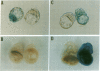
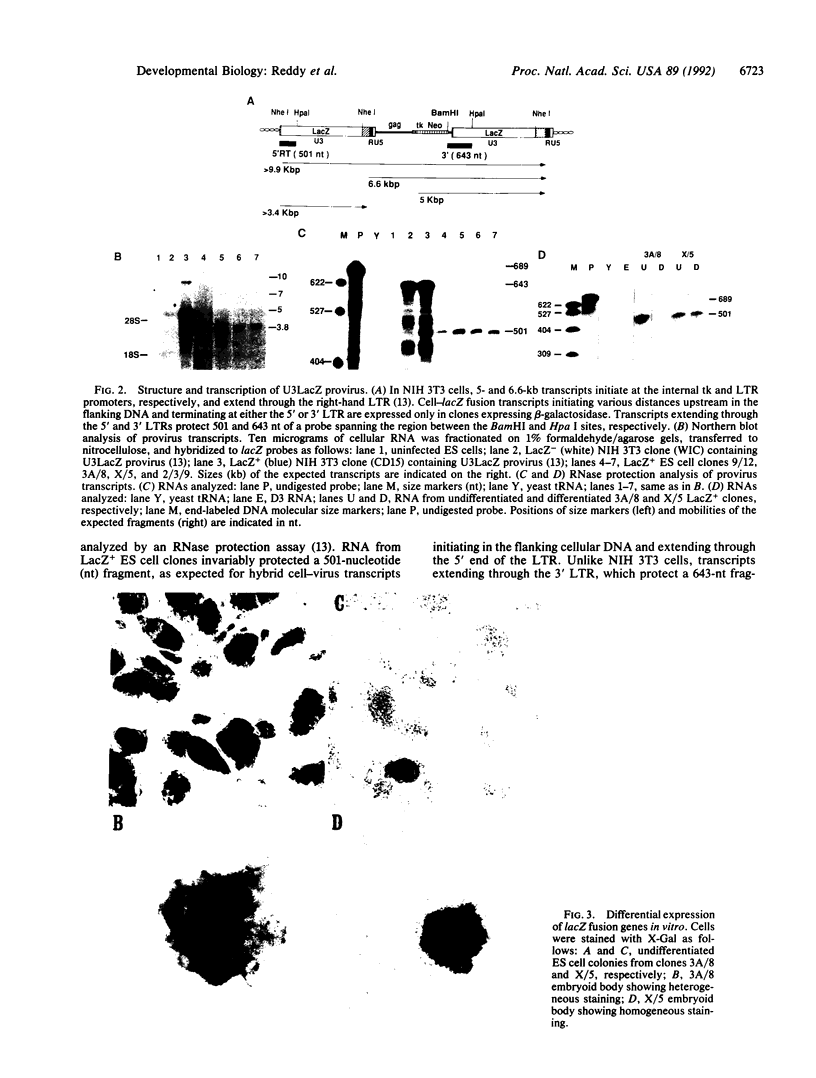
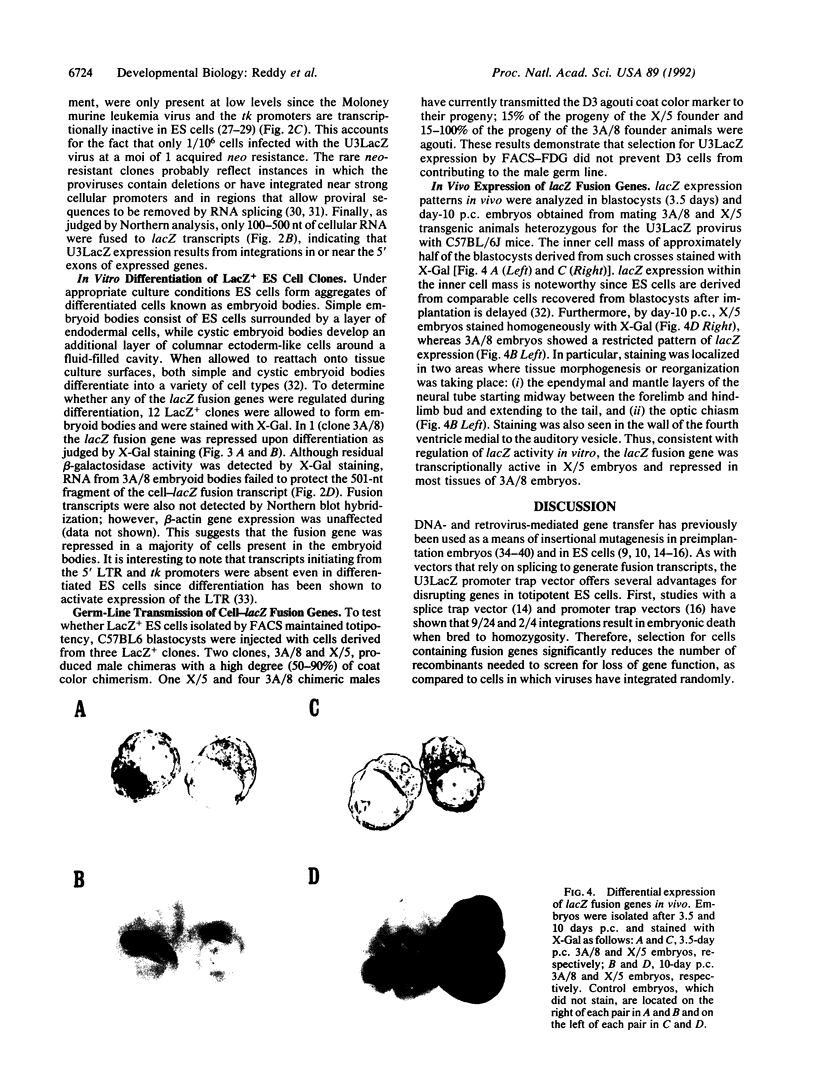
Abstract
Murine embryonic stem (ES) cells were infected with a retrovirus promoter trap vector, and clones expressing lacZ fusion genes (LacZ+) were isolated by fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS). Of 12 fusion genes tested, 1 was repressed when ES cells were allowed to differentiate in vitro. Two of three lacZ fusion genes tested were passed into the germ line, indicating that FACS does not significantly affect stem cell totipotency. The pattern of lacZ expression observed in vivo was consistent with that seen in vitro. Both fusion genes were expressed in preimplantation blastulas. However, a fusion gene whose expression was unaffected by in vitro differentiation was ubiquitously expressed in day-10 embryos, while the other, which showed regulated expression in vitro, was restricted to cells located along the posterior neural fold, the optic chiasm, and within the fourth ventricle. These results demonstrate the utility of using promoter trap vectors in conjunction with fluorescence sorting to disrupt developmentally regulated genes in mice.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akgün E., Ziegler M., Grez M. Determinants of retrovirus gene expression in embryonal carcinoma cells. J Virol. 1991 Jan;65(1):382–388. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.1.382-388.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barklis E., Mulligan R. C., Jaenisch R. Chromosomal position or virus mutation permits retrovirus expression in embryonal carcinoma cells. Cell. 1986 Nov 7;47(3):391–399. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90596-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley A., Evans M., Kaufman M. H., Robertson E. Formation of germ-line chimaeras from embryo-derived teratocarcinoma cell lines. Nature. 1984 May 17;309(5965):255–256. doi: 10.1038/309255a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner D. G., Lin-Chao S., Cohen S. N. Analysis of mammalian cell genetic regulation in situ by using retrovirus-derived "portable exons" carrying the Escherichia coli lacZ gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5517–5521. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costantini F., Radice G., Lee J. L., Chada K. K., Perry W., Son H. J. Insertional mutations in transgenic mice. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1989;36:159–169. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60169-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Covarrubias L., Nishida Y., Terao M., D'Eustachio P., Mintz B. Cellular DNA rearrangements and early developmental arrest caused by DNA insertion in transgenic mouse embryos. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;7(6):2243–2247. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.6.2243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans M. J., Kaufman M. H. Establishment in culture of pluripotential cells from mouse embryos. Nature. 1981 Jul 9;292(5819):154–156. doi: 10.1038/292154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiering S. N., Roederer M., Nolan G. P., Micklem D. R., Parks D. R., Herzenberg L. A. Improved FACS-Gal: flow cytometric analysis and sorting of viable eukaryotic cells expressing reporter gene constructs. Cytometry. 1991;12(4):291–301. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990120402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedrich G., Soriano P. Promoter traps in embryonic stem cells: a genetic screen to identify and mutate developmental genes in mice. Genes Dev. 1991 Sep;5(9):1513–1523. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.9.1513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Rigby P. W., Lane D. P. Negative regulation of viral enhancers in undifferentiated embryonic stem cells. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):519–526. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90109-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gossler A., Joyner A. L., Rossant J., Skarnes W. C. Mouse embryonic stem cells and reporter constructs to detect developmentally regulated genes. Science. 1989 Apr 28;244(4903):463–465. doi: 10.1126/science.2497519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harbers K., Kuehn M., Delius H., Jaenisch R. Insertion of retrovirus into the first intron of alpha 1(I) collagen gene to embryonic lethal mutation in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(5):1504–1508. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.5.1504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kothary R., Clapoff S., Brown A., Campbell R., Peterson A., Rossant J. A transgene containing lacZ inserted into the dystonia locus is expressed in neural tube. Nature. 1988 Sep 29;335(6189):435–437. doi: 10.1038/335435a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewin B. Units of transcription and translation: sequence components of heterogeneous nuclear RNA and messenger RNA. Cell. 1975 Feb;4(2):77–93. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90113-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linney E., Davis B., Overhauser J., Chao E., Fan H. Non-function of a Moloney murine leukaemia virus regulatory sequence in F9 embryonal carcinoma cells. 1984 Mar 29-Apr 4Nature. 308(5958):470–472. doi: 10.1038/308470a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loh T. P., Sievert L. L., Scott R. W. Evidence for a stem cell-specific repressor of Moloney murine leukemia virus expression in embryonal carcinoma cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):4045–4057. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.4045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macleod D., Lovell-Badge R., Jones S., Jackson I. A promoter trap in embryonic stem (ES) cells selects for integration of DNA into CpG islands. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jan 11;19(1):17–23. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.1.17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCoy J. P., Jr, Chambers W. H., Lakomy R., Campbell J. A., Stewart C. C. Sorting minor subpopulations of cells: use of fluorescence as the triggering signal. Cytometry. 1991;12(3):268–274. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990120310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L. The nucleotide sequence and transcript map of the herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Dec 20;8(24):5949–5964. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.24.5949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nolan G. P., Fiering S., Nicolas J. F., Herzenberg L. A. Fluorescence-activated cell analysis and sorting of viable mammalian cells based on beta-D-galactosidase activity after transduction of Escherichia coli lacZ. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2603–2607. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nüsslein-Volhard C., Wieschaus E. Mutations affecting segment number and polarity in Drosophila. Nature. 1980 Oct 30;287(5785):795–801. doi: 10.1038/287795a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellicer A., Wagner E. F., el-Kareh A., Dewey M. J., Reuser A. J., Silverstein S., Axel R., Mintz B. Introduction of a viral thymidine kinase gene and the human beta-globin gene into developmentally multipotential mouse teratocarcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):2098–2102. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.2098. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen R., Kempler G., Barklis E. A stem cell-specific silencer in the primer-binding site of a retrovirus. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1214–1221. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy S., DeGregori J. V., von Melchner H., Ruley H. E. Retrovirus promoter-trap vector to induce lacZ gene fusions in mammalian cells. J Virol. 1991 Mar;65(3):1507–1515. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.3.1507-1515.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reith A. D., Bernstein A. Molecular basis of mouse developmental mutants. Genes Dev. 1991 Jul;5(7):1115–1123. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.7.1115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanes J. R., Rubenstein J. L., Nicolas J. F. Use of a recombinant retrovirus to study post-implantation cell lineage in mouse embryos. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 1;5(12):3133–3142. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04620.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnieke A., Harbers K., Jaenisch R. Embryonic lethal mutation in mice induced by retrovirus insertion into the alpha 1(I) collagen gene. 1983 Jul 28-Aug 3Nature. 304(5924):315–320. doi: 10.1038/304315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorge J., Cutting A. E., Erdman V. D., Gautsch J. W. Integration-specific retrovirus expression in embryonal carcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6627–6631. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soriano P., Gridley T., Jaenisch R. Retroviruses and insertional mutagenesis in mice: proviral integration at the Mov 34 locus leads to early embryonic death. Genes Dev. 1987 Jun;1(4):366–375. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.4.366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spence S. E., Gilbert D. J., Swing D. A., Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A. Spontaneous germ line virus infection and retroviral insertional mutagenesis in eighteen transgenic Srev lines of mice. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jan;9(1):177–184. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.1.177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tickle C., Alberts B., Wolpert L., Lee J. Local application of retinoic acid to the limb bond mimics the action of the polarizing region. Nature. 1982 Apr 8;296(5857):564–566. doi: 10.1038/296564a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tickle C., Summerbell D., Wolpert L. Positional signalling and specification of digits in chick limb morphogenesis. Nature. 1975 Mar 20;254(5497):199–202. doi: 10.1038/254199a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukiyama T., Niwa O., Yokoro K. Mechanism of suppression of the long terminal repeat of Moloney leukemia virus in mouse embryonal carcinoma cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):4670–4676. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.4670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiher H., Noda T., Gray D. A., Sharpe A. H., Jaenisch R. Transgenic mouse model of kidney disease: insertional inactivation of ubiquitously expressed gene leads to nephrotic syndrome. Cell. 1990 Aug 10;62(3):425–434. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90008-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Melchner H., DeGregori J. V., Rayburn H., Reddy S., Friedel C., Ruley H. E. Selective disruption of genes expressed in totipotent embryonal stem cells. Genes Dev. 1992 Jun;6(6):919–927. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.6.919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Melchner H., Reddy S., Ruley H. E. Isolation of cellular promoters by using a retrovirus promoter trap. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(10):3733–3737. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.10.3733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Melchner H., Ruley H. E. Identification of cellular promoters by using a retrovirus promoter trap. J Virol. 1989 Aug;63(8):3227–3233. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.8.3227-3233.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]