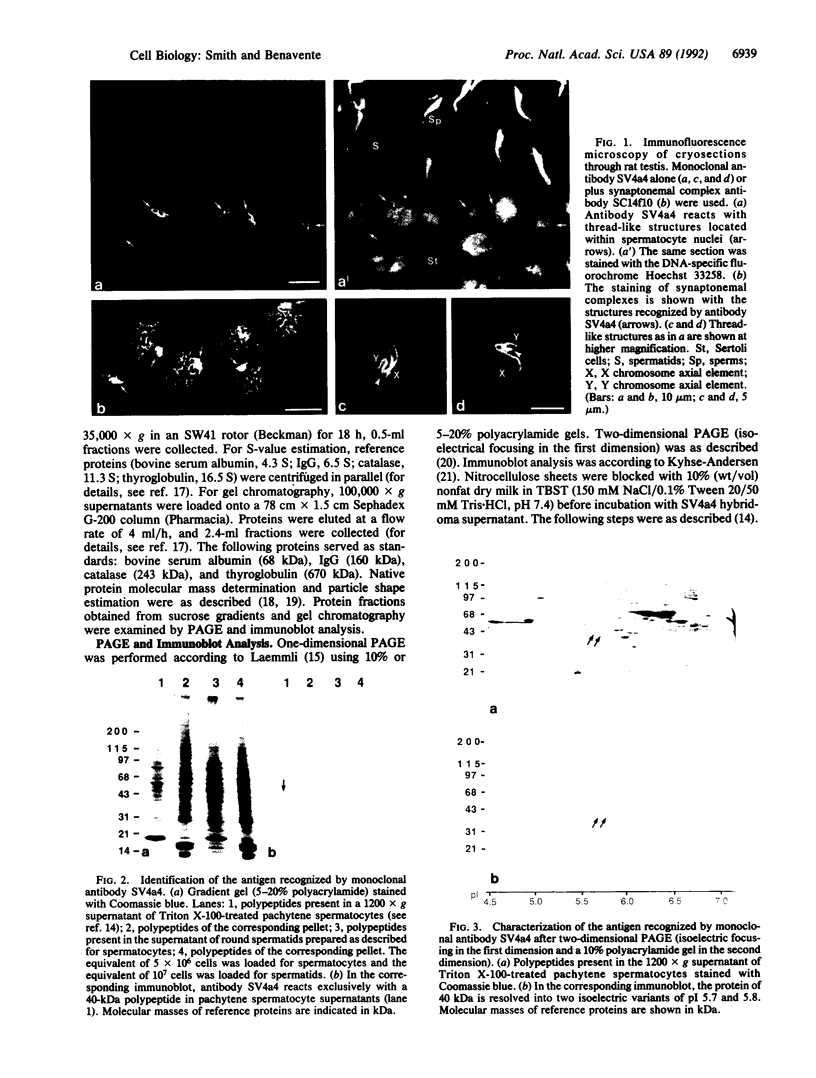
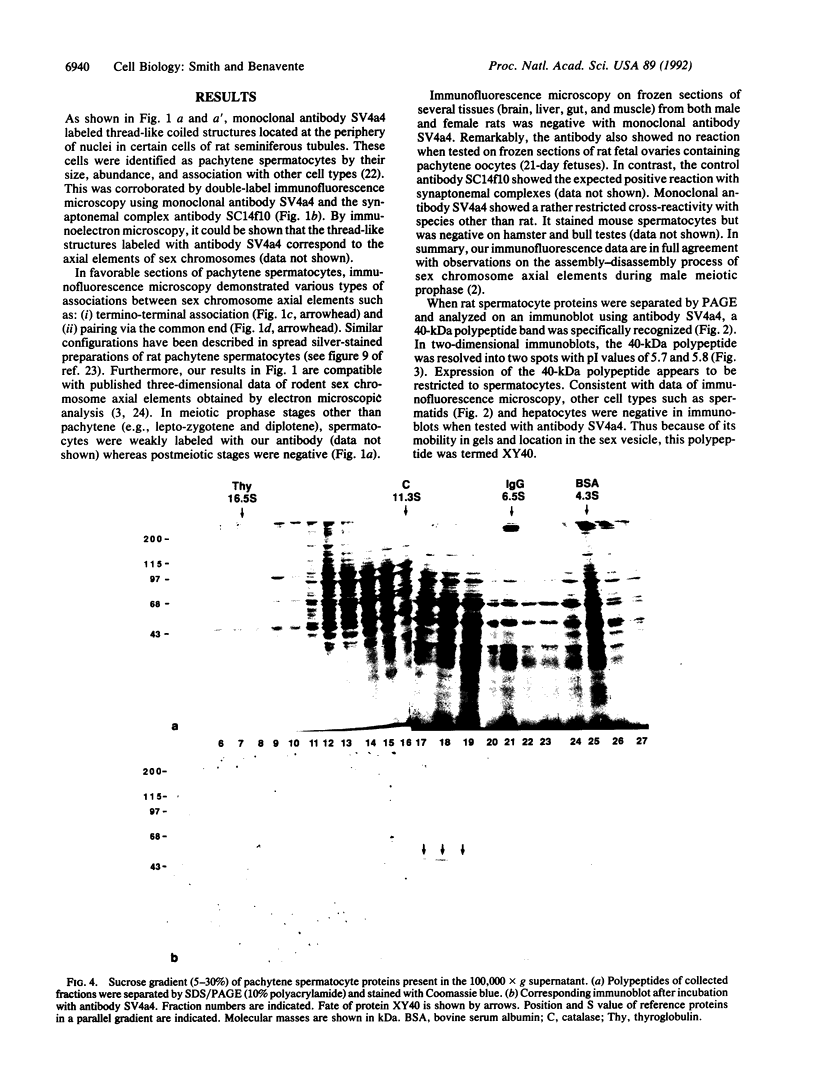
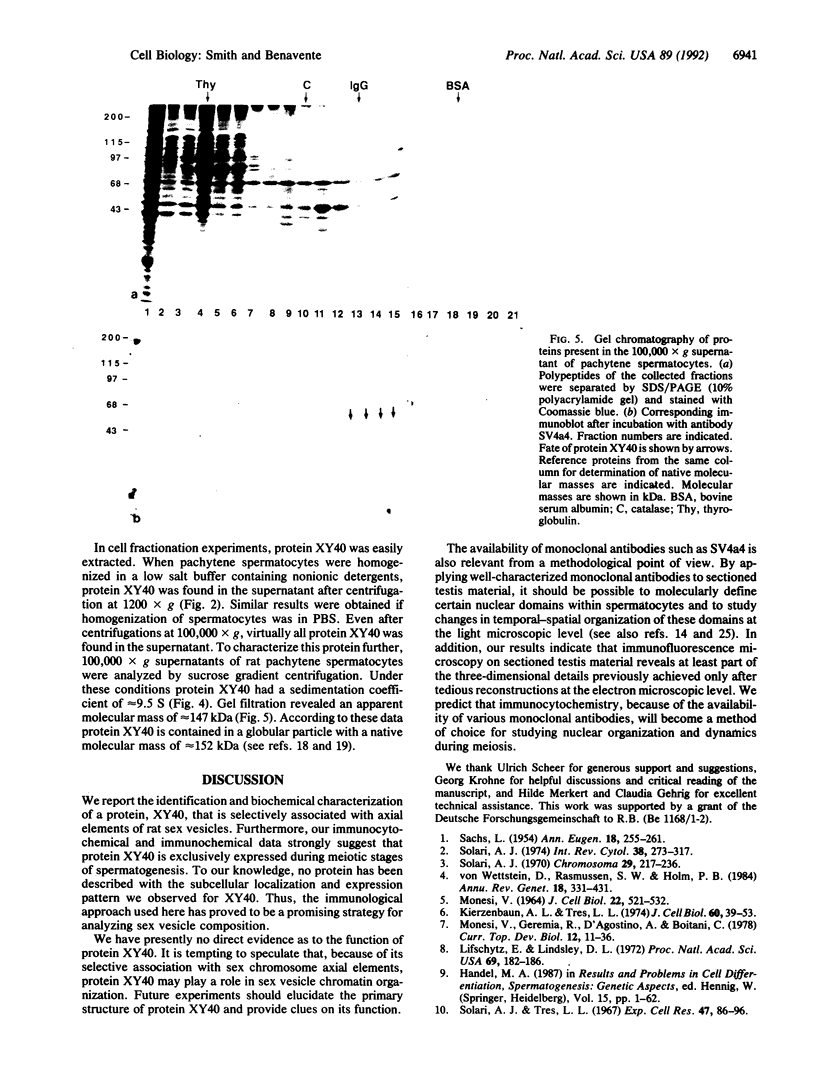
Abstract
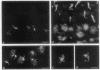
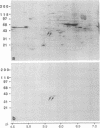
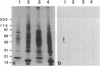
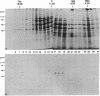
During the first meiotic prophase of mammalian spermatogenesis, the sex chromosomes X and Y show a characteristic allocyclic behavior with respect to the autosomes. This is particularly evident during pachytene stage when sex chromosomes form the so-called sex vesicle. This structure is characterized by the condensed state of chromatin, transcriptional inactivity, and the limited extension of chromosome pairing, which is usually restricted to a short segment of sex chromosome axial elements. The molecular basis and functional significance of sex vesicle formation during mammalian spermatogenesis remain obscure. Here we report on the identification of a meiosis-specific sex vesicle protein we called XY40. Immunocytochemical localization on rat testis cryosections with a XY40-specific monoclonal antibody revealed that the labeling is confined to the axial elements of sex chromosomes. Biochemical characterization showed that protein XY40 (40 kDa; pI 5.7-5.8) can be extracted from rat pachytene spermatocytes and recovered in particles of 9.5 S with a native molecular mass of approximately 152 kDa. We speculate that protein XY40 may be involved in the allocyclic behavior of sex chromosomes during male meiotic prophase.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benavente R., KrohneG Change of karyoskeleton during spermatogenesis of Xenopus: expression of lamin LIV, a nuclear lamina protein specific for the male germ line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(18):6176–6180. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhagirath T., Kundu S. C. Sequential analysis of synaptonemal complexes in the repopulating spermatocytes of Rattus norvegicus after restricting the germ cell population to spermatogonia by gossypol treatment. Eur J Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;40(2):226–232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dabauvalle M. C., Loos K., Scheer U. Identification of a soluble precursor complex essential for nuclear pore assembly in vitro. Chromosoma. 1990 Dec;100(1):56–66. doi: 10.1007/BF00337603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handel M. A. Genetic control of spermatogenesis in mice. Results Probl Cell Differ. 1987;15:1–62. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-47184-4_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyting C., Dettmers R. J., Dietrich A. J., Redeker E. J., Vink A. C. Two major components of synaptonemal complexes are specific for meiotic prophase nuclei. Chromosoma. 1988;96(4):325–332. doi: 10.1007/BF00286921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kierszenbaum A. L., Tres L. L. Nucleolar and perichromosomal RNA synthesis during meiotic prophase in the mouse testis. J Cell Biol. 1974 Jan;60(1):39–53. doi: 10.1083/jcb.60.1.39. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyhse-Andersen J. Electroblotting of multiple gels: a simple apparatus without buffer tank for rapid transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide to nitrocellulose. J Biochem Biophys Methods. 1984 Dec;10(3-4):203–209. doi: 10.1016/0165-022x(84)90040-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEBLOND C. P., CLERMONT Y. Definition of the stages of the cycle of the seminiferous epithelium in the rat. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1952 Nov 20;55(4):548–573. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1952.tb26576.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lifschytz E., Lindsley D. L. The role of X-chromosome inactivation during spermatogenesis (Drosophila-allocycly-chromosome evolution-male sterility-dosage compensation). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jan;69(1):182–186. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.1.182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MONESI V. RIBONUCLEIC ACID SYNTHESIS DURING MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS IN THE MOUSE TESTIS. J Cell Biol. 1964 Sep;22:521–532. doi: 10.1083/jcb.22.3.521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meistrich M. L., Longtin J., Brock W. A., Grimes S. R., Jr, Mace M. L. Purification of rat spermatogenic cells and preliminary biochemical analysis of these cells. Biol Reprod. 1981 Dec;25(5):1065–1077. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod25.5.1065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meistrich M. L. Separation of spermatogenic cells and nuclei from rodent testes. Methods Cell Biol. 1977;15:15–54. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60207-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monesi V., Geremia R., D'Agostino A., Boitani C. Biochemistry of male germ cell differentiation in mammals: RNA synthesis in meiotic and postmeiotic cells. Curr Top Dev Biol. 1978;12:11–36. doi: 10.1016/s0070-2153(08)60592-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offenberg H. H., Dietrich A. J., Heyting C. Tissue distribution of two major components of synaptonemal complexes of the rat. Chromosoma. 1991 Nov;101(2):83–91. doi: 10.1007/BF00357057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SACHS L. Sex-linkage and the sex chromosomes in man. Ann Eugen. 1954 Jan;18(3):255–261. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1952.tb02515.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel L. M., Monty K. J. Determination of molecular weights and frictional ratios of proteins in impure systems by use of gel filtration and density gradient centrifugation. Application to crude preparations of sulfite and hydroxylamine reductases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Feb 7;112(2):346–362. doi: 10.1016/0926-6585(66)90333-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A., Benavente R. Identification of a structural protein component of rat synaptonemal complexes. Exp Cell Res. 1992 Feb;198(2):291–297. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(92)90382-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solari A. J. The behavior of the XY pair in mammals. Int Rev Cytol. 1974;38(0):273–317. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)60928-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solari A. J. The spatial relationship of the X and Y chromosomes during meiotic prophase in mouse spermatocytes. Chromosoma. 1970;29(2):217–236. doi: 10.1007/BF00326080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solari A. J., Tres L. The localization of nucleic acids and the argentaffin substance in the sex vesicle of mouse spermatocytes. Exp Cell Res. 1967 Aug;47(1):86–96. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(67)90212-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ureña F., Solari A. J. Three dimensional reconstruction of the X-Y pair during pachytene in the rat (Rattus norvegicus). Chromosoma. 1970;30(2):258–268. doi: 10.1007/BF00282005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Wettstein D., Rasmussen S. W., Holm P. B. The synaptonemal complex in genetic segregation. Annu Rev Genet. 1984;18:331–413. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.18.120184.001555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]