Abstract
To compare the symptomatic improvement of nasal symptoms following septoplasty with partial inferior turbinectomy (groups A) versus septoplasty alone (groups B) and to assess the improvement of nasal symptoms in both surgical groups before and after surgery by NOSE scale. This Tertiary Hospital based study was carried out between August 2012 and April 2014. 60 cases with septal deviation and contralateral inferior turbinate hypertrophy. Nasal Obstruction Symptom Evaluation (NOSE) scale for evaluating nasal symptoms. Patients were alternatively divided into two surgical groups, group A. Septoplasty with partial inferior turbinectomy and group B septoplasty alone. Post-operative patient’s symptoms evaluated by NOSE scale at 1, 3 and 6 months. Data analysed using tables, graph and percentage and test of significance like paired t test, Friedman test, Chi square test used. Post operative improvement following both group A septoplasty with partial inferior turbinectomy and group B in those undergoing septoplasty alone was highly significant (p < 0.001) at post-op 1, 3 and 6 months subjectively. When both groups were compared those undergoing partial inferior turbinectomy surgery with septoplasty had highly significant results (p < 0.001) for subjective assessment by NOSE scale. This study showed that hypertrophied turbinate need to be addressed in chronic cases of nasal obstruction with deviated nasal septum and contralateral turbinate hypertrophy. partial inferior turbinectomy should be done in addition to septoplasty, its highly effective modality for the treatment of nasal obstruction in patients with deviated nasal septum. NOSE score can be used as a subjective tool for symptomatic measurement of patients with nasal obstruction.
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (doi:10.1007/s12070-015-0928-2) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Keywords: Deviated nasal septum, Turbinate hypertrophy, Septoplasty, Turbinectomy, NOSE scale
Introduction
Nasal obstruction is a common presenting symptom which an otorhinolaryngologist encounters in daily clinical practice. It affects 9.5–15 % of general population [1]. One of the most common cause of nasal obstruction is deviated nasal septum. Deviated nasal septum towards one side is often associated with overgrowth of inferior turbinate, which occupies expansive space on contralateral nasal cavity. Many authors believe that once septoplasty is done compensatory hypertrophy regresses on its own. On the other hand other authors claim that turbinate hypertrophy involves bone as well as the mucosa and they argued that these changes are not spontaneously reversible and should be corrected in conjunction with nasal septal surgery. Many otorhinolaryngologists perform septoplasty with or without turbinate reduction surgery and surgical methods relies largely on clinical judgement. Here by carrying out this study which is prospective randomised clinical study we can collect data and conclude which surgery in which cases are beneficial and therefore offer best surgical options.
Aims and Objectives
To compare the symptomatic improvement of nasal symptoms following septoplasty with partial inferior turbinectomy versus septoplasty alone.
To assess the improvement of nasal symptoms in both surgical groups A and B before and after surgery by NOSE scale.
Materials and Methods
All the patients above 18 years of age who underwent septoplasty with partial inferior turbinectomy and septoplasty alone in Department of ENT, Navodaya Medical College Hospital and Research Centre, Raichur were studied between August 2012 and April 2014.
Inclusion Criteria
Patients with deviated nasal septum with hypertrophy of inferior turbinate will be divided into two groups where one (group A) will be undergoing septoplasty with partial inferior turbinectomy and other (group B) septoplasty will be done. Nasal symptoms persisting after 2 months of medical therapy (topical corticosteroids with or without antihistamines) will be en-rolled for this study.
Age between 18 and 65 years.
Exclusion Criteria
Age < 18 years.
Previous surgery like septoplasty or submucous resection.
Acute and chronic rhino sinusitis.
Perforated nasal septum and insufficient nasal valve.
Granulomatous condition of nose and sinuses.
Craniofacial malformation.
Pregnancy.
HIV and HbsAg positive patients.
Study Area
Hospital Based (Navodaya Medical College Hospital and Research Centre, Raichur, Karnataka, India).
Design of Study
A prospective study.
60 patients with septal deviation and contralateral inferior turbinate hypertrophy were recruited in the study. Detailed history and clinical examination was done. After taking informed consent, patients were asked to fill questionnaires relating to severity of XI their symptoms using Nasal Obstruction Symptom Evaluation (NOSE) scale. Patients were then alternatively divided into two groups. In group A, reduction of partial inferior turbinectomy was performed to treat hypertrophied inferior turbinate together with septoplasty. In group B, only septoplasty was done. Post-operative patient’s symptoms were again evaluated using Nasal Obstruction Evaluation Scale (NOSE) at 1, 3 and 6 months. Data was analysed using tables, graph and percentage and test of significance like paired t test, Friedman test, Chi square test was used (Tables 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10).
Table 1.
Mean NOSE score for septoplasty with partial inferior turbinectomy surgery
| Mean | SD | Friedman test | p value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre total score | 14.15 | 2.3 | ||
| One month total | 3.80 | 3.0 | 158.50 | 0.001 |
| Three month total | 2.02 | 2.0 | ||
| Six month total | 1.90 | 1.9 |
Table 2.
Score for septoplasty surgery alone
| Mean | SD | Friedman test | p value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre score | 70.75 | 11.6 | ||
| One month score | 19.00 | 14.9 | 158.50 | 0.001 |
| Three month score | 10.08 | 12.5 | ||
| Six month score | 9.50 | 12.1 |
Friedman test is used for analysis, its a non-parametric statistical test similar to the parametric repeated measures ANOVA; it is used to detect differences in treatments across multiple test attempts
Table 3.
Septoplasty + partial inferior turbinectomy group A
| Statistical values | Preoperative total | 1st month score | 3rd month score | 6th month score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | 71.17 | 7.00 | 0.66 | 1.00 |
| SE | 10.5 | 1.1 | 0.5 | 0.7 |
| T test | 0.276 | −10.553 | −8.834 | −7.647 |
| p value | 0.784 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 |
Table 4.
Septoplasty group B
| Statistical values | Preoperative total | 1st month score | 3rd month score | 6th month score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | 70.33 | 31.00 | 19.50 | 18.00 |
| SE | 12.8 | 2.0 | 2.1 | 2.1 |
* p value 0.001, from the above observation the postoperative result after 3rd month is highly significant for septoplasty + partial inferior turbinectomy compared to septoplasty alone
Table 5.
Symptom wise mean NOSE score—septoplasty
| Symptoms | Pre-operative | 1-month | 3-month | 6-month |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nasal congestion | 60.83 | 40* | 30* | 29.17* |
| Nasal blockage or obstruction | 88.33 | 38.33** | 27.5** | 26.66** |
| Trouble breathing through nose | 85.83 | 36.67** | 22.5** | 20.83** |
| Trouble sleeping | 65.83 | 26.67** | 12.5** | 9.16** |
| Unable to get enough air during exertion | 50.83 | 16.66** | 5** | 4.17** |
Symbol * and ** significant values at p < 0.05 and p < 0.01
Table 6.
Mean symptom-wise change in NOSE score—septoplasty
| Symptoms | Change at 1-month | Change at 3-month | Change at 6-month |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nasal congestion | 20.83* | 30.83* | 31.66** |
| Nasal blockage or obstruction | 50** | 60.83** | 61.67** |
| Trouble breathing through nose | 49.16** | 63.33** | 65** |
| Trouble sleeping | 39.16** | 53.33** | 56.67** |
| Unable to get enough air during exertion | 34.17** | 45.83** | 46.66** |
Symbol * and ** significant values at p < 0.05 and p < 0.01
Table 7.
Mean symptom-wise NOSE score—septoplasty with partial inferior turbinectomy
| Symptoms | Pre-operative | 1-month | 3-month | 6-month |
|---|---|---|---|---|
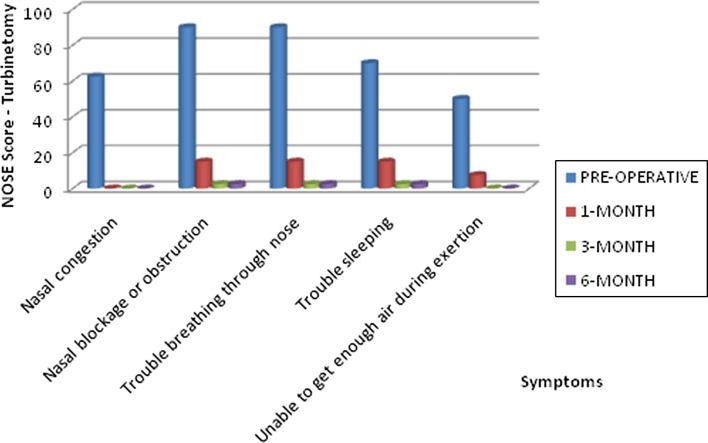
| Nasal congestion | 62.5 | 0** | 0** | 0** |
| Nasal blockage or obstruction | 90 | 15** | 2.5** | 2.5** |
| Trouble breathing through nose | 90 | 15** | 2.5** | 2.5** |
| Trouble sleeping | 70 | 15** | 2.5** | 2.5** |
| Unable to get enough air during exertion | 50 | 7.5** | 0** | 0** |
Symbol * and ** indicates significant values at p < 0.05 and p < 0.01
Table 8.
Mean symptom-wise change in NOSE score—septoplasty with partial inferior turbinectomy
| Symptoms | Change at 1-month | Change at 3-month | Change at 6-month |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nasal congestion | 62.5** | 62.5** | 62.5** |
| Nasal blockage or obstruction | 75** | 87.5** | 87.5** |
| Trouble breathing through nose | 75** | 87.5** | 87.5** |
| Trouble sleeping | 55** | 67.5** | 67.5** |
| Unable to get enough air during exertion | 42.5** | 50** | 50** |
Symbol * and ** indicates significant values at p < 0.05 and p < 0.01
Table 9.
Mean symptom-wise NOSE score comparison
| No. | Nasal symptoms | Assessment | Group A | Group B | p value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Nasal congestion | Preoperative | 62.5 | 60.83 | >0.05 |
| 1 month | 0 | 40 | <0.001 | ||
| 3 month | 0 | 30 | <0.001 | ||
| 6 month | 0 | 29.17 | <0.001 | ||
| 2 | Nasal blockage or obstruction | Preoperative | 90 | 88.33 | >0.05 |
| 1 month | 5 | 38.33 | <0.001 | ||
| 3 month | 2.5 | 27.5 | <0.001 | ||
| 6 month | 2.5 | 26.66 | <0.001 | ||
| 3 | Trouble breathing through nose | Preoperative | 90 | 85.83 | >0.05 |
| 1 month | 15 | 36.67 | <0.001 | ||
| 3 month | 2.5 | 22.5 | <0.001 | ||
| 6 month | 2.5 | 20.83 | <0.001 | ||
| 4 | Trouble sleeping | Preoperative | 70 | 65.83 | >0.05 |
| 1 month | 15 | 26.67 | <0.001 | ||
| 3 month | 2.5 | 12.5 | <0.001 | ||
| 6 month | 2.5 | 9.16 | <0.001 | ||
| 5 | Unable to get enough air during exertion | Preoperative | 50 | 50.83 | >0.05 |
| 1 month | 7.5 | 16.66 | <0.001 | ||
| 3 month | 0 | 5 | <0.001 | ||
| 6 month | 0 | 4.17 | <0.001 |
Group A—septoplasty with partial inferior turbinectomy
Group B—septoplasty alone
p value < 0.001 suggesting highly significant result favouring group a over group B
p value > 0.05 suggesting no statistically significant difference
Table 10.
Mean symptom-wise change in NOSE score comparison
| No. | Nasal symptoms | Assessment | Group A | Group B | p value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Nasal congestion | 1 month | 62.5 | 20.83 | <0.001 |
| 3 month | 62.5 | 30.83 | <0.001 | ||
| 6 month | 62.5 | 31.66 | <0.001 | ||
| 2 | Nasal blockage or obstruction | 1 month | 75 | 50 | <0.001 |
| 3 month | 87.5 | 60.83 | <0.001 | ||
| 6 month | 87.5 | 61.67 | <0.001 | ||
| 3 | Trouble breathing through nose | 1 month | 75 | 49.16 | <0.001 |
| 3 month | 87.5 | 63.33 | <0.001 | ||
| 6 month | 87.5 | 65 | <0.001 | ||
| 4 | Trouble sleeping | 1 month | 65 | 39.16 | <0.001 |
| 3 month | 67.5 | 53.33 | <0.001 | ||
| 6 month | 67.5 | 56.67 | <0.001 | ||
| 5 | Unable to get enough air during exertion | 1 month | 42.5 | 34.17 | <0.001 |
| 3 month | 50 | 45.83 | <0.001 | ||
| 6 month | 50 | 46.66 | <0.001 |
Group A—septoplasty with partial inferior turbinectomy
Group B—septoplasty alone
p value < 0.001 suggesting highly significant result favouring group a over group B
p value > 0.05 suggesting no statistically significant difference
For all patients a detailed history taken regarding complaints, history of present illness with special note of presence or absence of symptoms, like nasal obstruction, headache, nasal discharge, nasal bleeding, loss of smell and other associated manifestations. A detailed general physical examination and ENT examination was done on all the patients. All patients underwent routine blood investigations including Haemoglobin, Total Count, Differential Count, Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate, Bleeding Time, Clotting Time, Blood grouping and Rh typing, urine examination, random blood sugar, HIV, HBsAg. Computerised tomography Paranasal sinus, [3, 5] diagnostic nasal endoscopy was done and turbinate hypertrophy size were assess and graded. Grading of inferior turbinate size [2] (Fig. 2b).
Grade I—Mild enlargement with no obvious nasal obstruction.
Grade II—The inferior turbinate occupies half of the nasal cavity with nasal obstruction.
Grade III—Complete occlusion of the nasal cavity.
Fig. 2.
a Deviated nasal septum, b grading of inferior turbinate
Following this the patients were counselled for this study. A written informed consent was taken. A course of antibiotics is given for 5 days for patients presenting with upper respiratory tract infection. Pre-operatively injection of tetanus toxoid 0.5 ml intramuscular was given, lignocaine sensitivity test was done. Cotton strips soaked in 4 % lignocaine with 1:100,000 adrenaline were packed in both nasal cavities 10 min prior to surgery (Figs. 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7).
Fig. 1.
a Instrument of septal surgery and turbinectomy, b infiltration of septum, c freer’s incision, d elevation of flap, e partial inferior turbinectomy by turbinectomy scissors, f septal cartilage and partial inferior turbinate
Fig. 3.
Heymann turbinectomy scissors
Fig. 4.
Symptom wise mean NOSE score—septoplasty
Fig. 5.
Mean symptom-wise change in NOSE score—septoplasty
Fig. 6.
Mean symptom-wise NOSE score—septoplasty with partial inferior turbinectomy
Fig. 7.
Mean symptom-wise change in NOSE score—septoplasty with partial inferior turbinectomy
Procedure
Septoplasty surgery was performed alone in Group B.
Anaesthesia
Local or general.
Position
Reclining position with head-end of the table raised.
Technique
Infiltrate the septum with 2 % lignocaine with adrenaline, 1:100,000.
In cases of deviated septum, make a slightly curvilinear incision, 2–3 mm above the caudal end of septal cartilage on the concave side (Killian’s incision). In case of caudal dislocation, a transfix ion or hemitransfixion (Freer’s) incision is made.
Raise mucoperichondrial/mucoperiosteal flap on one side only.
Separate septal cartilage from the vomer and ethmoid plate and raise mucoperiosteal flap on the opposite side of septum.
Remove maxillary crest to realign the septal cartilage.
-
Correct the bony septum by removing the deformed parts. Deformed septal cartilage is corrected by various methods, such as:
-
(i)Scoring on the concave side.
-
(ii)Cross-hatching.
-
(iii)Shaving.
-
(iv)Wedge excision.
-
(i)
Trans-septal sutures are put to coapt mucoperichondrial flaps.
Nasal pack, which has to be removed after 48 h.
Septoplasty and Partial inferior turbinectomy was performed (by using Heymann Nasal Turbinectomy Scissors) in Group A.
Technique
Septoplasty procedure steps mentioned earlier.
Infiltrate the hypertrophied inferior turbinate side with 2 % lignocaine with adrenaline, 1:100,000.
Heymann Nasal Turbinectomy Scissors were used for this procedure. One blade was inserted beneath the inferior turbinate and the other on top of it after fracturing the turbinate medially.
Resection includes the anterior 1/3rd of the inferior turbinate mucosa and bone. Partial inferior turbinectomy done.
Nasal packing, which has to be removed after 48 h.
After 48 h, in both the group patients nasal pack was removed and 0.1 % Xylometazoline Nasal drops were instilled initially 3 drops both nostril every 30 min for the first 2 h followed by 3 drops three times daily for the rest of the day for 5 days.
Post operative day 3. Proper nasal douching was done. Patients were advised to perform frequent nasal douching throughout the day. Patient were then discharged and asked to come for regular follow up 1st month, 3rd month and 6th month.
Nasal Obstruction Symptom Evaluation Scale (NOSE SCORE) [3]—Used for subjective measurement of symptoms.
Scores taken pre-operatively, 1 month post-operatively, 3 months post-operatively, 6 months post-operatively. Total 5 symptoms, each symptoms is given points from 0 to 4 depending on severity of symptom. 0 minimum severity, 4 maximum severity. So total maximum points 5 × 4 = 20.
Total point = Q1 + Q2 + Q3 + Q4 + Q5. This is divided by 20 and multiplied by 100, to get score out of 100. i.e.
Total score from 0 to 100. 0—Minimum severity; 100—Maximum severity.
Change in pre to post operative at 1, 3 and 6 months is compared between group A i.e. Septoplasty with partial inferior turbinectomy and group B-septoplasty only. Each group consists of 30 patients.
Data Analysis
Data collected will be entered on excel spread sheet after coding and further processed using SPSS Version 17.0 (statistical package for social sciences). The data analysis will be done by computing proportions, mean of standard deviation. Appropriate test of significance will be used based on type of data. A p value < 0.05 will be considered significant.
Follow Up
All patients were followed regularly at 1st month, 3rd month, 6th month respectively. Patients were asked to fill up questionnaires related to severity of their symptoms using NOSE scale which were documented timely.
Results
Post operative improvement following both group A. Septoplasty with partial inferior turbinectomy and group B in those undergoing septoplasty alone was highly significant (p < 0.001) at post-op 1, 3 and 6 months subjectively. When both groups were compared those undergoing partial inferior turbinectomy surgery with septoplasty had highly significant results (p < 0.001) for subjective assessment by NOSE scale.
Discussion
Nasal obstruction is one of the most common complaints by patient which an otorhinolaryngologists encounters in day to day practice. It’s affecting 9.5–15 % of general population [1]. Nasal septum deviation and associated turbinate hypertrophy is one of its most frequent causes.
The present study was carried out to know whether septoplasty alone can treat nasal obstruction in patients with deviated nasal septum, to know whether hypertrophied turbinate needs to be addressed in patients with deviated nasal septum and also to know the effectiveness of Partial Inferior Turbinectomy with septoplasty for the treatment of nasal obstruction in patients with deviated nasal septum. In this study NOSE score was used for subjective evaluation in addition to existing methods of evaluation.
The present study showed highly significant positive result for post operative improvement for septoplasty with partial inferior turbinectomy group. According to NOSE score patients undergoing Partial Inferior Turbinectomy with septoplasty has more symptomatic relief compared to those undergoing septoplasty alone. Patients undergoing septoplasty alone gradually shows symptomatic improvement over the period of 6 months, whereas patient undergoing septoplasty with partial inferior turbinectomy definitely had overall greater improvement symptomatically compared to septoplasty alone, but their high post-op improvement remained static and does not improved over the period but at 6 month it was still significantly greater than septoplasty alone.
The results of our study are concomitant with majority of studies which favours Partial Inferior Turbinectomy in addition to septoplasty.
In a study done by Jun et al. [4] in St. Mary’s hospital, South Korea computed tomography of sinuses of 20 patients was done, the volume of the inferior turbinate was measured from the three-dimensional reconstruction, it was concluded that, the inferior turbinate on the concave side had a significantly greater volume and hence septoplasty and concomitant inferior turbinate surgery to manipulate conchal bone and soft tissues are necessary for treatment of those patients with unilateral nasal septal deviation and compensatory hypertrophy of the contralateral inferior turbinate.
In a study done by Gilead Berger et al. [5] to know the histopathology of inferior turbinate with compensatory hypertrophy in patients with deviated nasal septum, it was found that, the inferior turbinate bone underwent a two fold increase in thickness, result supported the decision to excise inferior turbinate bone at time of septoplasty because of significant bony expansion and relative minor role of mucosal hypertrophy.
Leandro Castro Velasco et al. [6] have shown that a prospective study which focused on evaluation of the main nasal symptoms, including nasal obstruction. It is found that septoplasty, with or without turbinectomy, resulted in improvement of all symptoms. Symptoms of sneezing and nasal pruritus regressed significantly on the first evaluations (7th day) and thereafter stabilized until the 60th postoperative day. Removing the nasal splint and avoiding contact between the mucosa of the nasal septum and the turbinates were the main improvement factors in the first evaluation.
The work of Kim et al. [7] who studied the effects of septoplasty alone on the thicknesses and cross-sectional areas of mucosa and conchal bone with computed tomography before the operations and at least 1 year after surgery. They found that the thickening of the mucosa of the inferior turbinate on the concave aspect and the thinning on the convex aspect, especially in the medial mucosa, reverses after septoplasty, but indicate further follow up was required to see if there are bony changes in the longer term.
The study by Stewart et al. [3] also has used NOSE score for subjective evaluation, as was used in our study and they concluded, in patients with septal deformity, nasal septoplasty results in significant improvement in disease-specific quality of life, high patient’s satisfaction, and decreased medication use.
In a study Wight et al. [8] showed anterior trimming of the inferior turbinate, whilst being an objective success in decreasing nasal resistance, frequently failed to produce a significant fall in subjective obstruction in the first 2 months.
Similar to majority of above mentioned studies our study also conclude that Partial Inferior turbinectomy in addition to septoplasty offers greater symptomatic relief compared to those undergoing septoplasty alone. Other studies where no significant improvement was found when Turbinate reduction surgery was added to septoplasty are in favour of longer follow up. Similar to present study, according to Stewart et al. NOSE score can be used for subjective evaluation of nasal obstruction, which can be used for pre to post operative evaluation and also for comparison among different surgeries.
In a study by, suggested by Berger et al. [9] targets of inferior turbinate reduction surgery are the medial and inferior mucosal layers. The medial layer shows the greatest thickening and obstructs the airway. They feel the lateral mucosal layer should be spared as it does not encroach on the airway and has an important role in humidifying the inspired air and maintaining mucociliary clearance.
Most troublesome symptom preoperative, according to NOSE score was nasal blockage with 88.33, closely followed by trouble breathing through nose 85.83 both among patients undergoing septoplasty and those undergoing Partial inferior Turbinectomy with septoplasty.
Patients undergoing septoplasty alone has higher NOSE score for nasal congestion postoperatively of 40 at 1 month, 30 at 3 months and 29.17 at 6 months compared to those undergoing Partial inferior Turbinectomy with septoplasty whose NOSE scores were 0 at 1 month, 3 and 6 months.
So nasal congestion symptoms were better relieved in patients in whom partial inferior turbinectomy and septoplasty surgeries were added. Septoplasty alone also helps in reducing sinusitis incidence, Upper respiratory tract infections, improvement in olfaction.
Symptoms of nasal blockage and trouble breathing through NOSE improvement was better in those undergoing Partial inferior Turbinectomy with septoplasty (by 15 in 1st month, 2.5 in 3rd month, 2.5 in 6th month) compared to those undergoing septoplasty alone.
Symptoms of trouble sleeping, unable to get enough air during exertion improvement was better in those undergoing partial inferior turbinectomy with septoplasty compared to those undergoing septoplasty alone.
Septoplasty with partial inferior turbinectomy group post surgery, few patients faced problems like nasal crusting, atrophic rhinitis which were managed appropriately by nasal douching, nasal bleeding managed by nasal packing with nasal decongestants and Botropase [10] (a hemocoagulase preparation used to arrest bleeding of different etiology) soaked cottonoids, synechiae formation which was released and nasal pack kept for half a day between two raw surfaces and then removed later, following which nasal douching were advised.
Though partial inferior turbinectomy, a simple and effective surgical procedure, it’s equally troublesome if bluntly resected. Perioperative bleeding, raw medial and inferior surface of the inferior turbinate which may form post operative synechiae with the nasal septum and floor of nasal cavity. Excessive resection of the inferior turbinate can also lead to bleeding, frequent post nasal blood drip, nasal crusting, atrophic rhinitis in post operative events. So with sharp angled nasal turbinectomy scissor and with proper technique of partial trimming of anterior 1/3rd of the hypertrophied inferior turbinate such complications can be avoided.
In this study, none of the patient presented with deviated nasal septum with ipsilateral inferior turbinate hypertrophy. The present study proved that although both groups of patients, those undergoing septoplasty alone and those undergoing partial inferior turbinectomy with septoplasty had highly significant post-operative improvement. Those undergoing partial inferior turbinectomy had the best result; hence partial inferior turbinectomy can be considered in addition to septoplasty.
The present study results are comparable to previously published data. However longer follow up, larger sample size can be considered for further studies.
Conclusion
The results in this study showed that hypertrophied inferior turbinate needs to be addressed in chronic cases of nasal obstruction with deviated nasal septum. In these patient partial inferior turbinectomy should be done in addition to septoplasty. Partial inferior turbinectomy in addition to septoplasty are highly effective surgical procedure for management of nasal symptoms in patients with deviated nasal septum with inferior turbinate hypertrophy. NOSE score can be used as a subjective tool for assessment of patients with nasal symptoms preoperative and postoperatively in addition to existing methods of evaluation.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Compliance with Ethical Standards
Conflict of interests
None.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Contributor Information
Rajendran Dinesh Kumar, Email: dinuraj1186@gmail.com.
M. Rajashekar, Email: drmrajashekar@gmail.com
References
- 1.Akerlund A, Millqvist E, Oberg D, Bende M. Prevalence of upper and lower airway symptoms: the Skovde population-based study. Acta Otolaryngol. 2006;126:483–488. doi: 10.1080/00016480500416835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Friedman M, Tanyeri H, Lim J, Landsberg R, Caldarelli D. A safe, alternative technique for inferior turbinate reduction. Laryngoscope. 1999;109(11):1834–1837. doi: 10.1097/00005537-199911000-00021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Stewart MG, Smith TL, Weaver EM, et al. Outcomes after nasal septoplasty: results from the nasal obstuction septoplasty effectiveness(NOSE) study. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2004;130(3):283–290. doi: 10.1016/j.otohns.2003.12.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Jun BC, Kim SW, Cho JH, Park YJ, Yoon HR. Is turbinate surgery necessary when performing a septoplasty? Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2009;266(7):975–980. doi: 10.1007/s00405-008-0855-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Berger G, Hammel I, Berger R, Avraham S, Ophir D. Histopathology of the inferior turbinate with compensatory hypertrophy in patients with deviated nasal septum. Laryngoscope. 2000;110(12):2100–2105. doi: 10.1097/00005537-200012000-00024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Velasco LC, et al. Assessment of symptom improvement following nasal septoplasty with or without turbinectomy. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2011;77(5):577–583. doi: 10.1590/S1808-86942011000500007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Kim DH, Park HY, Kim HS, et al. Effect of septoplasty on inferior turbinate hypertrophy. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2008;134:419–423. doi: 10.1001/archotol.134.4.419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Wight RG, Jones AS, Clegg RT. A comparison of anterior and radical trimming of the inferior turbinates and their effect on nasal resistance to airflow. Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci. 1988;13:223–226. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2273.1988.tb01122.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Berger G, Gass S, Ophir D. The histopathology of the hypertrophic inferior turbinate. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2006;132:588–594. doi: 10.1001/archotol.132.6.588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Bell WR., Jr Defibrinogenating enzymes. Drugs. 1997;54(Suppl 3):18–30. doi: 10.2165/00003495-199700543-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.