Abstract
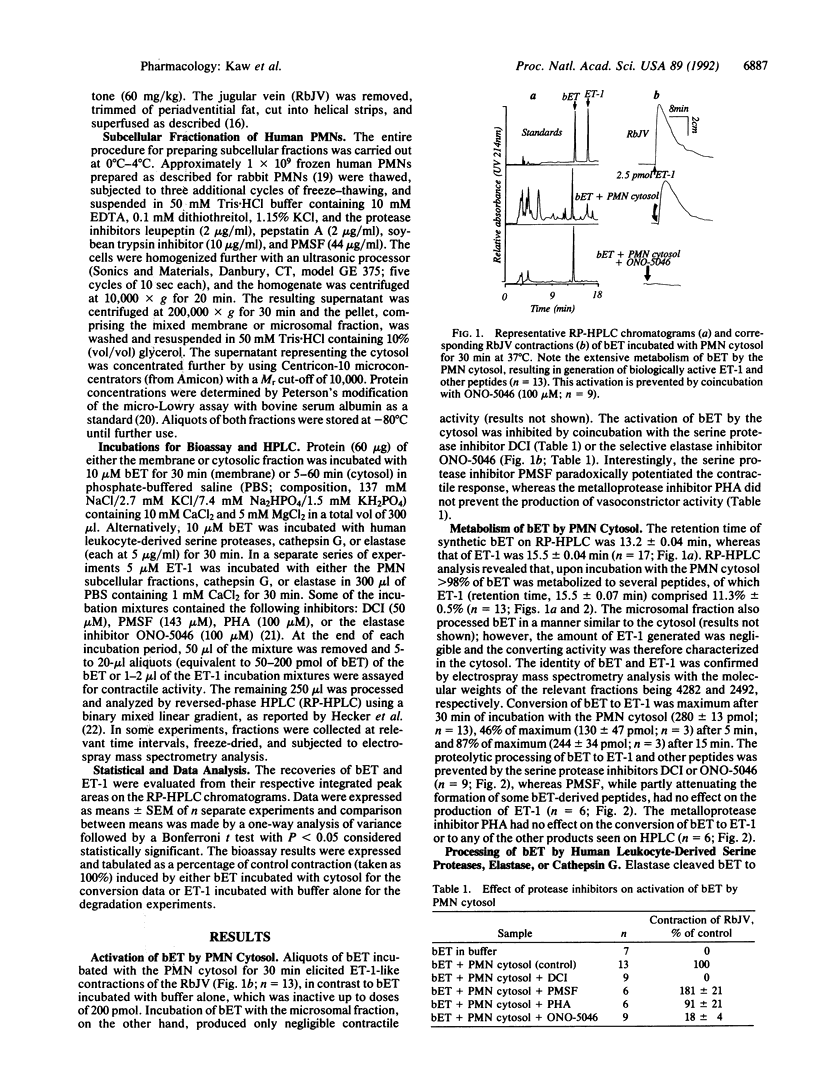
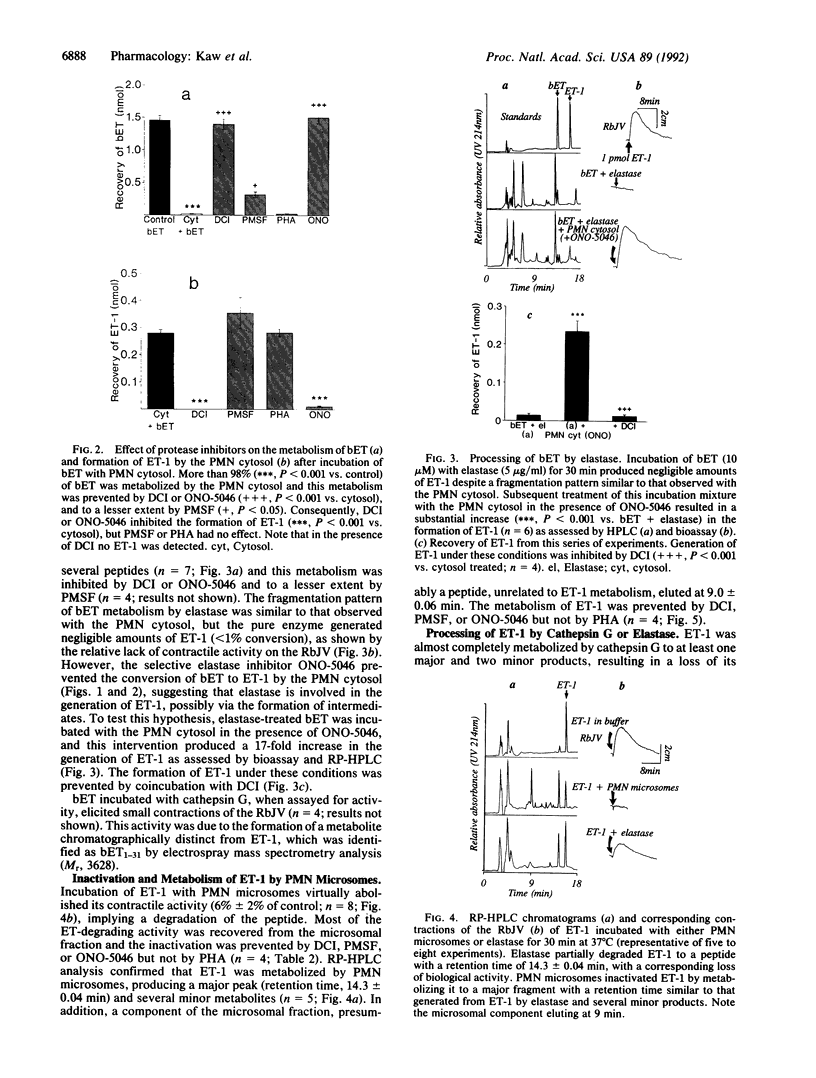
The metabolism of big endothelin 1 (bET) and endothelin 1 (ET-1) by subcellular fractions from human polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMNs) was investigated by bioassay and reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography. More than 80% of endothelin-converting activity was recovered from the cytosolic fraction, which in addition to ET-1 generated other peptides from bET. The processing of bET to all its metabolites including ET-1 was prevented by the serine protease inhibitor 3,4-dichloroisocoumarin (DCI; 50 microM) or the elastase inhibitor ONO-5046 (100 microM) but not by phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride (PMSF; 143 microM), another serine protease inhibitor. Paradoxically, human leukocyte elastase, despite generating a bET fragmentation pattern similar to that of PMN cytosol, produced very little ET-1. However, subsequent treatment of the elastase-derived metabolites of bET with PMN cytosol in the presence of ONO-5046 dramatically increased the amount of ET-1 formed. The generation of ET-1 following this intervention was inhibited by DCI. The PMN membrane preparation degraded ET-1 to a major metabolite, similar to that produced from ET-1 by elastase, and several minor products, paralleled by a loss of its smooth muscle contracting activity. The degradation of ET-1 by PMN microsomes was prevented by DCI, PMSF, or ONO-5046. Our results suggest that an elastase-initiated serine protease cascade is responsible for the sequential conversion of bET to ET-1 by the PMN cytosol. Elastase also partly accounts for the ET-metabolizing properties of PMN microsomes.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Branch D. W., Dudley D. J., Mitchell M. D. Preliminary evidence for homoeostatic mechanism regulating endothelin production in pre-eclampsia. Lancet. 1991 Apr 20;337(8747):943–945. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)91572-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickinson K. E., Tymiak A. A., Cohen R. B., Liu E. C., Webb M. L., Hedberg A. Vascular A10 cell membranes contain an endothelin metabolizing neutral endopeptidase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Apr 15;176(1):423–430. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)90941-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greer I. A., Haddad N. G., Dawes J., Johnstone F. D., Calder A. A. Neutrophil activation in pregnancy-induced hypertension. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1989 Aug;96(8):978–982. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1989.tb03358.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greer I. A., Leask R., Hodson B. A., Dawes J., Kilpatrick D. C., Liston W. A. Endothelin, elastase, and endothelial dysfunction in pre-eclampsia. Lancet. 1991 Mar 2;337(8740):558–558. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)91349-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groutas W. C. Inhibitors of leukocyte elastase and leukocyte cathepsin G. Agents for the treatment of emphysema and related ailments. Med Res Rev. 1987 Apr-Jun;7(2):227–241. doi: 10.1002/med.2610070205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hecker M., Kaw S., Walsh D. T. Determination of endothelin-converting enzyme activity by high-performance liquid chromatography-on-line radioactive flow monitoring. J Chromatogr. 1992 Feb 14;574(2):344–348. doi: 10.1016/0378-4347(92)80050-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawabata K., Suzuki M., Sugitani M., Imaki K., Toda M., Miyamoto T. ONO-5046, a novel inhibitor of human neutrophil elastase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Jun 14;177(2):814–820. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91862-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lees W. E., Kalinka S., Meech J., Capper S. J., Cook N. D., Kay J. Generation of human endothelin by cathepsin E. FEBS Lett. 1990 Oct 29;273(1-2):99–102. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81060-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason D. Y., Cramer E. M., Massé J. M., Crystal R., Bassot J. M., Breton-Gorius J. Alpha 1-antitrypsin is present within the primary granules of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Am J Pathol. 1991 Sep;139(3):623–628. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumura Y., Ikegawa R., Tsukahara Y., Takaoka M., Morimoto S. Conversion of big endothelin-1 to endothelin-1 by two-types of metalloproteinases of cultured porcine vascular smooth muscle cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Aug 15;178(3):899–905. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)90976-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahon E. G., Fok K. F., Moore W. M., Smith C. E., Siegel N. R., Trapani A. J. In vitro and in vivo activity of chymotrypsin-activated big endothelin (porcine 1-40). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Jun 15;161(2):406–413. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92613-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahon E. G., Palomo M. A., Moore W. M., McDonald J. F., Stern M. K. Phosphoramidon blocks the pressor activity of porcine big endothelin-1-(1-39) in vivo and conversion of big endothelin-1-(1-39) to endothelin-1-(1-21) in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 1;88(3):703–707. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.3.703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyauchi T., Yanagisawa M., Tomizawa T., Sugishita Y., Suzuki N., Fujino M., Ajisaka R., Goto K., Masaki T. Increased plasma concentrations of endothelin-1 and big endothelin-1 in acute myocardial infarction. Lancet. 1989 Jul 1;2(8653):53–54. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90303-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modin A., Pernow J., Lundberg J. M. Phosphoramidon inhibits the vasoconstrictor effects evoked by big endothelin-1 but not the elevation of plasma endothelin-1 in vivo. Life Sci. 1991;49(22):1619–1625. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(91)90056-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morel D. R., Lacroix J. S., Hemsen A., Steinig D. A., Pittet J. F., Lundberg J. M. Increased plasma and pulmonary lymph levels of endothelin during endotoxin shock. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Aug 29;167(3):427–428. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90454-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlstein E. H., Arleth A., Ezekiel M., Horohonich S., Ator M. A., Caltabiano M. M., Sung C. P. Biosynthesis and modulation of endothelin from bovine pulmonary arterial endothelial cells. Life Sci. 1990;46(3):181–188. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(90)90103-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada K., Miyazaki Y., Takada J., Matsuyama K., Yamaki T., Yano M. Conversion of big endothelin-1 by membrane-bound metalloendopeptidase in cultured bovine endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Sep 28;171(3):1192–1198. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)90811-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patrignani P., Del Maschio A., Bazzoni G., Daffonchio L., Hernandez A., Modica R., Montesanti L., Volpi D., Patrono C., Dejana E. Inactivation of endothelin by polymorphonuclear leukocyte-derived lytic enzymes. Blood. 1991 Nov 15;78(10):2715–2720. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable. Anal Biochem. 1977 Dec;83(2):346–356. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawamura T., Kasuya Y., Matsushita Y., Suzuki N., Shinmi O., Kishi N., Sugita Y., Yanagisawa M., Goto K., Masaki T. Phosphoramidon inhibits the intracellular conversion of big endothelin-1 to endothelin-1 in cultured endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Jan 31;174(2):779–784. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91485-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawamura T., Kimura S., Shinmi O., Sugita Y., Kobayashi M., Mitsui Y., Yanagisawa M., Goto K., Masaki T. Characterization of endothelin converting enzyme activities in soluble fraction of bovine cultured endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Jun 29;169(3):1138–1144. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)92014-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sessa W. C., Kaw S., Hecker M., Vane J. R. The biosynthesis of endothelin-1 by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Jan 31;174(2):613–618. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91461-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sessa W. C., Kaw S., Zembowicz A., Anggård E., Hecker M., Vane J. R. Human polymorphonuclear leukocytes generate and degrade endothelin-1 by two distinct neutral proteases. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1991;17 (Suppl 7):S34–S38. doi: 10.1097/00005344-199100177-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takaoka M., Hukumori Y., Shiragami K., Ikegawa R., Matsumura Y., Morimoto S. Proteolytic processing of porcine big endothelin-1 catalyzed by cathepsin D. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Dec 31;173(3):1218–1223. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)80916-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travis J. Structure, function, and control of neutrophil proteinases. Am J Med. 1988 Jun 24;84(6A):37–42. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(88)90156-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vijayaraghavan J., Scicli A. G., Carretero O. A., Slaughter C., Moomaw C., Hersh L. B. The hydrolysis of endothelins by neutral endopeptidase 24.11 (enkephalinase). J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 25;265(24):14150–14155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wypij D. M., Nichols J. S., Novak P. J., Stacy D. L., Berman J., Wiseman J. S. Role of mast cell chymase in the extracellular processing of big-endothelin-1 to endothelin-1 in the perfused rat lung. Biochem Pharmacol. 1992 Feb 18;43(4):845–853. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(92)90252-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagisawa M., Kurihara H., Kimura S., Tomobe Y., Kobayashi M., Mitsui Y., Yazaki Y., Goto K., Masaki T. A novel potent vasoconstrictor peptide produced by vascular endothelial cells. Nature. 1988 Mar 31;332(6163):411–415. doi: 10.1038/332411a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagisawa M., Masaki T. Endothelin, a novel endothelium-derived peptide. Pharmacological activities, regulation and possible roles in cardiovascular control. Biochem Pharmacol. 1989 Jun 15;38(12):1877–1883. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(89)90484-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]