Abstract
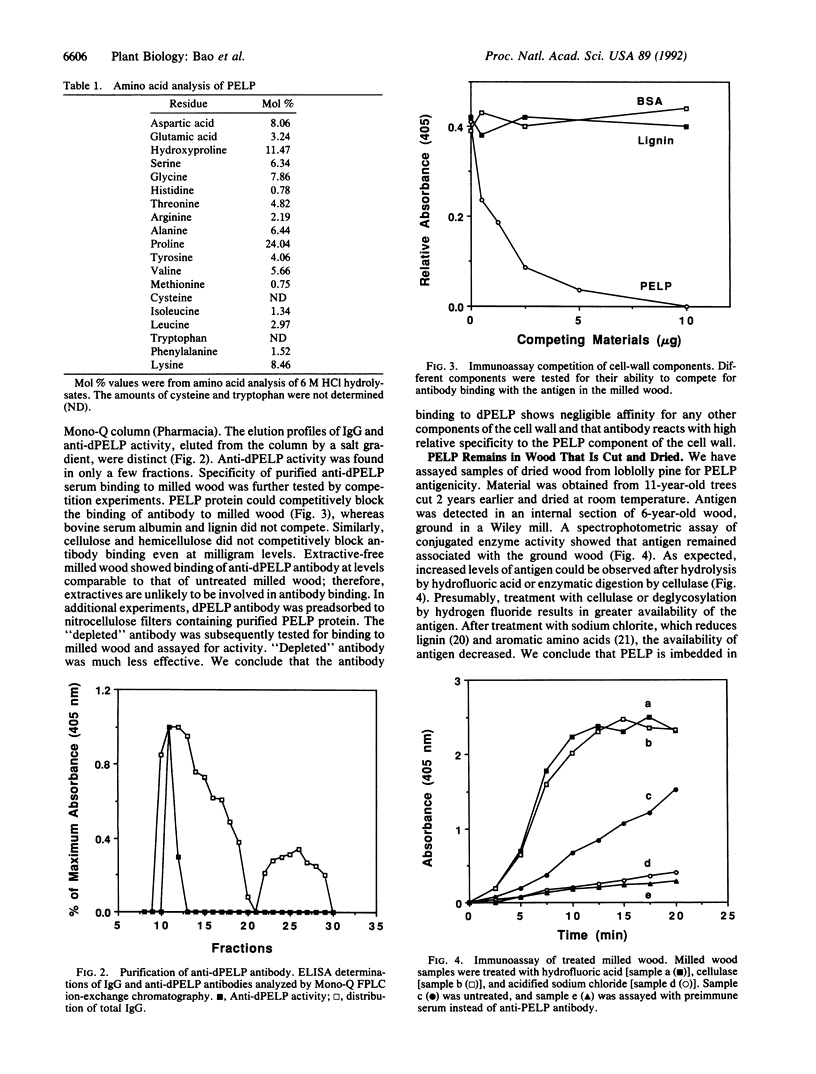
A pine extensin-like protein (PELP) has been localized in metabolically active cells of differentiating xylem and in mature wood of loblolly pine (Pinus taeda L.). This proline-rich glycosylated protein was purified from cell walls of differentiating xylem by differential solubility and gel electrophoresis. Polyclonal rabbit antibodies were raised against the deglycosylated purified protein (dPELP) and purified antibody was used for immunolocalization. Immunogold and alkaline phosphatase secondary antibody staining both show antigen in secondary cell walls of earlywood and less staining in latewood. Immunoassays of milled dry wood were developed and used to show increased availability of antigen after hydrogen fluoride or cellulase treatment and decreased antigen after chlorite treatment. The specificity of the antigen-antibody reaction was confirmed by competition assays and by preadsorption of antibody to the purified protein. We propose that extensin-like protein is present in xylem cell walls during lignification and that the protein remains as a structural component of cell walls in wood for many years after xylogenesis. We suggest that such structural proteins play important roles in the differentiation of xylem and thereby could affect the properties of wood.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Biggs K. J., Fry S. C. Solubilization of covalently bound extensin from capsicum cell walls. Plant Physiol. 1990 Jan;92(1):197–204. doi: 10.1104/pp.92.1.197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassab G. I., Nieto-Sotelo J., Cooper J. B., van Holst G. J., Varner J. E. A developmentally regulated hydroxyproline-rich glycoprotein from the cell walls of soybean seed coats. Plant Physiol. 1985 Mar;77(3):532–535. doi: 10.1104/pp.77.3.532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. B., Varner J. E. Cross-linking of soluble extensin in isolated cell walls. Plant Physiol. 1984 Oct;76(2):414–417. doi: 10.1104/pp.76.2.414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fry S. C. Isodityrosine, a new cross-linking amino acid from plant cell-wall glycoprotein. Biochem J. 1982 May 15;204(2):449–455. doi: 10.1042/bj2040449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOLLAR S. J., JARAI M. Biochemical chlorination in Streptomvces aureofaciens. Nature. 1960 Nov 19;188:665–665. doi: 10.1038/188665a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller B., Templeton M. D., Lamb C. J. Specific localization of a plant cell wall glycine-rich protein in protoxylem cells of the vascular system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1529–1533. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meltzer N. M., Tous G. I., Gruber S., Stein S. Gas-phase hydrolysis of proteins and peptides. Anal Biochem. 1987 Feb 1;160(2):356–361. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90060-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mort A. J., Lamport D. T. Anhydrous hydrogen fluoride deglycosylates glycoproteins. Anal Biochem. 1977 Oct;82(2):289–309. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90165-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Showalter A. M., Bell J. N., Cramer C. L., Bailey J. A., Varner J. E., Lamb C. J. Accumulation of hydroxyproline-rich glycoprotein mRNAs in response to fungal elicitor and infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6551–6555. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ye Z. H., Song Y. R., Marcus A., Varner J. E. Comparative localization of three classes of cell wall proteins. Plant J. 1991 Sep;1(2):175–183. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313x.1991.00175.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ye Z. H., Varner J. E. Tissue-Specific Expression of Cell Wall Proteins in Developing Soybean Tissues. Plant Cell. 1991 Jan;3(1):23–37. doi: 10.1105/tpc.3.1.23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]