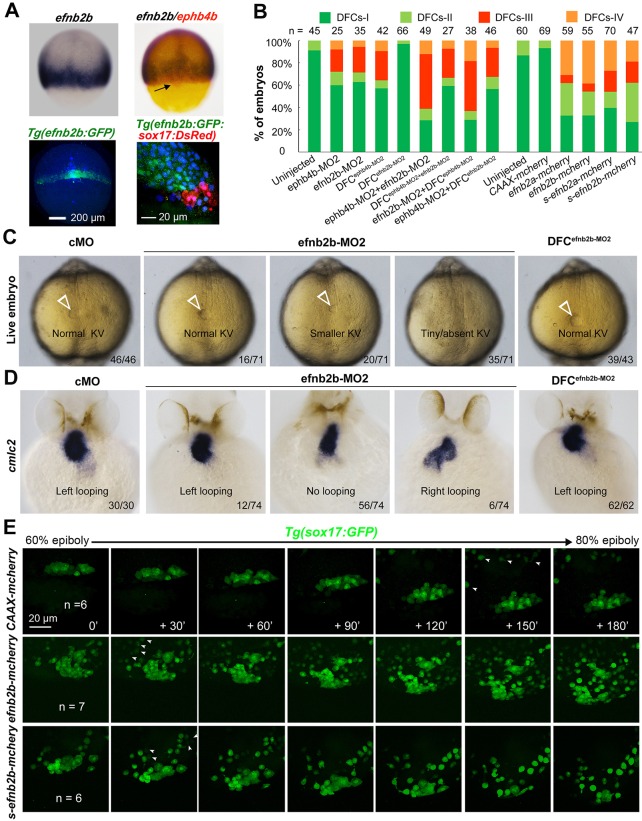
Fig. 5.
efnb2b expression outside DFCs is required for DFC aggregation, KV formation and laterality development. (A) efnb2b is not expressed in DFCs. Top panels: efnb2b (black)/ephb4b (red) in situ patterns with DFCs indicated (arrow) at 75% ES; bottom panels: Tg(efnb2b:GFP) embryo expressing GFP in the blastodermal margin at shield stage (left panel; dorsal view), and GFP+ mesoderm precursors located next to DsRed+ DFCs in Tg(efnb2b:GFP;sox17:DsRed) embryo at 75% ES (right panel: lateral view). (B) efnb2b knockdown in the whole embryo caused disaggregation of DFCs. Wild-type embryos were injected at the one-cell or 512-cell stage (DFCX) and probed at midgastrulation stages for sox17 expression by in situ hybridization. The distribution patterns of DFCs were categorized as shown in Fig. 3N. (C,D) Effect of efnb2b knockdown on KV at 10 SS (C) and on cmlc2-labeled heart looping at 48 hpf (D). Arrowheads indicate the KV. Proportion of embryos exhibiting each phenotype is indicated. (E) Time-lapse observation of DFC migration during gastrulation in living embryos. Tg(sox17:GFP) embryos injected with the indicated mRNA at the one-cell stage were dynamically observed by confocal microscopy starting at 60% ES. Arrowheads indicate GFP-positive endoderm progenitors. The relative time points are indicated. Embryos were orientated with anterior to the top. n, number of observed embryos. See also Movies 5-7.