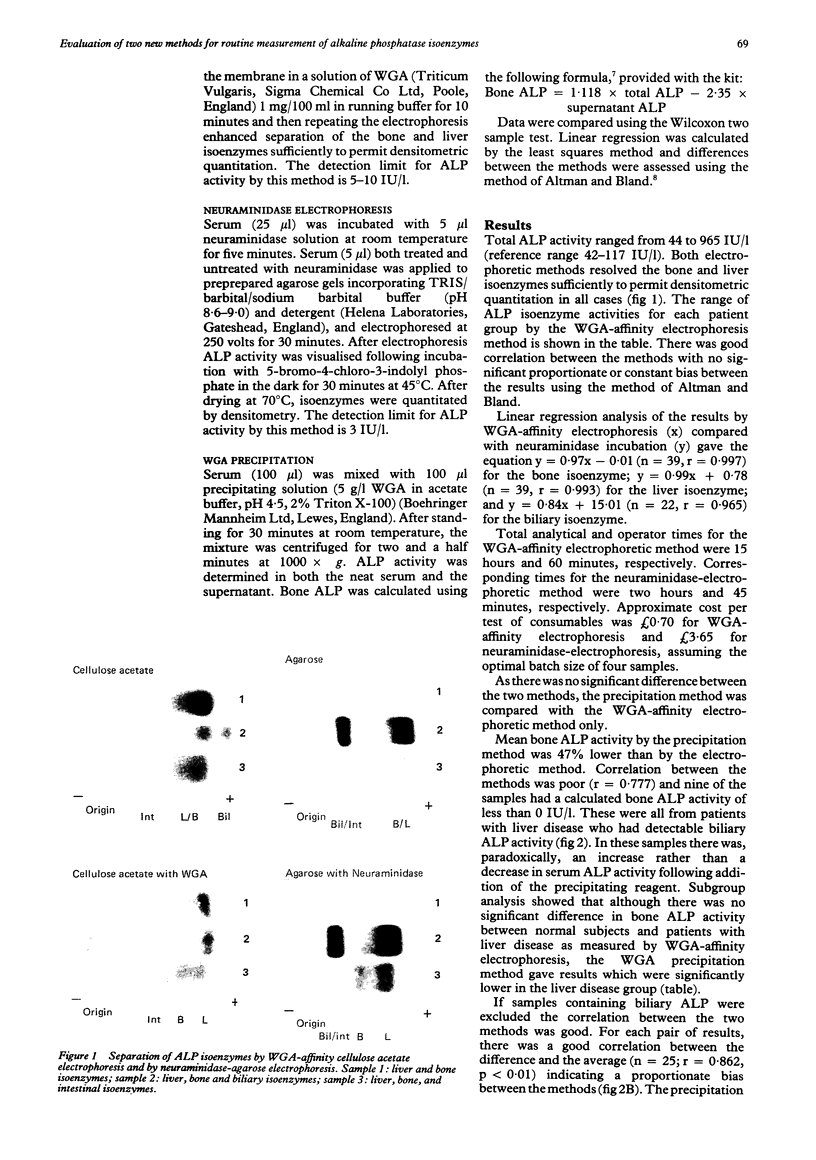
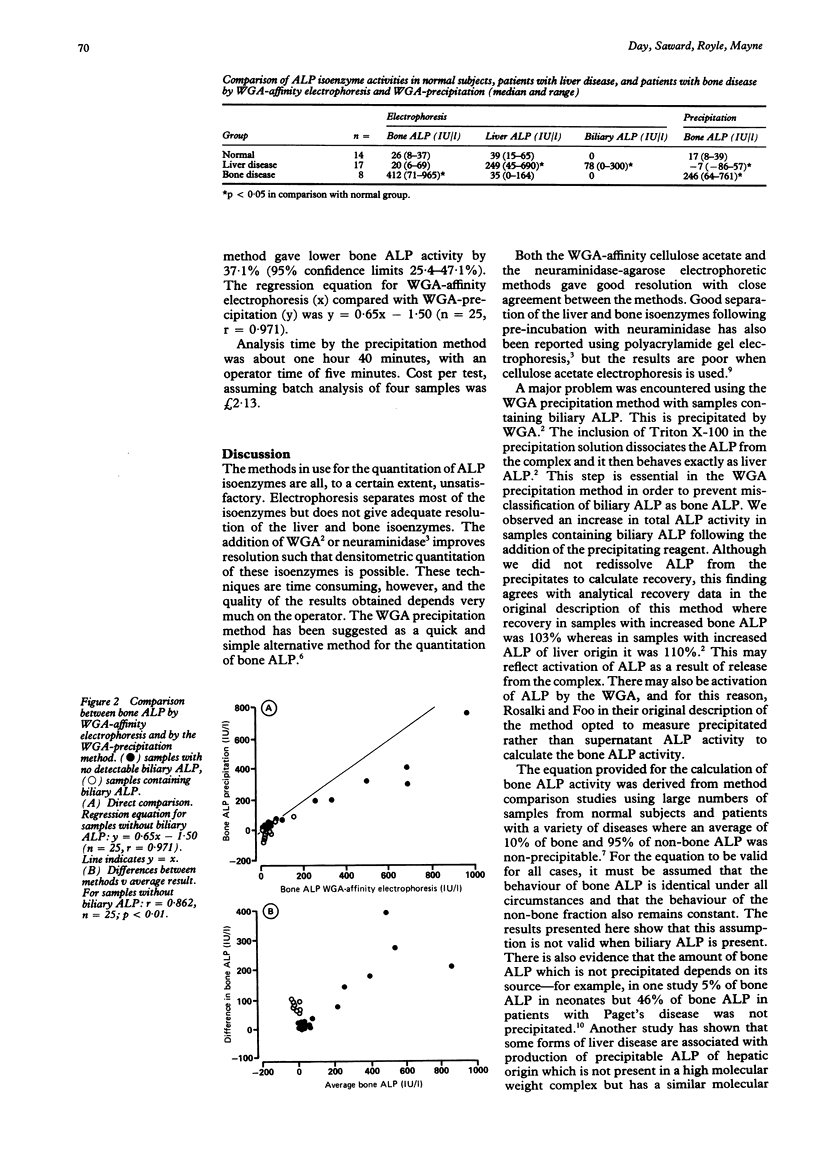
Abstract
AIMS: To evaluate the performance of two new methods for the analysis of alkaline phosphatase (ALP) isoenzymes designed for use in the routine chemical pathology laboratory: pre-incubation with neuraminidase before agarose electrophoresis; and selective precipitation of the bone isoenzyme with wheat germ agglutinin (WGA). METHODS: Serum samples from 39 patients were analysed. Seventeen were from patients with liver disease, eight from patients with bone disease, and 14 from patients with normal ALP activity and no evidence of liver or bone disease. The two new methods were compared with the established method, wheat germ agglutinin affinity electrophoresis. RESULTS: There was good correlation between the neuraminidase and WGA electrophoretic methods. The WGA precipitation method showed negative interference in the measurement of bone isoenzyme activity in samples containing biliary alkaline phosphatase. Both the new methods had advantages of speed and simplicity over the existing method, but cost per test was considerably higher. CONCLUSIONS: The neuraminidase electrophoretic method is a satisfactory alternative to the WGA affinity electrophoretic method, although it is more expensive. The WGA precipitation method cannot be recommended for use with serum samples from patients with suspected liver disease.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Behr W., Barnert J. Quantification of bone alkaline phosphatase in serum by precipitation with wheat-germ lectin: a simplified method and its clinical plausibility. Clin Chem. 1986 Oct;32(10):1960–1966. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koyama I., Sakagishi Y., Komoda T. Different lectin affinities in rat alkaline phosphatase isozymes: multiple forms of the isozyme isolated by heterogeneities of sugar moieties. J Chromatogr. 1986 Jan 10;374(1):51–59. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)83252-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massoubre C., Verdier P., Meflah K., Masliah C., Perrin D., Orsonneau J. L., Harb J. Lectin binding to serum 5'-nucleotidase and alkaline phosphatase in liver disease. Clin Chim Acta. 1990 Oct 31;191(1-2):87–92. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(90)90061-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miura M., Matsuzaki H. Evaluation of a new method for separating bone-type alkaline phosphatase. Ann Clin Biochem. 1990 Sep;27(Pt 5):501–502. doi: 10.1177/000456329002700516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss D. W. Alkaline phosphatase isoenzymes. Clin Chem. 1982 Oct;28(10):2007–2016. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss D. W., Edwards R. K. Improved electrophoretic resolution of bone and liver alkaline phosphatases resulting from partial digestion with neuraminidase. Clin Chim Acta. 1984 Nov 15;143(2):177–182. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(84)90227-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosalki S. B., Foo A. Y. Incubation with neuraminidase and affinity electrophoresis with wheat-germ lectin compared for separating and quantifying alkaline phosphatase isoenzymes in plasma. Clin Chem. 1985 Jul;31(7):1198–1200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Hoof V. O., Lepoutre L. G., Hoylaerts M. F., Chevigné R., De Broe M. E. Improved agarose electrophoretic method for separating alkaline phosphatase isoenzymes in serum. Clin Chem. 1988 Sep;34(9):1857–1862. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]