Abstract
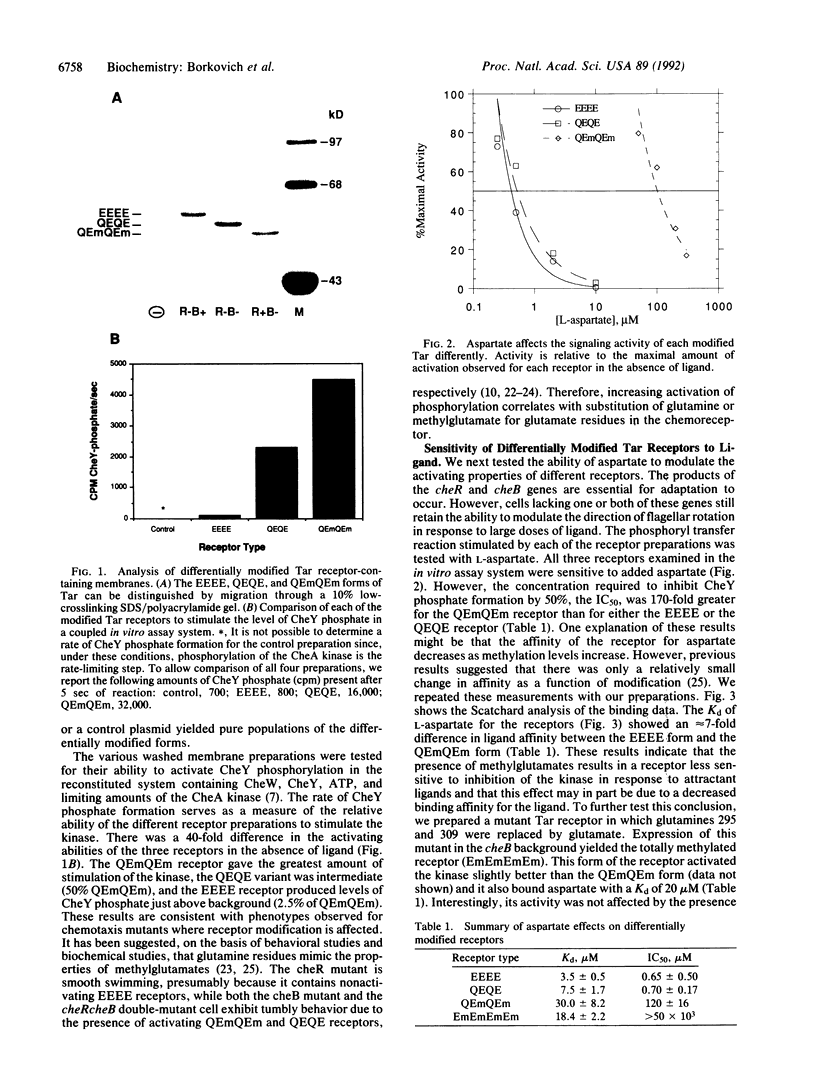
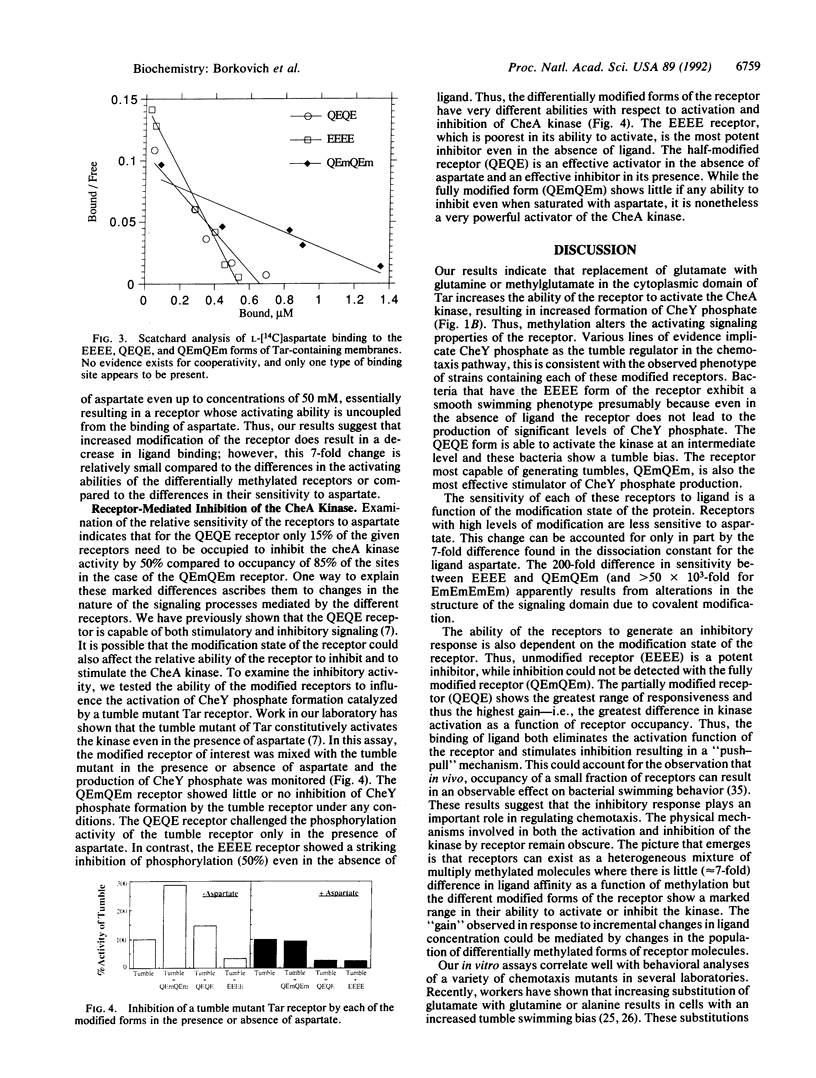
The Tar receptor is a transmembrane protein that regulates bacterial chemotaxis in response to changes in the level of aspartic acid in the medium. The extracellular portion of the protein can bind aspartate, and the cytoplasmic portion modulates CheA kinase activity. The receptor can either activate or inhibit the kinase. The cytoplasmic portion of the receptor can be modified by carboxymethylation of specific glutamic acid residues. To test the effects of differential methylation on receptor function, we prepared membranes from cells that have specifically modified forms of the receptor and tested the relative ability of each of these forms to activate or inhibit CheA kinase. Completely demethylated receptor was a potent inhibitor and poor activator of the kinase, while the fully modified receptor was an excellent activator but an inefficient inhibitor. Partially modified receptor could act both as an effective inhibitor and as an activator. Reversible modification provides a mechanism that allows the cell to accumulate a population of receptor molecules capable of generating a wide range of signaling intensities.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berg H. C., Brown D. A. Chemotaxis in Escherichia coli analysed by three-dimensional tracking. Nature. 1972 Oct 27;239(5374):500–504. doi: 10.1038/239500a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Block S. M., Segall J. E., Berg H. C. Impulse responses in bacterial chemotaxis. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):215–226. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90421-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borkovich K. A., Kaplan N., Hess J. F., Simon M. I. Transmembrane signal transduction in bacterial chemotaxis involves ligand-dependent activation of phosphate group transfer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(4):1208–1212. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.4.1208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borkovich K. A., Simon M. I. The dynamics of protein phosphorylation in bacterial chemotaxis. Cell. 1990 Dec 21;63(6):1339–1348. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90429-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourret R. B., Borkovich K. A., Simon M. I. Signal transduction pathways involving protein phosphorylation in prokaryotes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:401–441. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.002153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourret R. B., Hess J. F., Simon M. I. Conserved aspartate residues and phosphorylation in signal transduction by the chemotaxis protein CheY. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(1):41–45. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.1.41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd A., Simon M. I. Multiple electrophoretic forms of methyl-accepting chemotaxis proteins generated by stimulus-elicited methylation in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;143(2):809–815. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.2.809-815.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke S., Koshland D. E., Jr Membrane receptors for aspartate and serine in bacterial chemotaxis. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 10;254(19):9695–9702. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunten P., Koshland D. E., Jr Tuning the responsiveness of a sensory receptor via covalent modification. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 25;266(3):1491–1496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goy M. F., Springer M. S., Adler J. Failure of sensory adaptation in bacterial mutants that are defective in a protein methylation reaction. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1231–1240. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90049-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goy M. F., Springer M. S., Adler J. Sensory transduction in Escherichia coli: role of a protein methylation reaction in sensory adaptation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4964–4968. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess J. F., Oosawa K., Kaplan N., Simon M. I. Phosphorylation of three proteins in the signaling pathway of bacterial chemotaxis. Cell. 1988 Apr 8;53(1):79–87. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90489-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess J. F., Oosawa K., Matsumura P., Simon M. I. Protein phosphorylation is involved in bacterial chemotaxis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7609–7613. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imae Y., Mizuno T., Maeda K. Chemosensory and thermosensory excitation in adaptation-deficient mutants of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jul;159(1):368–374. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.1.368-374.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kehry M. R., Bond M. W., Hunkapiller M. W., Dahlquist F. W. Enzymatic deamidation of methyl-accepting chemotaxis proteins in Escherichia coli catalyzed by the cheB gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3599–3603. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kehry M. R., Dahlquist F. W. Adaptation in bacterial chemotaxis: CheB-dependent modification permits additional methylations of sensory transducer proteins. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):761–772. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90438-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krikos A., Mutoh N., Boyd A., Simon M. I. Sensory transducers of E. coli are composed of discrete structural and functional domains. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):615–622. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90442-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milburn M. V., Privé G. G., Milligan D. L., Scott W. G., Yeh J., Jancarik J., Koshland D. E., Jr, Kim S. H. Three-dimensional structures of the ligand-binding domain of the bacterial aspartate receptor with and without a ligand. Science. 1991 Nov 29;254(5036):1342–1347. doi: 10.1126/science.1660187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan D. L., Koshland D. E., Jr Site-directed cross-linking. Establishing the dimeric structure of the aspartate receptor of bacterial chemotaxis. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 5;263(13):6268–6275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park C., Dutton D. P., Hazelbauer G. L. Effects of glutamines and glutamates at sites of covalent modification of a methyl-accepting transducer. J Bacteriol. 1990 Dec;172(12):7179–7187. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.12.7179-7187.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson J. S., Houts S. E. Isolation and behavior of Escherichia coli deletion mutants lacking chemotaxis functions. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jul;151(1):106–113. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.1.106-113.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson J. S., Revello P. T. Sensory adaptation mutants of E. coli. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1221–1230. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90048-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segall J. E., Block S. M., Berg H. C. Temporal comparisons in bacterial chemotaxis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):8987–8991. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.8987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer M. S., Goy M. F., Adler J. Protein methylation in behavioural control mechanisms and in signal transduction. Nature. 1979 Jul 26;280(5720):279–284. doi: 10.1038/280279a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer W. R., Koshland D. E., Jr Identification of a protein methyltransferase as the cheR gene product in the bacterial sensing system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):533–537. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart R. C., Roth A. F., Dahlquist F. W. Mutations that affect control of the methylesterase activity of CheB, a component of the chemotaxis adaptation system in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jun;172(6):3388–3399. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.6.3388-3399.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stock A. M., Wylie D. C., Mottonen J. M., Lupas A. N., Ninfa E. G., Ninfa A. J., Schutt C. E., Stock J. B. Phosphoproteins involved in bacterial signal transduction. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1988;53(Pt 1):49–57. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1988.053.01.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stock J. B., Koshland D. E., Jr A protein methylesterase involved in bacterial sensing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3659–3663. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stock J. B., Maderis A. M., Koshland D. E., Jr Bacterial chemotaxis in the absence of receptor carboxylmethylation. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):37–44. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90358-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stock J., Kersulis G., Koshland D. E., Jr Neither methylating nor demethylating enzymes are required for bacterial chemotaxis. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):683–690. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90125-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe A. J., Conley M. P., Berg H. C. Acetyladenylate plays a role in controlling the direction of flagellar rotation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6711–6715. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





