cell line differ in their antiviral and gene-inducing responses to interferons. J Virol. 1987 Sep;61(9):2727–2732. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.9.2727-2732.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laiho M., DeCaprio J. A., Ludlow J. W., Livingston D. M., Massagué J. Growth inhibition by TGF-beta linked to suppression of retinoblastoma protein phosphorylation. Cell. 1990 Jul 13;62(1):175–185. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90251-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. H., Bookstein R., Hong F., Young L. J., Shew J. Y., Lee E. Y. Human retinoblastoma susceptibility gene: cloning, identification, and sequence. Science. 1987 Mar 13;235(4794):1394–1399. doi: 10.1126/science.3823889. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibovitz A., Stinson J. C., McCombs W. B., 3rd, McCoy C. E., Mazur K. C., Mabry N. D. Classification of human colorectal adenocarcinoma cell lines. Cancer Res. 1976 Dec;36(12):4562–4569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lengyel P. Biochemistry of interferons and their actions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:251–282. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.001343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludlow J. W., DeCaprio J. A., Huang C. M., Lee W. H., Paucha E., Livingston D. M. SV40 large T antigen binds preferentially to an underphosphorylated member of the retinoblastoma susceptibility gene product family. Cell. 1989 Jan 13;56(1):57–65. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90983-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahon M., Stark G. R., Kerr I. M. Interferon-induced gene expression in wild-type and interferon-resistant human lymphoblastoid (Daudi) cells. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):362–366. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.362-366.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mihara K., Cao X. R., Yen A., Chandler S., Driscoll B., Murphree A. L., T'Ang A., Fung Y. K. Cell cycle-dependent regulation of phosphorylation of the human retinoblastoma gene product. Science. 1989 Dec 8;246(4935):1300–1303. doi: 10.1126/science.2588006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore R. N., Larsen H. S., Horohov D. W., Rouse B. T. Endogenous regulation of macrophage proliferative expansion by colony-stimulating factor-induced interferon. Science. 1984 Jan 13;223(4632):178–181. doi: 10.1126/science.6606850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moses H. L., Yang E. Y., Pietenpol J. A. TGF-beta stimulation and inhibition of cell proliferation: new mechanistic insights. Cell. 1990 Oct 19;63(2):245–247. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90155-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeffer L. M., Donner D. B. The down-regulation of alpha-interferon receptors in human lymphoblastoid cells: relation to cellular responsiveness to the antiproliferative action of alpha-interferon. Cancer Res. 1990 May 1;50(9):2654–2657. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickering L. A., Kronenberg L. H., Stewart W. E., 2nd Spontaneous production of human interferon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5938–5942. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5938. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samid D., Chang E. H., Friedman R. M. Biochemical correlates of phenotypic reversion in interferon-treated mouse cells transformed by a human oncogene. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Feb 29;119(1):21–28. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91612-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strohmeyer T., Reissmann P., Cordon-Cardo C., Hartmann M., Ackermann R., Slamon D. Correlation between retinoblastoma gene expression and differentiation in human testicular tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 1;88(15):6662–6666. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.15.6662. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiwari R. K., Kusari J., Sen G. C. Functional equivalents of interferon-mediated signals needed for induction of an mRNA can be generated by double-stranded RNA and growth factors. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3373–3378. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02659.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van de Vijver M. J., Kumar R., Mendelsohn J. Ligand-induced activation of A431 cell epidermal growth factor receptors occurs primarily by an autocrine pathway that acts upon receptors on the surface rather than intracellularly. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 25;266(12):7503–7508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg R. A. The retinoblastoma gene and cell growth control. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 May;15(5):199–202. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90162-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zullo J. N., Cochran B. H., Huang A. S., Stiles C. D. Platelet-derived growth factor and double-stranded ribonucleic acids stimulate expression of the same genes in 3T3 cells. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):793–800. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90252-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]