Abstract
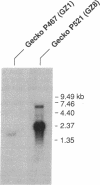
The Tokay gecko (Gekko gekko), a nocturnal lizard, has two kinds of visual pigments, P467 and P521. In spite of the pure-rod morphology of the photoreceptor cells, the biochemical properties of P521 and P467 resemble those of iodopsin (the chicken red-sensitive cone visual pigment) and rhodopsin, respectively. We have found that the amino acid sequence of P521 deduced from the cDNA was very similar to that of iodopsin. In addition, P467 has the highest homology with the chicken green-sensitive cone visual pigment, although it also has a relatively high homology with rhodopsins. These results give additional strength to the transmutation theory of Walls [Walls, G. L. (1934) Am. J. Ophthalmol. 17, 892-915], who proposed that the rod-shaped photoreceptor cells of lizards have been derived from ancestral cone-like photoreceptors. Apparently amino acid sequences of visual pigments are less changeable than the morphology of the photoreceptor cells in the course of evolution.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARDEN G. B., TANSLEY K. The electroretinogram of a diurnal gecko. J Gen Physiol. 1962 Jul;45:1145–1161. doi: 10.1085/jgp.45.6.1145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crescitelli F., Dartnall H. J., Loew E. R. The gecko visual pigments: a microspectrophotometric study. J Physiol. 1977 Jun;268(2):559–573. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dartnall H. J., Bowmaker J. K., Mollon J. D. Human visual pigments: microspectrophotometric results from the eyes of seven persons. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1983 Nov 22;220(1218):115–130. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1983.0091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldsmith T. H. Optimization, constraint, and history in the evolution of eyes. Q Rev Biol. 1990 Sep;65(3):281–322. doi: 10.1086/416840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hargrave P. A., McDowell J. H., Curtis D. R., Wang J. K., Juszczak E., Fong S. L., Rao J. K., Argos P. The structure of bovine rhodopsin. Biophys Struct Mech. 1983;9(4):235–244. doi: 10.1007/BF00535659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hisatomi O., Iwasa T., Tokunaga F., Yasui A. Isolation and characterization of lamprey rhodopsin cDNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Feb 14;174(3):1125–1132. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91537-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuwata O., Imamoto Y., Okano T., Kokame K., Kojima D., Matsumoto H., Morodome A., Fukada Y., Shichida Y., Yasuda K. The primary structure of iodopsin, a chicken red-sensitive cone pigment. FEBS Lett. 1990 Oct 15;272(1-2):128–132. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80465-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laties A. M., Bok D., Liebman P. Procion yellow: a marker dye for outer segment disc patency and for rod renewal. Exp Eye Res. 1976 Aug;23(2):139–148. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(76)90197-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNaughton P. A. Light response of vertebrate photoreceptors. Physiol Rev. 1990 Jul;70(3):847–883. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1990.70.3.847. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama T. A., Khorana H. G. Mapping of the amino acids in membrane-embedded helices that interact with the retinal chromophore in bovine rhodopsin. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 5;266(7):4269–4275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathans J. Determinants of visual pigment absorbance: identification of the retinylidene Schiff's base counterion in bovine rhodopsin. Biochemistry. 1990 Oct 16;29(41):9746–9752. doi: 10.1021/bi00493a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathans J. Determinants of visual pigment absorbance: role of charged amino acids in the putative transmembrane segments. Biochemistry. 1990 Jan 30;29(4):937–942. doi: 10.1021/bi00456a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathans J., Hogness D. S. Isolation and nucleotide sequence of the gene encoding human rhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4851–4855. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathans J., Thomas D., Hogness D. S. Molecular genetics of human color vision: the genes encoding blue, green, and red pigments. Science. 1986 Apr 11;232(4747):193–202. doi: 10.1126/science.2937147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neitz M., Neitz J., Jacobs G. H. Spectral tuning of pigments underlying red-green color vision. Science. 1991 May 17;252(5008):971–974. doi: 10.1126/science.1903559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okano T., Fukada Y., Artamonov I. D., Yoshizawa T. Purification of cone visual pigments from chicken retina. Biochemistry. 1989 Oct 31;28(22):8848–8856. doi: 10.1021/bi00448a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okano T., Kojima D., Fukada Y., Shichida Y., Yoshizawa T. Primary structures of chicken cone visual pigments: vertebrate rhodopsins have evolved out of cone visual pigments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 1;89(13):5932–5936. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.13.5932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedler C., Tilly R. The nature of the Gecko visual cell. A light and electron microscopic study. Vision Res. 1964 Nov;4(10):499–510. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(64)90056-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh E. N., Jr, Cobbs W. H. Visual transduction in vertebrate rods and cones: a tale of two transmitters, calcium and cyclic GMP. Vision Res. 1986;26(10):1613–1643. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(86)90051-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakmar T. P., Franke R. R., Khorana H. G. Glutamic acid-113 serves as the retinylidene Schiff base counterion in bovine rhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8309–8313. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takao M., Yasui A., Tokunaga F. Isolation and sequence determination of the chicken rhodopsin gene. Vision Res. 1988;28(4):471–480. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(88)90169-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UNDERWOOD G. Reptilian retinas. Nature. 1951 Feb 3;167(4240):183–185. doi: 10.1038/167183a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALD G., BROWN P. K. The molar extinction of rhodopsin. J Gen Physiol. 1953 Nov 20;37(2):189–200. doi: 10.1085/jgp.37.2.189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokoyama R., Yokoyama S. Convergent evolution of the red- and green-like visual pigment genes in fish, Astyanax fasciatus, and human. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(23):9315–9318. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.23.9315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida M. Some observations on the patency in the outer segments of photoreceptors of the nocturnal gecko. Vision Res. 1978;18(2):137–143. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(78)90178-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhukovsky E. A., Oprian D. D. Effect of carboxylic acid side chains on the absorption maximum of visual pigments. Science. 1989 Nov 17;246(4932):928–930. doi: 10.1126/science.2573154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]