Abstract
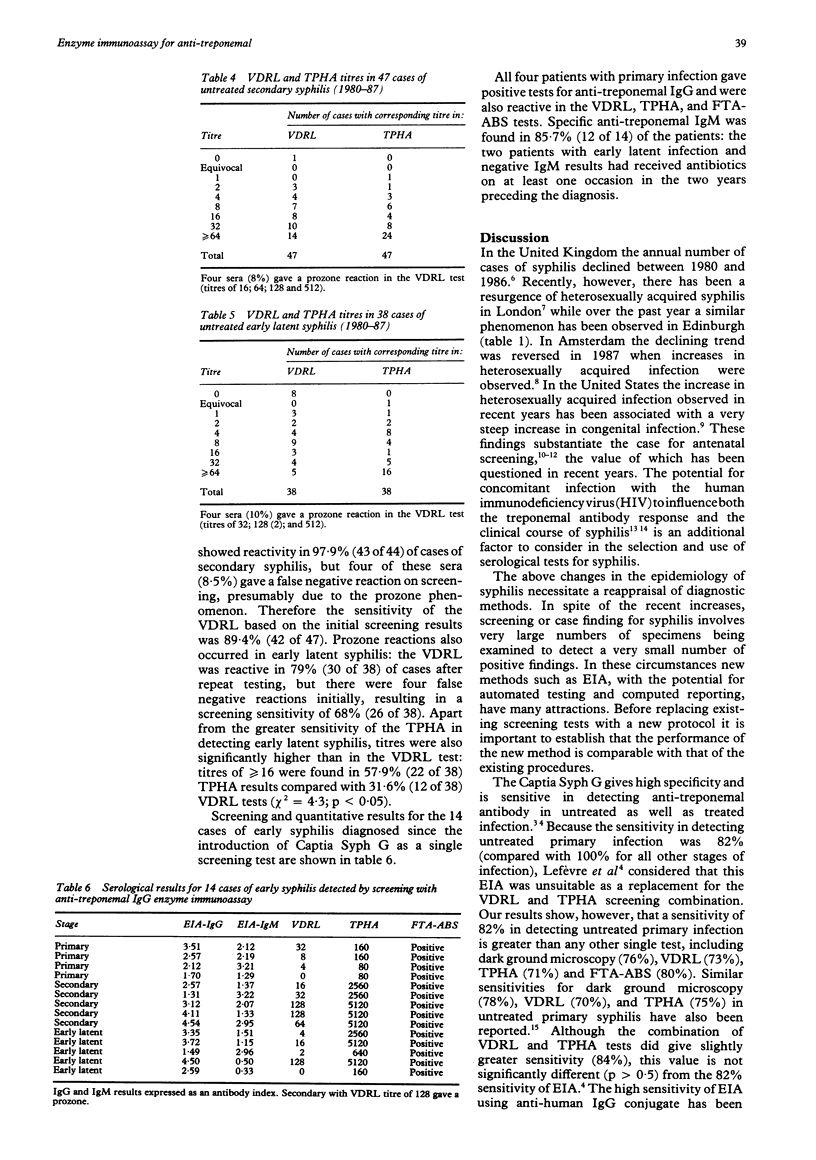
AIMS: To review the performance of the Venereal Diseases Research Laboratory (VDRL) test and the Treponema pallidum haemagglutination assay (TPHA) as a combined screen for syphilis to provide a baseline for assessing screening by anti-treponemal IGG EIA. METHODS: Between 1980 and 1987 all serum samples were screened by both VDRL and TPHA tests. The FTA-ABS test was also used in suspected early primary syphilis, or when one of the other tests was positive. A positive result in a screening test was confirmed by quantitative testing. From 1988 all specimens were screened with an enzyme immunoassay (Captia Syph G) as a single screening test. RESULTS: Of the 44 primary, 47 secondary, and 38 early latent cases of syphilis, the VDRL and TPHA detected 32 (73%) and 31 (71%) of the primary cases; the combination detected 37 (84%). All 85 cases of cases of secondary and early latent infection were reactive in the TPHA test, whereas the VDRL was reactive in only 68 (80%). EIA had a reported sensitivity of 82% for primary infection. CONCLUSIONS: EIA can be used as a single screening test for detecting early syphilis because its results are comparable with those of the combined VDRL and TPHA tests. The conventional VDRL test should not be used as a single screening test.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson J., Mindel A., Tovey S. J., Williams P. Primary and secondary syphilis, 20 years' experience. 3: Diagnosis, treatment, and follow up. Genitourin Med. 1989 Aug;65(4):239–243. doi: 10.1136/sti.65.4.239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker-Zander S. A., Hook E. W., 3rd, Bonin P., Handsfield H. H., Lukehart S. A. Antigens of Treponema pallidum recognized by IgG and IgM antibodies during syphilis in humans. J Infect Dis. 1985 Feb;151(2):264–272. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.2.264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkowitz K., Baxi L., Fox H. E. False-negative syphilis screening: the prozone phenomenon, nonimmune hydrops, and diagnosis of syphilis during pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1990 Sep;163(3):975–977. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(90)91107-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farshy C. E., Hunter E. F., Larsen S. A., Cerny E. H. Double-conjugate enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for immunoglobulins G and M against Treponema pallidum. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Dec;20(6):1109–1113. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.6.1109-1113.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feraru E. R., Aronow H. A., Lipton R. B. Neurosyphilis in AIDS patients: initial CSF VDRL may be negative. Neurology. 1990 Mar;40(3 Pt 1):541–543. doi: 10.1212/wnl.40.3_part_1.541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garland S. M., Kelly V. N. Is antenatal screening for syphilis worth while? Med J Aust. 1989 Oct 2;151(7):368–372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert G. L. Congenital syphilis--should we worry? Med J Aust. 1988 Feb 15;148(4):162–164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hicks C. B., Benson P. M., Lupton G. P., Tramont E. C. Seronegative secondary syphilis in a patient infected with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) with Kaposi sarcoma. A diagnostic dilemma. Ann Intern Med. 1987 Oct;107(4):492–495. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-107-4-492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rufli T. Syphilis and HIV infection. Dermatologica. 1989;179(3):113–117. doi: 10.1159/000248335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPANGLER A. S., JACKSON J. H., FIUMARA N. J., WARTHIN T. A. SYPHILIS WITH A NEGATIVE BLOOD TEST REACTION. JAMA. 1964 Jul 13;189:87–90. doi: 10.1001/jama.1964.03070020015003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens R. W., Schmitt M. E. Evaluation of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for treponemal antibody. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Mar;21(3):399–402. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.3.399-402.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang A., Barlow D. Resurgence of heterosexually acquired early syphilis in London. Lancet. 1989 Jul 15;2(8655):166–167. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90232-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veldkamp J., Visser A. M. Application of the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) in the serodiagnosis of syphilis. Br J Vener Dis. 1975 Aug;51(4):227–231. doi: 10.1136/sti.51.4.227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young H., Henrichsen C., Robertson D. H. Treponema pallidum haemagglutination test as a screening procedure for the diagnosis of syphilis. Br J Vener Dis. 1974 Oct;50(5):341–346. doi: 10.1136/sti.50.5.341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young H., Moyes A., McMillan A., Robertson D. H. Screening for treponemal infection by a new enzyme immunoassay. Genitourin Med. 1989 Apr;65(2):72–78. doi: 10.1136/sti.65.2.72. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Hoek J. A., van der Linden M. M., Coutinho R. A. Increase of infectious syphilis among heterosexuals in Amsterdam: its relationship to drug use and prostitution. Genitourin Med. 1990 Feb;66(1):31–32. doi: 10.1136/sti.66.1.31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


