Abstract
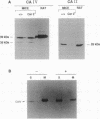
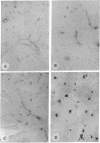
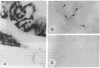
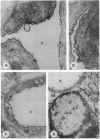
Carbonic anhydrase (CA) activity plays an important role in controlling cerebrospinal fluid production and also influences neuroexcitation and susceptibility to seizures. Until recently, CA II was the only CA demonstrated in brain. Its distribution is limited to the epithelial cells of the choroid plexus and to the myelin-forming cells, the oligodendrocytes. In this report, we present immunoblots, using an antibody raised to CA IV from rat lung, that show that CA IV is also present in rat and mouse brain. Results of immunohistochemistry and immunoelectron microscopy on sections from rat and mouse brain are presented that show the distribution of CA IV to be quite distinct from that of CA II. CA IV is expressed on and is limited to the luminal surface of endothelial cells of cerebral capillaries. These results establish CA IV as a cytochemical marker associated with the blood-brain barrier and suggest an important role for CA IV in CO2 and HCO3- homeostasis in brain.
Full text
PDF


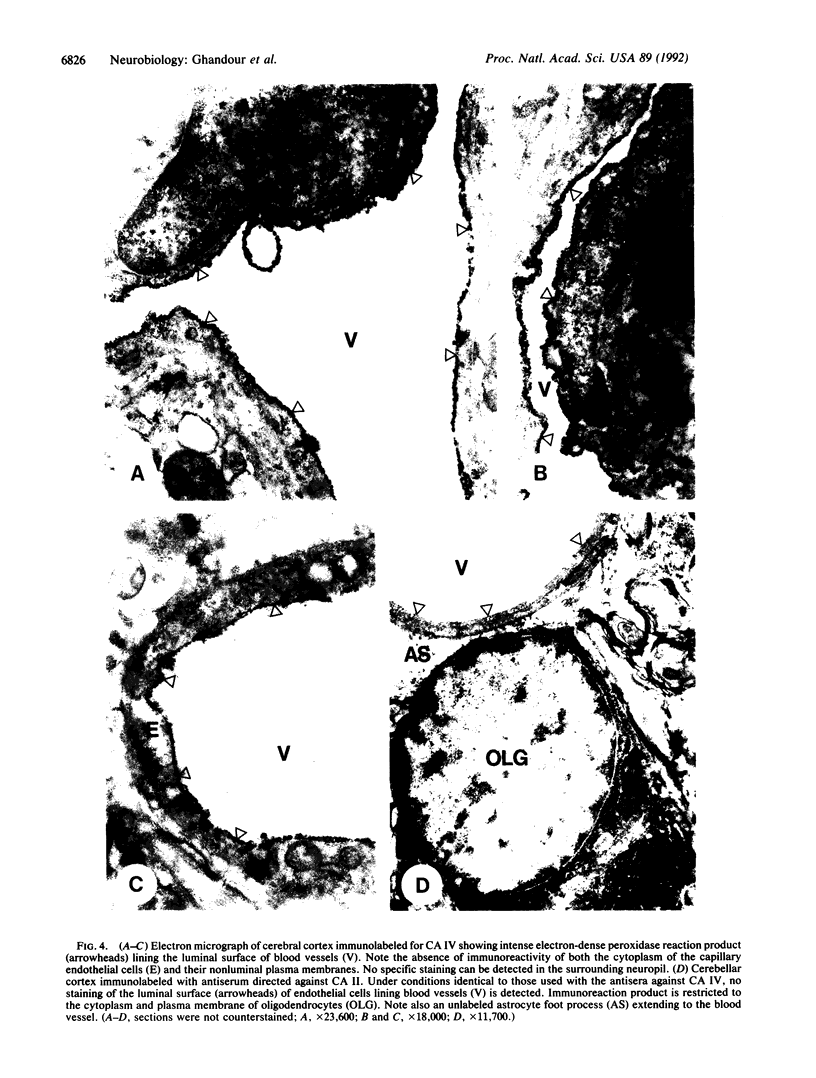

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Betz A. L. Epithelial properties of brain capillary endothelium. Fed Proc. 1985 Jul;44(10):2614–2615. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bidani A., Crandall E. D. Velocity of CO2 exchanges in the lungs. Annu Rev Physiol. 1988;50:639–652. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.50.030188.003231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D., Zhu X. L., Sly W. S. Localization of membrane-associated carbonic anhydrase type IV in kidney epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7457–7461. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell P. R., Seegal B. C., Hsu K. C., Das M., Soffer R. L. Angiotensin-converting enzyme: vascular endothelial localization. Science. 1976 Mar 12;191(4231):1050–1051. doi: 10.1126/science.175444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cammer W., Sacchi R., Sapirstein V. Immunocytochemical localization of carbonic anhydrase in the spinal cords of normal and mutant (shiverer) adult mice with comparisons among fixation methods. J Histochem Cytochem. 1985 Jan;33(1):45–54. doi: 10.1177/33.1.3917467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crandall E. D., O'Brasky J. E. Direct evidence of participation of rat lung carbonic anhydrase in CO2 reactions. J Clin Invest. 1978 Sep;62(3):618–622. doi: 10.1172/JCI109168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crone C., Olesen S. P. Electrical resistance of brain microvascular endothelium. Brain Res. 1982 Jun 3;241(1):49–55. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)91227-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeBault L. E., Cancilla P. A. gamma-Glutamyl transpeptidase in isolated brain endothelial cells: induction by glial cells in vitro. Science. 1980 Feb 8;207(4431):653–655. doi: 10.1126/science.6101511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Effros R. M., Shapiro L., Silverman P. Carbonic anhydrase activity of rabbit lungs. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1980 Oct;49(4):589–600. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1980.49.4.589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filippi D., Sciaky M., Limozin N., Laurent G. Anhydrase carbonique du système nerveux central dur rat. Isolement et propriétés. Biochimie. 1978;60(1):99–102. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(78)80206-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghandour M. S., Langley O. K., Varga V. Immunohistological localization of gamma-glutamyltranspeptidase in cerebellum at light and electron microscope levels. Neurosci Lett. 1980 Nov;20(2):125–129. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(80)90133-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghandour M. S., Langley O. K., Vincendon G., Gombos G. Double labeling immunohistochemical technique provides evidence of the specificity of glial cell markers. J Histochem Cytochem. 1979 Dec;27(12):1634–1637. doi: 10.1177/27.12.118210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghandour M. S., Skoff R. P. Double-labeling in situ hybridization analysis of mRNAs for carbonic anhydrase II and myelin basic protein: expression in developing cultured glial cells. Glia. 1991;4(1):1–10. doi: 10.1002/glia.440040102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghandour M. S., Skoff R. P., Venta P. J., Tashian R. E. Oligodendrocytes express a normal phenotype in carbonic anhydrase II-deficient mice. J Neurosci Res. 1989 Jun;23(2):180–190. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490230208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghandour M. S., Vincendon G., Gombos G., Limozin N., Filippi D., Dalmasso C., Laurent G. Carbonic anhydrase and oligodendroglia in developing rat cerebellum: a biochemical and imunohistological study. Dev Biol. 1980 Jun 1;77(1):73–83. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(80)90457-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein G. W. Relation of potassium transport to oxidative metabolism in isolated brain capillaries. J Physiol. 1979 Jan;286:185–195. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D., Moran J., Braun D., Birdwell C. Clonal growth of bovine vascular endothelial cells: fibroblast growth factor as a survival agent. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):4120–4124. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.4120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griot C., Vandevelde M. Transferrin, carbonic anhydrase C and ferritin in dissociated murine brain cell cultures. J Neuroimmunol. 1988 Jul;18(4):333–340. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(88)90054-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hageman G. S., Zhu X. L., Waheed A., Sly W. S. Localization of carbonic anhydrase IV in a specific capillary bed of the human eye. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 1;88(7):2716–2720. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.7.2716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klocke R. A. Rate of bicarbonate-chloride exchange in human red cells at 37 degrees C. J Appl Physiol. 1976 May;40(5):707–714. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1976.40.5.707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumpulainen T., Korhonen L. K. Immunohistochemical localization of carbonic anhydrase isoenzyme C in the central and peripheral nervous system of the mouse. J Histochem Cytochem. 1982 Apr;30(4):283–292. doi: 10.1177/30.4.6801110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumpulainen T., Nyström S. H. Immunohistochemical localization of carbonic anhydrase isoenzyme C in human brain. Brain Res. 1981 Sep 7;220(1):220–225. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90230-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langley O. K., Aunis D. Ultrastructural immunocytochemical demonstration of D2-protein in adrenal medulla. Cell Tissue Res. 1984;238(3):497–502. doi: 10.1007/BF00219864. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lisanti M. P., Caras I. W., Davitz M. A., Rodriguez-Boulan E. A glycophospholipid membrane anchor acts as an apical targeting signal in polarized epithelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;109(5):2145–2156. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.5.2145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lönnerholm G. Pulmonary carbonic anhydrase in the human, monkey, and rat. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1982 Feb;52(2):352–356. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1982.52.2.352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okuyama T., Sato S., Zhu X. L., Waheed A., Sly W. S. Human carbonic anhydrase IV: cDNA cloning, sequence comparison, and expression in COS cell membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 15;89(4):1315–1319. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.4.1315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlowski M., Sessa G., Green J. P. Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase in brain capillaries: possible site of a blood-brain barrier for amino acids. Science. 1974 Apr 5;184(4132):66–68. doi: 10.1126/science.184.4132.66. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardridge W. M., Triguero D., Buciak J. L. Beta-endorphin chimeric peptides: transport through the blood-brain barrier in vivo and cleavage of disulfide linkage by brain. Endocrinology. 1990 Feb;126(2):977–984. doi: 10.1210/endo-126-2-977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rix E., Ganten D., Schüll B., Unger T., Taugner R. Converting-enzyme in the choroid plexus, brain, and kidney: immunocytochemical and biochemical studies in rats. Neurosci Lett. 1981 Mar 10;22(2):125–130. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(81)90075-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sapirstein V. S., Strocchi P., Wesolowski M., Gilbert J. M. Characterization and biosynthesis of soluble and membrane-bound carbonic anhydrase in brain. J Neurochem. 1983 May;40(5):1251–1261. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1983.tb13563.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spicer S. S., Ge Z. H., Tashian R. E., Hazen-Martin D. J., Schulte B. A. Comparative distribution of carbonic anhydrase isozymes III and II in rodent tissues. Am J Anat. 1990 Jan;187(1):55–64. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001870107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spicer S. S., Stoward P. J., Tashian R. E. The immunohistolocalization of carbonic anhydrase in rodent tissues. J Histochem Cytochem. 1979 Apr;27(4):820–831. doi: 10.1177/27.4.109495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tashian R. E. The carbonic anhydrases: widening perspectives on their evolution, expression and function. Bioessays. 1989 Jun;10(6):186–192. doi: 10.1002/bies.950100603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tashian R. E., Venta P. J., Nicewander P. H., Hewett-Emmett D. Evolution, structure, and expression of the carbonic anhydrase multigene family. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1990;344:159–175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wade R., Gunning P., Eddy R., Shows T., Kedes L. Nucleotide sequence, tissue-specific expression, and chromosome location of human carbonic anhydrase III: the human CAIII gene is located on the same chromosome as the closely linked CAI and CAII genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9571–9575. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waheed A., Zhu X. L., Sly W. S. Membrane-associated carbonic anhydrase from rat lung. Purification, characterization, tissue distribution, and comparison with carbonic anhydrase IVs of other mammals. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 15;267(5):3308–3311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wistrand P. J., Knuuttila K. G. Renal membrane-bound carbonic anhydrase. Purification and properties. Kidney Int. 1989 Mar;35(3):851–859. doi: 10.1038/ki.1989.63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wistrand P. J. The use of carbonic anhydrase inhibitors in ophthalmology and clinical medicine. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1984;429:609–619. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1984.tb12398.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu X. L., Sly W. S. Carbonic anhydrase IV from human lung. Purification, characterization, and comparison with membrane carbonic anhydrase from human kidney. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 25;265(15):8795–8801. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]