Abstract
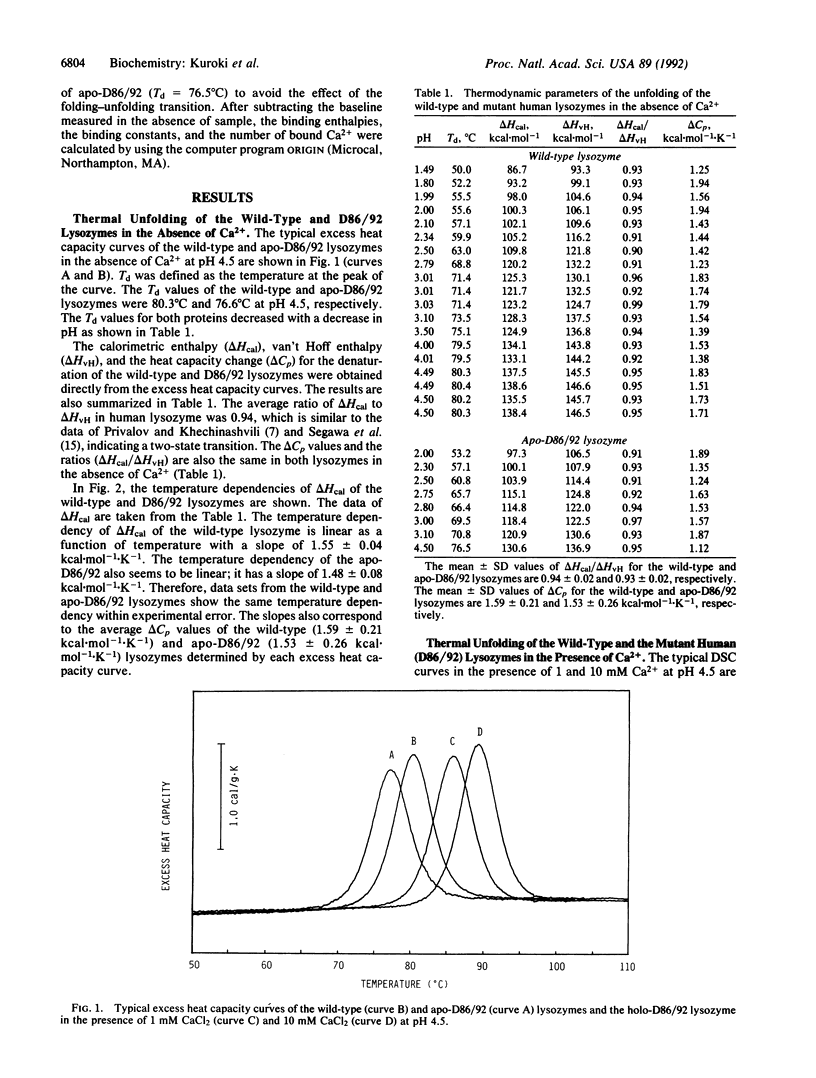
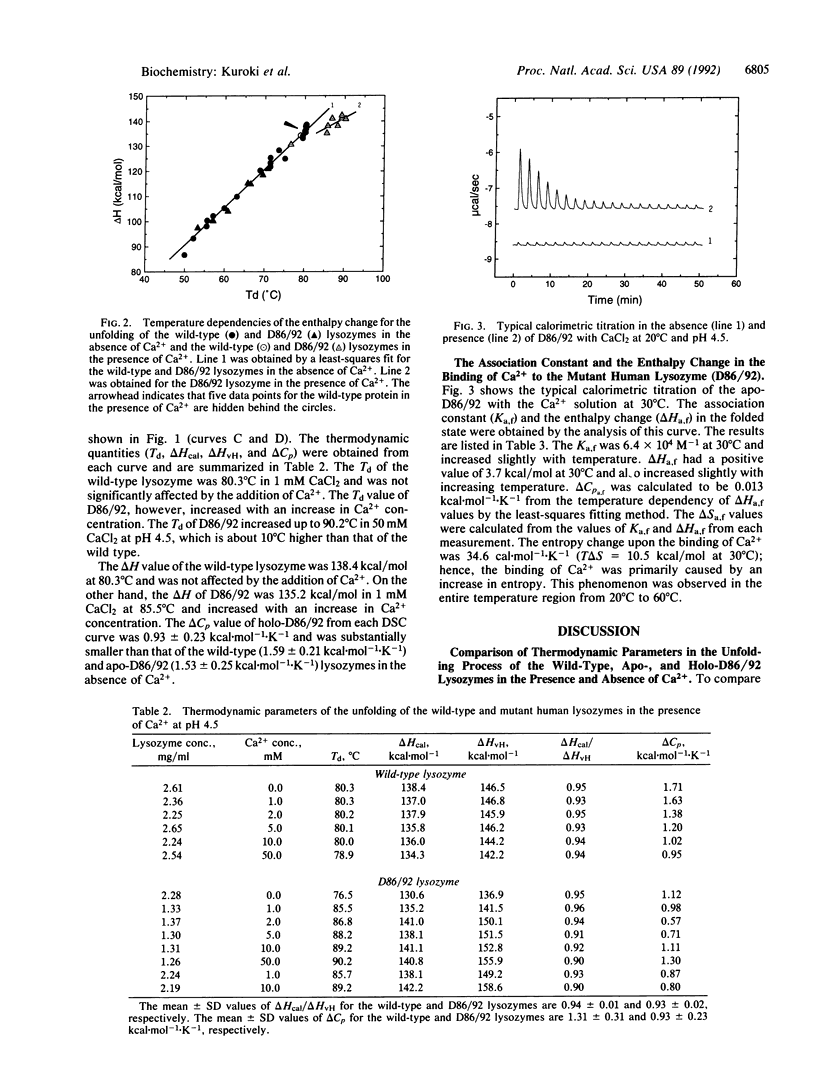
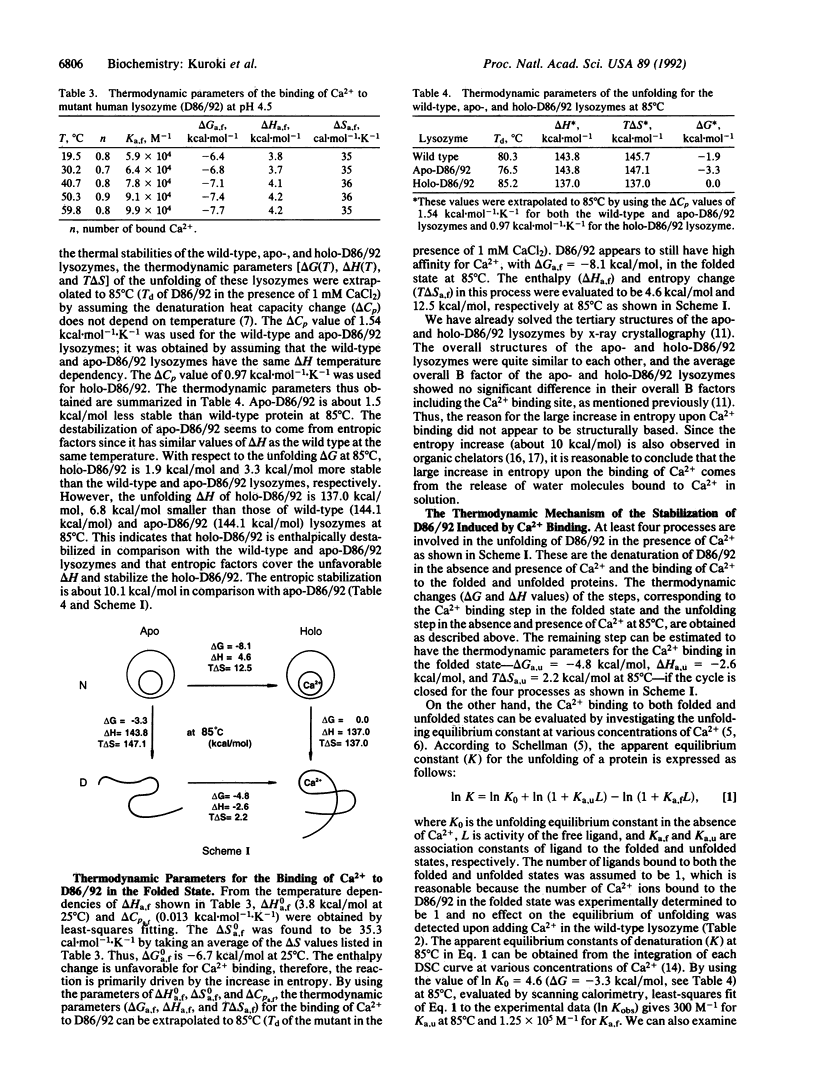
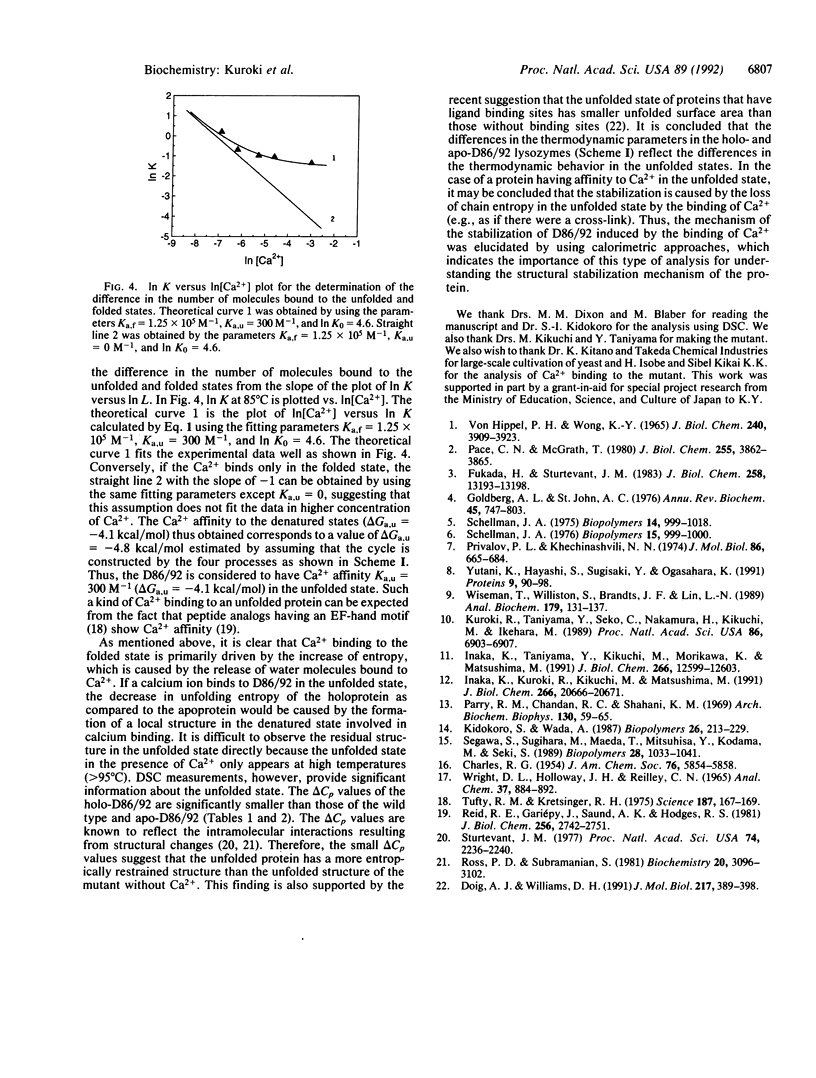
The stabilization mechanism of the mutant human lysozyme with a calcium binding site (D86/92) was investigated by using calorimetric approaches. By differential scanning calorimetry, the enthalpy change (delta H) in the unfolding of holo-D86/92 was found to be 6.8 kcal/mol smaller than that of the wild-type and apo-D86/92 lysozymes at 85 degrees C. However, the unfolding Gibbs energy change (delta G) of the holo mutant was 3.3 kcal/mol greater than the apo type at 85 degrees C, indicating a significant decrease of entropy (T delta S = 10.1 kcal/mol) in the presence of Ca2+. Subsequently, the Ca2+ binding process in the folded state of the mutant was analyzed by using titration isothermal calorimetry. The binding enthalpy change was estimated to be 4.5 kcal/mol, and delta G was -8.1 kcal/mol at 85 degrees C, which indicates that the binding was caused by a large increase in entropy (T delta S = 12.6 kcal/mol). From these analyses, the unfolded holo mutant was determined to bind Ca2+ with a binding delta G of -4.8 kcal/mol (delta H = -2.6 kcal/mol, T delta S = 2.2 kcal/mol) at 85 degrees C. Therefore, the major cause of stabilization of holo-D86/92 is the decrease in entropy of the peptide chain due to Ca2+ binding to the unfolded protein.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Doig A. J., Williams D. H. Is the hydrophobic effect stabilizing or destabilizing in proteins? The contribution of disulphide bonds to protein stability. J Mol Biol. 1991 Jan 20;217(2):389–398. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90551-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukada H., Sturtevant J. M., Quiocho F. A. Thermodynamics of the binding of L-arabinose and of D-galactose to the L-arabinose-binding protein of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 10;258(21):13193–13198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg A. L., St John A. C. Intracellular protein degradation in mammalian and bacterial cells: Part 2. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:747–803. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.003531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inaka K., Kuroki R., Kikuchi M., Matsushima M. Crystal structures of the apo- and holomutant human lysozymes with an introduced Ca2+ binding site. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 5;266(31):20666–20671. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inaka K., Taniyama Y., Kikuchi M., Morikawa K., Matsushima M. The crystal structure of a mutant human lysozyme C77/95A with increased secretion efficiency in yeast. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 5;266(19):12599–12603. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuroki R., Taniyama Y., Seko C., Nakamura H., Kikuchi M., Ikehara M. Design and creation of a Ca2+ binding site in human lysozyme to enhance structural stability. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):6903–6907. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.6903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pace C. N., McGrath T. Substrate stabilization of lysozyme to thermal and guanidine hydrochloride denaturation. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 10;255(9):3862–3865. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parry R. M., Jr, Chandan R. C., Shahani K. M. Isolation and characterization of human milk lysozyme. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Mar;130(1):59–65. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90009-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Privalov P. L., Khechinashvili N. N. A thermodynamic approach to the problem of stabilization of globular protein structure: a calorimetric study. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jul 5;86(3):665–684. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90188-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid R. E., Gariépy J., Saund A. K., Hodges R. S. Calcium-induced protein folding. Structure-affinity relationships in synthetic analogs of the helix-loop-helix calcium binding unit. J Biol Chem. 1981 Mar 25;256(6):2742–2751. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross P. D., Subramanian S. Thermodynamics of protein association reactions: forces contributing to stability. Biochemistry. 1981 May 26;20(11):3096–3102. doi: 10.1021/bi00514a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segawa S., Sugihara M., Maeda T., Mitsuhisa Y., Kodama M., Seki S., Sakiyama M. Calorimetric study of the effect of intrachain cross-linking on lysozyme unfolding. Biopolymers. 1989 Jun;28(6):1033–1041. doi: 10.1002/bip.360280602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturtevant J. M. Heat capacity and entropy changes in processes involving proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jun;74(6):2236–2240. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.6.2236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tufty R. M., Kretsinger R. H. Troponin and parvalbumin calcium binding regions predicted in myosin light chain and T4 lysozyme. Science. 1975 Jan 17;187(4172):167–169. doi: 10.1126/science.1111094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Von Hippel P. H., Wong K. Y. On the conformational stability of globular proteins. The effects of various electrolytes and nonelectrolytes on the thermal ribonuclease transition. J Biol Chem. 1965 Oct;240(10):3909–3923. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiseman T., Williston S., Brandts J. F., Lin L. N. Rapid measurement of binding constants and heats of binding using a new titration calorimeter. Anal Biochem. 1989 May 15;179(1):131–137. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90213-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yutani K., Hayashi S., Sugisaki Y., Ogasahara K. Role of conserved proline residues in stabilizing tryptophan synthase alpha subunit: analysis by mutants with alanine or glycine. Proteins. 1991;9(2):90–98. doi: 10.1002/prot.340090203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


