Abstract
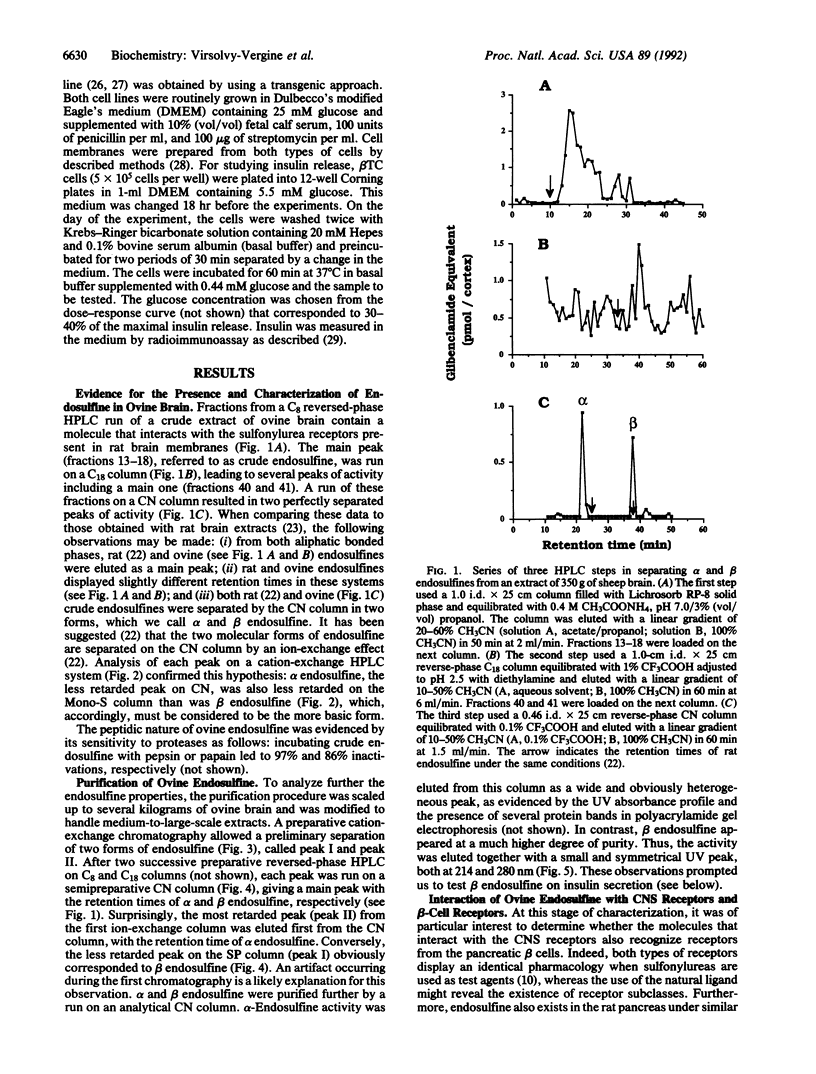
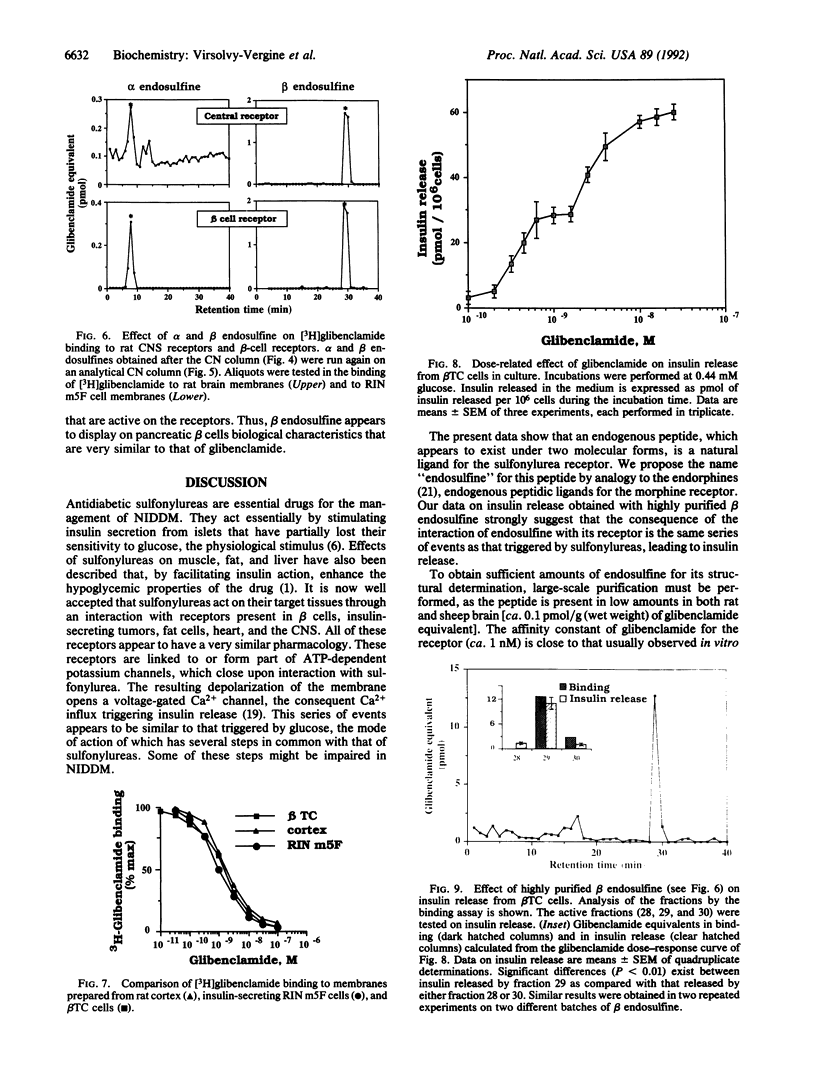
Antidiabetic sulfonylureas act through receptors coupled to ATP-dependent potassium channels. Using the binding of [3H]glibenclamide, a highly potent sulfonylurea, to rat brain membranes to follow the purification procedure, we extracted from ovine brain, purified, and partially characterized two peptides that are endogenous ligands for the central nervous system sulfonylurea receptors. These peptides, referred to as alpha and beta endosulfine, differ by their isoelectric points, the beta form being more basic. Each form of endosulfine is recognized equally by the sulfonylurea receptors from the central nervous system and from insulin-secreting beta cells. In the same concentration range that is active on the receptors, beta endosulfine releases insulin from a beta-cell line. Endosulfine is a good candidate for being implicated in the physiology of beta cells and their disorders (e.g., type II diabetes) and in certain pathologies related to modifications of ion fluxes.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashcroft F. M. Adenosine 5'-triphosphate-sensitive potassium channels. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1988;11:97–118. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.11.030188.000525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashcroft F. M., Harrison D. E., Ashcroft S. J. Glucose induces closure of single potassium channels in isolated rat pancreatic beta-cells. 1984 Nov 29-Dec 5Nature. 312(5993):446–448. doi: 10.1038/312446a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom F. E. The endorphins: a growing family of pharmacologically pertinent peptides. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1983;23:151–170. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.23.040183.001055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerasi E., Luft R., Efendic S. Decreased sensitivity of the pancreatic beta cells to glucose in prediabetic and diabetic subjects. A glucose dose-response study. Diabetes. 1972 Apr;21(4):224–234. doi: 10.2337/diab.21.4.224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook D. L., Hales C. N. Intracellular ATP directly blocks K+ channels in pancreatic B-cells. Nature. 1984 Sep 20;311(5983):271–273. doi: 10.1038/311271a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Ambra R., Surana M., Efrat S., Starr R. G., Fleischer N. Regulation of insulin secretion from beta-cell lines derived from transgenic mice insulinomas resembles that of normal beta-cells. Endocrinology. 1990 Jun;126(6):2815–2822. doi: 10.1210/endo-126-6-2815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efrat S., Linde S., Kofod H., Spector D., Delannoy M., Grant S., Hanahan D., Baekkeskov S. Beta-cell lines derived from transgenic mice expressing a hybrid insulin gene-oncogene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):9037–9041. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.9037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fosset M., De Weille J. R., Green R. D., Schmid-Antomarchi H., Lazdunski M. Antidiabetic sulfonylureas control action potential properties in heart cells via high affinity receptors that are linked to ATP-dependent K+ channels. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 15;263(17):7933–7936. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaines K. L., Hamilton S., Boyd A. E., 3rd Characterization of the sulfonylurea receptor on beta cell membranes. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 25;263(6):2589–2592. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gazdar A. F., Chick W. L., Oie H. K., Sims H. L., King D. L., Weir G. C., Lauris V. Continuous, clonal, insulin- and somatostatin-secreting cell lines established from a transplantable rat islet cell tumor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3519–3523. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisen K., Hitzel V., Okomonopoulos R., Pünter J., Weyer R., Summ H. D. Inhibition of 3H-glibenclamide binding to sulfonylurea receptors by oral antidiabetics. Arzneimittelforschung. 1985;35(4):707–712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Göke R., Cole T., Conlon J. M. Characterization of the receptor for glucagon-like peptide-1(7-36)amide on plasma membranes from rat insulinoma-derived cells by covalent cross-linking. J Mol Endocrinol. 1989 Mar;2(2):93–98. doi: 10.1677/jme.0.0020093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellman B. Factors affecting the uptake of glibenclamide in microdissected pancreatic islets rich in beta-cells. Pharmacology. 1974;11(5):257–267. doi: 10.1159/000136498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaubisch N., Hammer R., Wollheim C., Renold A. E., Offord R. E. Specific receptors for sulfonylureas in brain and in a beta-cell tumor of the rat. Biochem Pharmacol. 1982 Mar 15;31(6):1171–1174. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(82)90363-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lupo B., Bataille D. A binding site for [3H]glipizide in the rat cerebral cortex. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Aug 11;140(2):157–169. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90801-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mourre C., Ben Ari Y., Bernardi H., Fosset M., Lazdunski M. Antidiabetic sulfonylureas: localization of binding sites in the brain and effects on the hyperpolarization induced by anoxia in hippocampal slices. Brain Res. 1989 May 1;486(1):159–164. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)91288-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popiela H., Moore W. Tolbutamide stimulates proliferation of pancreatic beta cells in culture. Pancreas. 1991 Jul;6(4):464–469. doi: 10.1097/00006676-199107000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid-Antomarchi H., De Weille J., Fosset M., Lazdunski M. The receptor for antidiabetic sulfonylureas controls the activity of the ATP-modulated K+ channel in insulin-secreting cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 25;262(33):15840–15844. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid-Antomarchi H., De Weille J., Fosset M., Lazdunski M. The receptor for antidiabetic sulfonylureas controls the activity of the ATP-modulated K+ channel in insulin-secreting cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 25;262(33):15840–15844. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virsolvy-Vergine A., Brück M., Dufour M., Cauvin A., Lupo B., Bataille D. An endogenous ligand for the central sulfonylurea receptor. FEBS Lett. 1988 Dec 19;242(1):65–69. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80986-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westermark P., Wilander E. The influence of amyloid deposits on the islet volume in maturity onset diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia. 1978 Nov;15(5):417–421. doi: 10.1007/BF01219652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




