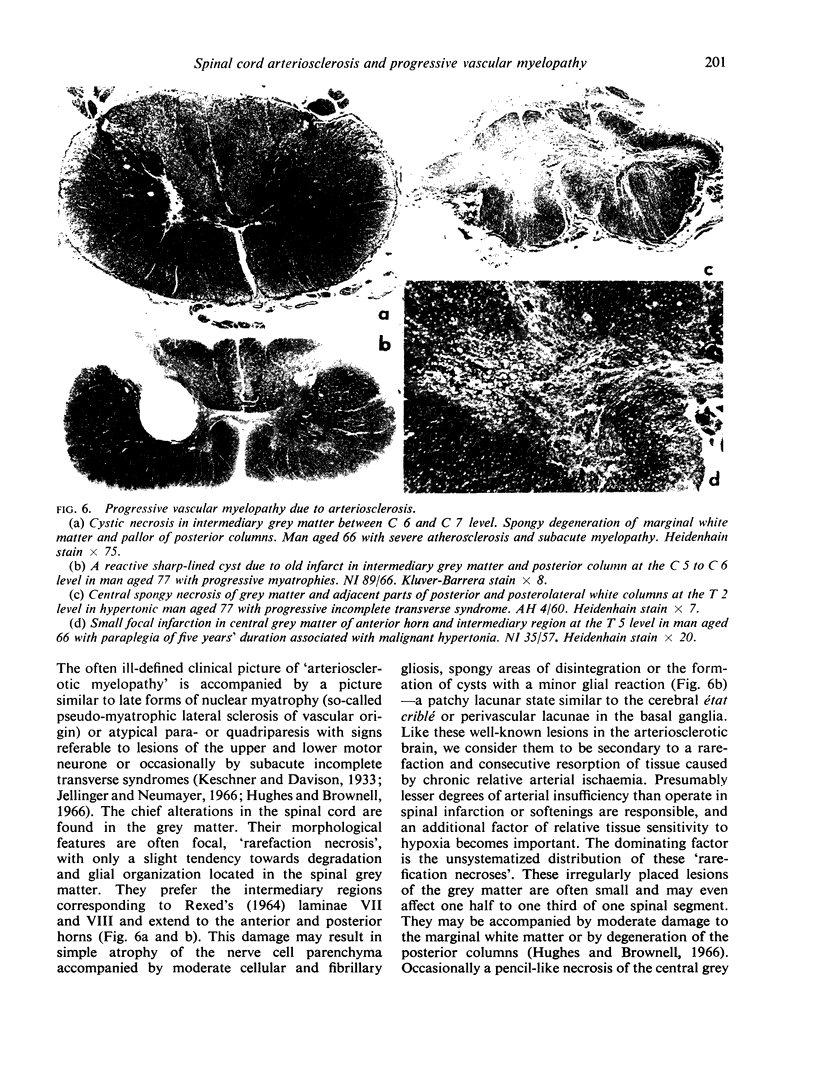
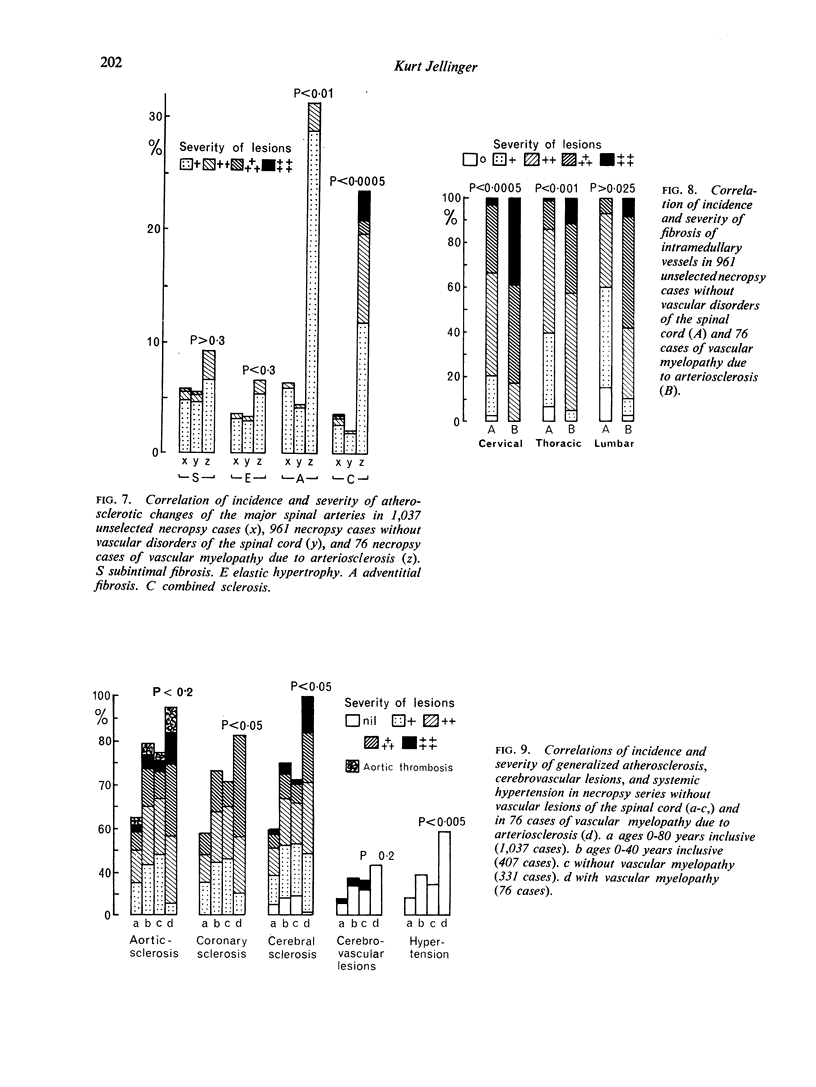
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARENDT A., WUNSCHER W. Beitrag zur Arterio- und Arteriolosklerose der Rückenmarkgefässe. Psychiatr Neurol Med Psychol (Leipz) 1954 Mar;6(3):69–77. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arendt A., Bachmann P. Intracerebrale Gefässwandveränderungen bei Hypertonischer Hirnmassenblutung. Acta Neuropathol. 1966 Sep 1;7(1):79–85. doi: 10.1007/BF00686611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAILEY A. A. Changes with age in the spinal cord. AMA Arch Neurol Psychiatry. 1953 Sep;70(3):299–309. doi: 10.1001/archneurpsyc.1953.02320330024003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAKER A. B., IANNONE A. Cerebrovascular disease. II. The smaller intracerebral arteries. Neurology. 1959 Jun;9(6):391–396. doi: 10.1212/wnl.9.6.391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLAISDELL F. W., COOLEY D. A. The mechanism of paraplegia after temporary thoracic aortic occlusion and its relationship to spinal fluid pressure. Surgery. 1962 Mar;51:351–355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breig A., Turnbull I., Hassler O. Effects of mechanical stresses on the spinal cord in cervical spondylosis. A study on fresh cadaver material. J Neurosurg. 1966 Jul;25(1):45–56. doi: 10.3171/jns.1966.25.1.0045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHRAST B., KORBICKA J. [The alteration of flow relations in the vertebral artery by different head and neck positions. Testiometric study]. Dtsch Z Nervenheilkd. 1962;183:426–448. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARCIN R., GRUNER J. Nécrose cavitaire des cornes antérieures de la moelle au cours d'un syndrome réalisant une forme pseudo-polynévritique des sclérose latérale amyotrophique. Presse Med. 1953 Dec 23;61(82):1723–1724. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARSTKA M. Atherosclerotic occlusion of nutrient branches of the anterior spinal artery. Ill Med J. 1953 May;103(5):305–310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garland H., Greenberg J., Harriman D. G. Infarction of the spinal cord. Brain. 1966 Dec;89(4):645–662. doi: 10.1093/brain/89.4.645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HASSLER O. Media defects and physiological intima cushions in the spinal arteries. Acta Soc Med Ups. 1961;66:267–270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUTCHINSON E. C., YATES P. O. The cervical portion of the vertebral artery; a clinico-pathological study. Brain. 1956 Jun;79(2):319–331. doi: 10.1093/brain/79.2.319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogan E. L., Romanul F. C. Spinal cord infarction occurring during insertion of aortic graft. Neurology. 1966 Jan;16(1):67–74. doi: 10.1212/wnl.16.1.67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes J. T., Brownell B. Spinal cord ischemia due to arteriosclerosis. Arch Neurol. 1966 Aug;15(2):189–202. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1966.00470140079011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JELLINGER K., NEUMAYER E. [Progressive spinal cord disease of vascular origin. Anatomo-clinical contribution to syndromes caused by chronic hypovascularization of the spinal cord]. Acta Neurol Psychiatr Belg. 1962 Oct;62:944–956. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KILLEN D. A., ADKINS R. B., Jr STUDIES OF SPINAL ARTERIAL BED PRESSURE FOLLOWING EXTENSIVE MOBILIZATION OF THE AORTA FROM THE POSTERIOR PARIETES. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1965 Feb;49:231–240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LASSEN N. A., HOEDT-RASMUSSEN K., SORENSEN S. C., SKINHOJ E., CRONQUIST S., BODFORSS B., INGVAR D. H. REGIONAL CEREBRAL BLOOD FLOW IN MAN DETERMINED BY KRYPTON. Neurology. 1963 Sep;13:719–727. doi: 10.1212/wnl.13.9.719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazorthes G., Gouazé A., Bastide G., Soutoul J. H., Zadeh O., Santini J. J. La vascularisation artérielle du renflement lombaire. Etude des variations et des suppléances. Rev Neurol (Paris) 1966 Feb;114(2):109–122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OTOMO E., WOLBARSHT M. L., VAN BUSKIRK C., DAVIDSON M. A comparison of spinal cord, cortical and superficial circulation. J Nerv Ment Dis. 1960 Nov;131:418–427. doi: 10.1097/00005053-196011000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROMANUL F. C., ABRAMOWICZ A. CHANGES IN BRAIN AND PIAL VESSELS IN ARTERIAL BORDER ZONES; A STUDY OF 13 CASES. Arch Neurol. 1964 Jul;11:40–65. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1964.00460190044004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAYLOR A. R. VASCULAR FACTORS IN THE MYELOPATHY ASSOCIATED WITH CERVICAL SPONDYLOSIS. Neurology. 1964 Jan;14:62–68. doi: 10.1212/wnl.14.1.62. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnbull I. M., Brieg A., Hassler O. Blood supply of cervical spinal cord in man. A microangiographic cadaver study. J Neurosurg. 1966 Jun;24(6):951–965. doi: 10.3171/jns.1966.24.6.0951. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZOLLINGER H. U. Die hypertensive Arteriolopathie. Schweiz Z Pathol Bakteriol. 1959;22(3):262–285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zschoch H. Die Herz- und Gefässkrankheiten in der Sektionsstatistik. Ergeb Allg Pathol Pathol Anat. 1966;47:58–143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]