Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CAVANAGH J. B. ORGANO-PHOSPHORUS NEUROTOXICITY: A MODEL "DYING BACK" PROCESS COMPARABLE TO CERTAIN HUMAN NEUROLOGICAL DISORDERS. Guys Hosp Rep. 1963;112:303–319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAVANAGH J. B., PASSINGHAM R. J., VOGT J. A. STAINING OF SENSORY AND MOTOR NERVES IN MUSCLES WITH SUDAN BLACK B. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1964 Jul;88:89–92. doi: 10.1002/path.1700880111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE MATTEIS F., RIMINGTON C. The biochemical disturbance in acute intermittent and experimental porphyria. Lancet. 1962 Jun 23;1(7243):1332–1334. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(62)92427-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DRURY R. A. A nerve biopsy in acute intermittent porphyria. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1956 Apr;71(2):511–511. doi: 10.1002/path.1700710223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
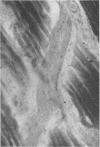
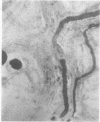
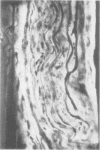
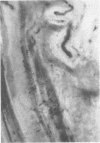
- GIBSON J. B., GOLDBERG A. The neuropathology of acute porphyria. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1956 Apr;71(2):495–509. doi: 10.1002/path.1700710222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDBERG A. Acute intermittent porphyria: a study of 50 cases. Q J Med. 1959 Apr;28(110):183–209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIERONS R. Changes in the nervous system in acute porphyria. Brain. 1957 Jun;80(2):176–192. doi: 10.1093/brain/80.2.176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]