Abstract
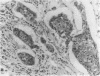
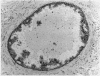
AIMS: To assess c-erbB-2 immunostaining in relation to morphological type of in situ and invasive breast carcinoma. METHODS: Formalin fixed, wax embedded archival tissue was used. Invasive carcinomas comprised 50 infiltrating ductal (NOS); seven medullary, 10 tubular, 15 mucinous and 24 classic invasive lobular. In situ carcinomas comprised 48 ductal (DCIS) and 10 cases of lobular (LCIS). The antibodies used were pAB1 (polyclonal) which stains cell lines that over express the c-erbB-2 oncogene, and ICR 12 (monoclonal) which stains sections of breast carcinoma known to show c-erbB-2 amplification. RESULTS: Immunostaining consistent with c-erbB-2 overexpression was found in 10 out of 50 cases of infiltrating ductal carcinoma (NOS), one of 24 infiltrating lobular carcinomas and one of seven medullary carcinomas only. Seventy per cent of ICR 12 positive cases of infiltrating ductal carcinoma also had extratumoral DCIS. Forty six per cent of pure DCIS lesions also showed strong membrane staining for c-erbB-2 protein, confined to large cell types. CONCLUSIONS: Immunostaining for c-erb B-2 oncoprotein occurs mainly in large cell DCIS and infiltrating ductal carcinoma NOS, especially those with an extratumoral DCIS component. There is a low incidence in other types of breast cancer, including those associated with a better prognosis. Different biological mechanisms may be responsible for histologically distinct types of breast carcinoma.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bargmann C. I., Hung M. C., Weinberg R. A. The neu oncogene encodes an epidermal growth factor receptor-related protein. Nature. 1986 Jan 16;319(6050):226–230. doi: 10.1038/319226a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes D. M., Lammie G. A., Millis R. R., Gullick W. L., Allen D. S., Altman D. G. An immunohistochemical evaluation of c-erbB-2 expression in human breast carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 1988 Oct;58(4):448–452. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1988.238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger M. S., Locher G. W., Saurer S., Gullick W. J., Waterfield M. D., Groner B., Hynes N. E. Correlation of c-erbB-2 gene amplification and protein expression in human breast carcinoma with nodal status and nuclear grading. Cancer Res. 1988 Mar 1;48(5):1238–1243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper H. S., Patchefsky A. S., Krall R. A. Tubular carcinoma of the breast. Cancer. 1978 Nov;42(5):2334–2342. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197811)42:5<2334::aid-cncr2820420534>3.0.co;2-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbett I. P., Henry J. A., Angus B., Watchorn C. J., Wilkinson L., Hennessy C., Gullick W. J., Tuzi N. L., May F. E., Westley B. R. NCL-CB11, a new monoclonal antibody recognizing the internal domain of the c-erbB-2 oncogene protein effective for use on formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue. J Pathol. 1990 May;161(1):15–25. doi: 10.1002/path.1711610105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon J. M., Anderson T. J., Page D. L., Lee D., Duffy S. W. Infiltrating lobular carcinoma of the breast. Histopathology. 1982 Mar;6(2):149–161. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1982.tb02712.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon J. M., Anderson T. J., Page D. L., Lee D., Duffy S. W., Stewart H. J. Infiltrating lobular carcinoma of the breast: an evaluation of the incidence and consequence of bilateral disease. Br J Surg. 1983 Sep;70(9):513–516. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800700902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gusterson B. A., Machin L. G., Gullick W. J., Gibbs N. M., Powles T. J., Elliott C., Ashley S., Monaghan P., Harrison S. c-erbB-2 expression in benign and malignant breast disease. Br J Cancer. 1988 Oct;58(4):453–457. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1988.239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanna W., Kahn H. J., Andrulis I., Pawson T. Distribution and patterns of staining of Neu oncogene product in benign and malignant breast diseases. Mod Pathol. 1990 Jul;3(4):455–461. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King C. R., Kraus M. H., Aaronson S. A. Amplification of a novel v-erbB-related gene in a human mammary carcinoma. Science. 1985 Sep 6;229(4717):974–976. doi: 10.1126/science.2992089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kommoss F., Colley M., Hart C. E., Franklin W. A. In situ distribution of oncogene products and growth factor receptors in breast carcinoma: c-erbB-2 oncoprotein, EGFr, and PDGFr-beta-subunit. Mol Cell Probes. 1990 Feb;4(1):11–23. doi: 10.1016/0890-8508(90)90035-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodato R. F., Maguire H. C., Jr, Greene M. I., Weiner D. B., LiVolsi V. A. Immunohistochemical evaluation of c-erbB-2 oncogene expression in ductal carcinoma in situ and atypical ductal hyperplasia of the breast. Mod Pathol. 1990 Jul;3(4):449–454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramachandra S., Machin L., Ashley S., Monaghan P., Gusterson B. A. Immunohistochemical distribution of c-erbB-2 in in situ breast carcinoma--a detailed morphological analysis. J Pathol. 1990 May;161(1):7–14. doi: 10.1002/path.1711610104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen B. B., Rose C., Christensen I. B. Prognostic factors in primary mucinous breast carcinoma. Am J Clin Pathol. 1987 Feb;87(2):155–160. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/87.2.155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridolfi R. L., Rosen P. P., Port A., Kinne D., Miké V. Medullary carcinoma of the breast: a clinicopathologic study with 10 year follow-up. Cancer. 1977 Oct;40(4):1365–1385. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197710)40:4<1365::aid-cncr2820400402>3.0.co;2-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schechter A. L., Hung M. C., Vaidyanathan L., Weinberg R. A., Yang-Feng T. L., Francke U., Ullrich A., Coussens L. The neu gene: an erbB-homologous gene distinct from and unlinked to the gene encoding the EGF receptor. Science. 1985 Sep 6;229(4717):976–978. doi: 10.1126/science.2992090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semba K., Kamata N., Toyoshima K., Yamamoto T. A v-erbB-related protooncogene, c-erbB-2, is distinct from the c-erbB-1/epidermal growth factor-receptor gene and is amplified in a human salivary gland adenocarcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6497–6501. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slamon D. J., Clark G. M., Wong S. G., Levin W. J., Ullrich A., McGuire W. L. Human breast cancer: correlation of relapse and survival with amplification of the HER-2/neu oncogene. Science. 1987 Jan 9;235(4785):177–182. doi: 10.1126/science.3798106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soomro S., Shousha S., Taylor P., Shepard H. M., Feldmann M. c-erbB-2 expression in different histological types of invasive breast carcinoma. J Clin Pathol. 1991 Mar;44(3):211–214. doi: 10.1136/jcp.44.3.211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Styles J. M., Harrison S., Gusterson B. A., Dean C. J. Rat monoclonal antibodies to the external domain of the product of the C-erbB-2 proto-oncogene. Int J Cancer. 1990 Feb 15;45(2):320–324. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910450219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venter D. J., Tuzi N. L., Kumar S., Gullick W. J. Overexpression of the c-erbB-2 oncoprotein in human breast carcinomas: immunohistological assessment correlates with gene amplification. Lancet. 1987 Jul 11;2(8550):69–72. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)92736-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright C., Angus B., Nicholson S., Sainsbury J. R., Cairns J., Gullick W. J., Kelly P., Harris A. L., Horne C. H. Expression of c-erbB-2 oncoprotein: a prognostic indicator in human breast cancer. Cancer Res. 1989 Apr 15;49(8):2087–2090. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Ikawa S., Akiyama T., Semba K., Nomura N., Miyajima N., Saito T., Toyoshima K. Similarity of protein encoded by the human c-erb-B-2 gene to epidermal growth factor receptor. Nature. 1986 Jan 16;319(6050):230–234. doi: 10.1038/319230a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokota J., Yamamoto T., Toyoshima K., Terada M., Sugimura T., Battifora H., Cline M. J. Amplification of c-erbB-2 oncogene in human adenocarcinomas in vivo. Lancet. 1986 Apr 5;1(8484):765–767. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)91782-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeillinger R., Kury F., Czerwenka K., Kubista E., Sliutz G., Knogler W., Huber J., Zielinski C., Reiner G., Jakesz R. HER-2 amplification, steroid receptors and epidermal growth factor receptor in primary breast cancer. Oncogene. 1989 Jan;4(1):109–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou D., Battifora H., Yokota J., Yamamoto T., Cline M. J. Association of multiple copies of the c-erbB-2 oncogene with spread of breast cancer. Cancer Res. 1987 Nov 15;47(22):6123–6125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Vijver M. J., Peterse J. L., Mooi W. J., Wisman P., Lomans J., Dalesio O., Nusse R. Neu-protein overexpression in breast cancer. Association with comedo-type ductal carcinoma in situ and limited prognostic value in stage II breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 1988 Nov 10;319(19):1239–1245. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198811103191902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Vijver M., van de Bersselaar R., Devilee P., Cornelisse C., Peterse J., Nusse R. Amplification of the neu (c-erbB-2) oncogene in human mammmary tumors is relatively frequent and is often accompanied by amplification of the linked c-erbA oncogene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):2019–2023. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.2019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]