VOLUME 290 (2015) PAGES 26383–26392
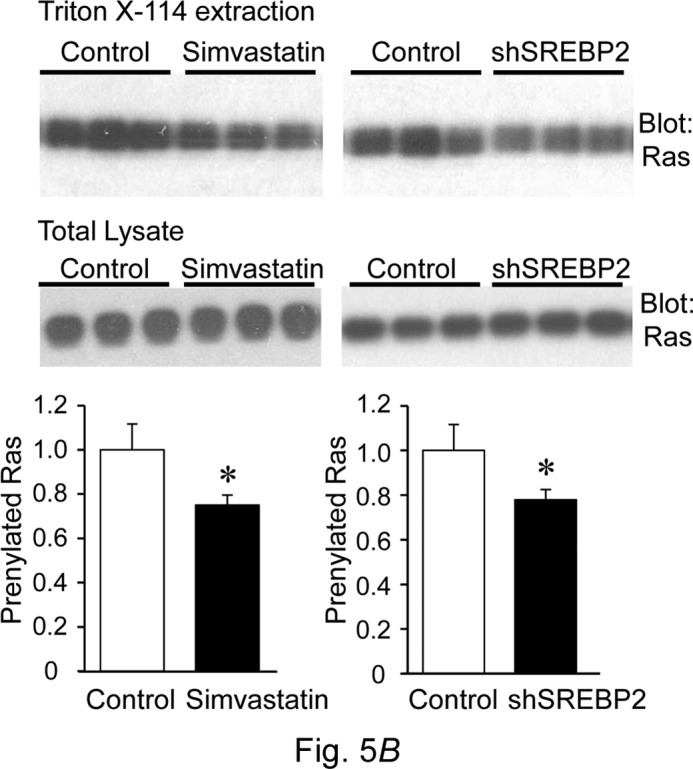
During preparation of this manuscript, an incorrect immunoblot was unintentionally inserted into the lower panel of Fig. 5B. This error has now been corrected and does not affect the results or conclusions of this work. However, for clarity of reference to the two panels of this figure, the last paragraph of the results on page 26387 should now read: “As shown in Fig. 5B, the hydrophobic membrane was rich in prenylated Ras (upper panels), whereas unprenylated Ras was extracted in the aqueous cytosolic fraction. As expected from its pharmacological effect, prenylated Ras was decreased in simvastatin-treated cells. SREBP2 knockdown cells also exhibited a reduction in prenylated Ras, whereas total Ras protein levels were not changed by either method of cholesterol depletion (lower panels).”