Abstract
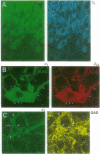
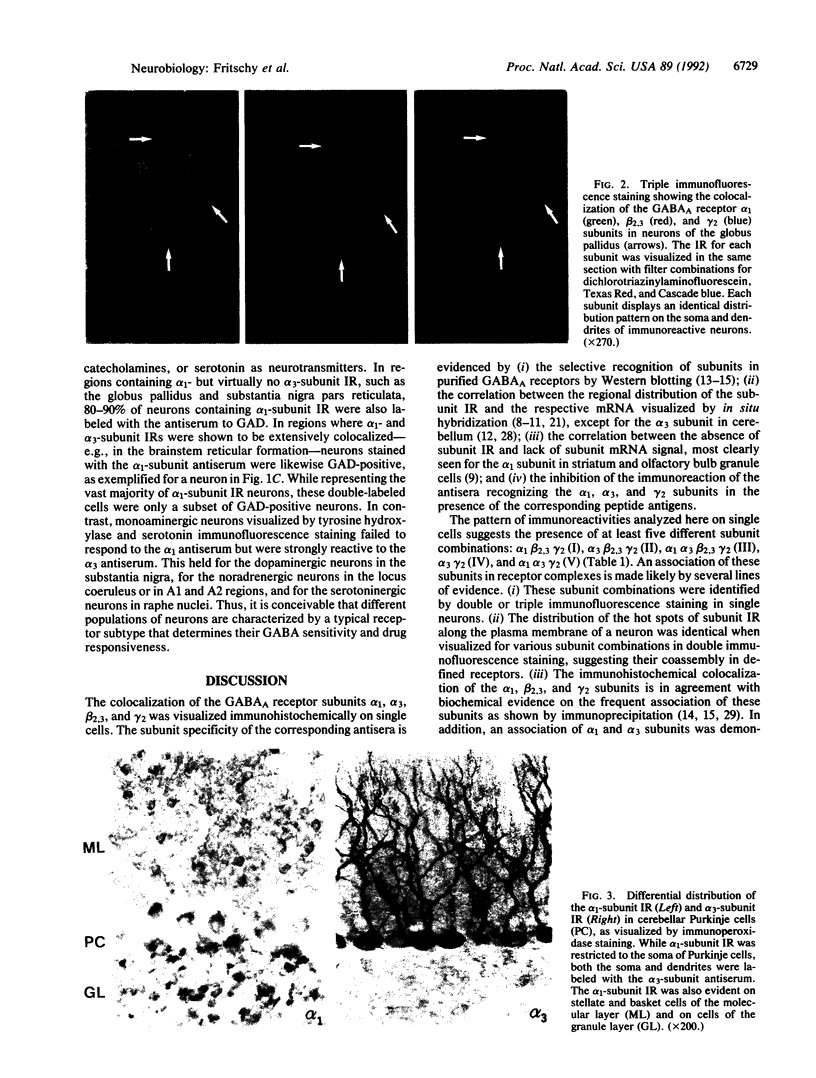
The extraordinary structural diversity of subunits forming type A gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABAA) receptors in the brain is expected to give rise to different modes of GABAergic synaptic inhibition and different profiles of modulatory drugs effective in anxiolytic, hypnotic, and antiepileptic therapy. To identify receptor subtypes in situ, the most prevalent subunits were visualized by double and triple immunofluorescence staining in rat brain, using polyclonal antibodies to the alpha 1, alpha 3, and gamma 2 subunits and a monoclonal antibody to locate both the beta 2 and the beta 3 subunit. At both cellular and subcellular levels five distinct patterns of subunit colocalization were identified: I, alpha 1 beta 2,3 gamma 2; II, alpha 3 beta 2,3 gamma 2; III, alpha 1 alpha 3 beta 2,3 gamma 2; IV, alpha 3 gamma 2; and V, alpha 1 alpha 3 gamma 2. As analyzed by confocal laser microscopy, different subunits displayed the same local variations of staining intensity ("hot spots") along the plasma membrane. The covisualized subunits appear therefore to be coassembled in receptor subtypes. Most neurons expressed only a single major receptor subtype with no apparent distinction between synaptic and extrasynaptic sites. However, in some neurons, most notably in Purkinje cells, the subunit composition varied between the soma and the dendrites, pointing to the existence of receptor heterogeneity within single neurons. Furthermore, different populations of neurons may be characterized by particular receptor subtypes. Cells displaying alpha 1-subunit immunoreactivity were mostly identified as GABAergic, whereas monoaminergic neurons displayed intense alpha 3-subunit immunoreactivity but virtually no alpha 1-subunit immunoreactivity. The allocation of defined GABAA receptor subtypes to identified neurons opens the way for a functional analysis of receptor heterogeneity.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Araki T., Tohyama M. Region-specific expression of GABAA receptor alpha 3 and alpha 4 subunits mRNAs in the rat brain. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1992 Feb;12(4):293–314. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(92)90132-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benke D., Cicin-Sain A., Mertens S., Mohler H. Immunochemical identification of the alpha 1- and alpha 3-subunits of the GABAA-receptor in rat brain. J Recept Res. 1991;11(1-4):407–424. doi: 10.3109/10799899109066418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benke D., Mertens S., Trzeciak A., Gillessen D., Mohler H. GABAA receptors display association of gamma 2-subunit with alpha 1- and beta 2/3-subunits. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 5;266(7):4478–4483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benke D., Mertens S., Trzeciak A., Gillessen D., Mohler H. Identification and immunohistochemical mapping of GABAA receptor subtypes containing the delta-subunit in rat brain. FEBS Lett. 1991 May 20;283(1):145–149. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80573-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutting G. R., Lu L., O'Hara B. F., Kasch L. M., Montrose-Rafizadeh C., Donovan D. M., Shimada S., Antonarakis S. E., Guggino W. B., Uhl G. R. Cloning of the gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) rho 1 cDNA: a GABA receptor subunit highly expressed in the retina. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 1;88(7):2673–2677. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.7.2673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewert M., Shivers B. D., Lüddens H., Möhler H., Seeburg P. H. Subunit selectivity and epitope characterization of mAbs directed against the GABAA/benzodiazepine receptor. J Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;110(6):2043–2048. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.6.2043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hironaka T., Morita Y., Hagihira S., Tateno E., Kita H., Tohyama M. Localization of GABAA-receptor alpha 1 subunit mRNA-containing neurons in the lower brainstem of the rat. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1990 May;7(4):335–345. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(90)90083-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Raine L., Fanger H. Use of avidin-biotin-peroxidase complex (ABC) in immunoperoxidase techniques: a comparison between ABC and unlabeled antibody (PAP) procedures. J Histochem Cytochem. 1981 Apr;29(4):577–580. doi: 10.1177/29.4.6166661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüddens H., Killisch I., Seeburg P. H. More than one alpha variant may exist in a GABAA/benzodiazepine receptor complex. J Recept Res. 1991;11(1-4):535–551. doi: 10.3109/10799899109066426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüddens H., Pritchett D. B., Köhler M., Killisch I., Keinänen K., Monyer H., Sprengel R., Seeburg P. H. Cerebellar GABAA receptor selective for a behavioural alcohol antagonist. Nature. 1990 Aug 16;346(6285):648–651. doi: 10.1038/346648a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüddens H., Wisden W. Function and pharmacology of multiple GABAA receptor subunits. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1991 Feb;12(2):49–51. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(91)90495-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLennan A. J., Brecha N., Khrestchatisky M., Sternini C., Tillakaratne N. J., Chiang M. Y., Anderson K., Lai M., Tobin A. J. Independent cellular and ontogenetic expression of mRNAs encoding three alpha polypeptides of the rat GABAA receptor. Neuroscience. 1991;43(2-3):369–380. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(91)90301-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malherbe P., Sigel E., Baur R., Persohn E., Richards J. G., Mohler H. Functional characteristics and sites of gene expression of the alpha 1, beta 1, gamma 2-isoform of the rat GABAA receptor. J Neurosci. 1990 Jul;10(7):2330–2337. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.10-07-02330.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malherbe P., Sigel E., Baur R., Persohn E., Richards J. G., Möhler H. Functional expression and sites of gene transcription of a novel alpha subunit of the GABAA receptor in rat brain. FEBS Lett. 1990 Jan 29;260(2):261–265. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80118-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKernan R. M., Quirk K., Prince R., Cox P. A., Gillard N. P., Ragan C. I., Whiting P. GABAA receptor subtypes immunopurified from rat brain with alpha subunit-specific antibodies have unique pharmacological properties. Neuron. 1991 Oct;7(4):667–676. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90379-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohler H., Malherbe P., Draguhn A., Richards J. G. GABAA-receptors: structural requirements and sites of gene expression in mammalian brain. Neurochem Res. 1990 Feb;15(2):199–207. doi: 10.1007/BF00972210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oertel W. H., Schmechel D. E., Tappaz M. L., Kopin I. J. Production of a specific antiserum to rat brain glutamic acid decarboxylase by injection of an antigen-antibody complex. Neuroscience. 1981;6(12):2689–2700. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(81)90113-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen R. W., Tobin A. J. Molecular biology of GABAA receptors. FASEB J. 1990 Mar;4(5):1469–1480. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.4.5.2155149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchett D. B., Seeburg P. H. Gamma-aminobutyric acidA receptor alpha 5-subunit creates novel type II benzodiazepine receptor pharmacology. J Neurochem. 1990 May;54(5):1802–1804. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb01237.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puia G., Vicini S., Seeburg P. H., Costa E. Influence of recombinant gamma-aminobutyric acid-A receptor subunit composition on the action of allosteric modulators of gamma-aminobutyric acid-gated Cl- currents. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Jun;39(6):691–696. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards J. G., Schoch P., Häring P., Takacs B., Möhler H. Resolving GABAA/benzodiazepine receptors: cellular and subcellular localization in the CNS with monoclonal antibodies. J Neurosci. 1987 Jun;7(6):1866–1886. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-06-01866.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoch P., Richards J. G., Häring P., Takacs B., Stähli C., Staehelin T., Haefely W., Möhler H. Co-localization of GABA receptors and benzodiazepine receptors in the brain shown by monoclonal antibodies. Nature. 1985 Mar 14;314(6007):168–171. doi: 10.1038/314168a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schofield P. R., Shivers B. D., Seeburg P. H. The role of receptor subtype diversity in the CNS. Trends Neurosci. 1990 Jan;13(1):8–11. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(90)90052-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shivers B. D., Killisch I., Sprengel R., Sontheimer H., Köhler M., Schofield P. R., Seeburg P. H. Two novel GABAA receptor subunits exist in distinct neuronal subpopulations. Neuron. 1989 Sep;3(3):327–337. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90257-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigel E., Baur R., Trube G., Möhler H., Malherbe P. The effect of subunit composition of rat brain GABAA receptors on channel function. Neuron. 1990 Nov;5(5):703–711. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90224-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somogyi P., Takagi H. A note on the use of picric acid-paraformaldehyde-glutaraldehyde fixative for correlated light and electron microscopic immunocytochemistry. Neuroscience. 1982 Jul;7(7):1779–1783. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(82)90035-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staines W. A., Meister B., Melander T., Nagy J. I., Hökfelt T. Three-color immunofluorescence histochemistry allowing triple labeling within a single section. J Histochem Cytochem. 1988 Feb;36(2):145–151. doi: 10.1177/36.2.2891745. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Séquier J. M., Richards J. G., Malherbe P., Price G. W., Mathews S., Möhler H. Mapping of brain areas containing RNA homologous to cDNAs encoding the alpha and beta subunits of the rat GABAA gamma-aminobutyrate receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7815–7819. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson-Shaw D., Robinson M., Gambarana C., Siegel R. E., Sikela J. M. A novel gamma subunit of the GABAA receptor identified using the polymerase chain reaction. FEBS Lett. 1991 Jun 24;284(2):211–215. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80687-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ymer S., Draguhn A., Wisden W., Werner P., Keinänen K., Schofield P. R., Sprengel R., Pritchett D. B., Seeburg P. H. Structural and functional characterization of the gamma 1 subunit of GABAA/benzodiazepine receptors. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3261–3267. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07525.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang J. H., Sato M., Tohyama M. Region-specific expression of the mRNAs encoding beta subunits (beta 1, beta 2, and beta 3) of GABAA receptor in the rat brain. J Comp Neurol. 1991 Jan 22;303(4):637–657. doi: 10.1002/cne.903030409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimprich F., Zezula J., Sieghart W., Lassmann H. Immunohistochemical localization of the alpha 1, alpha 2 and alpha 3 subunit of the GABAA receptor in the rat brain. Neurosci Lett. 1991 Jun 10;127(1):125–128. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(91)90910-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]