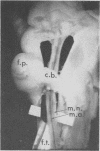
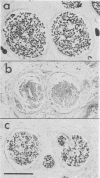
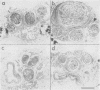
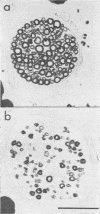
Full text
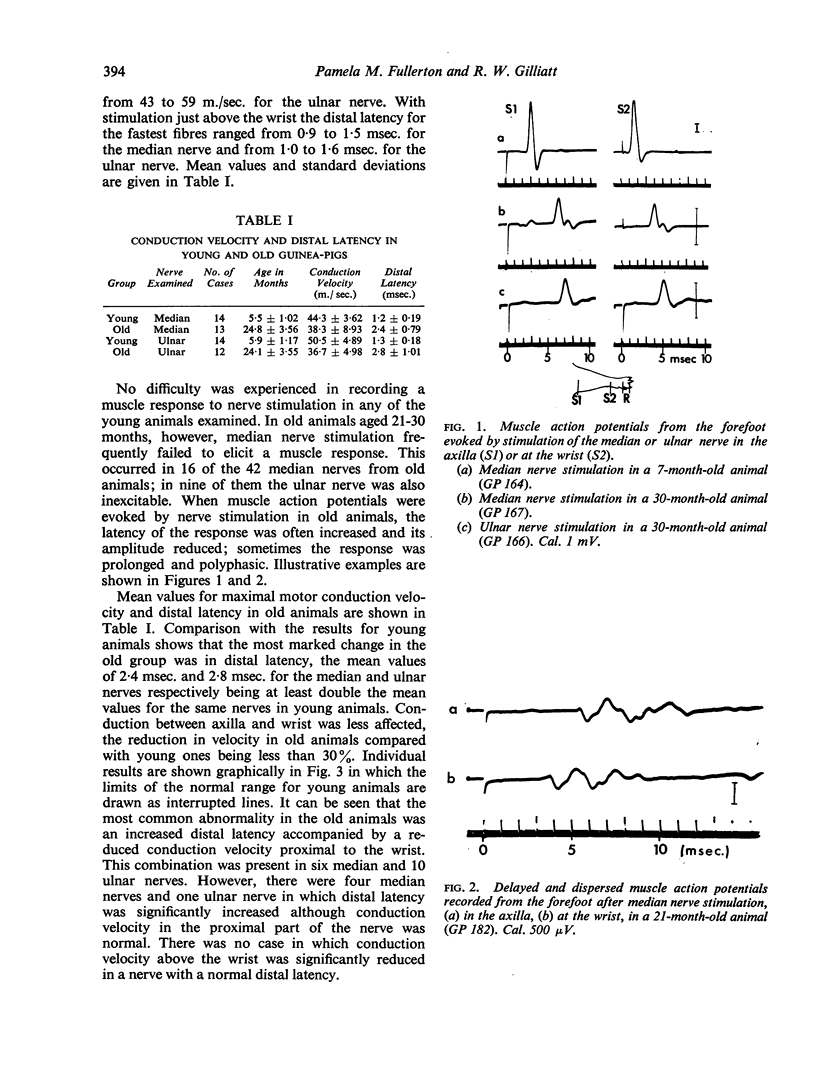
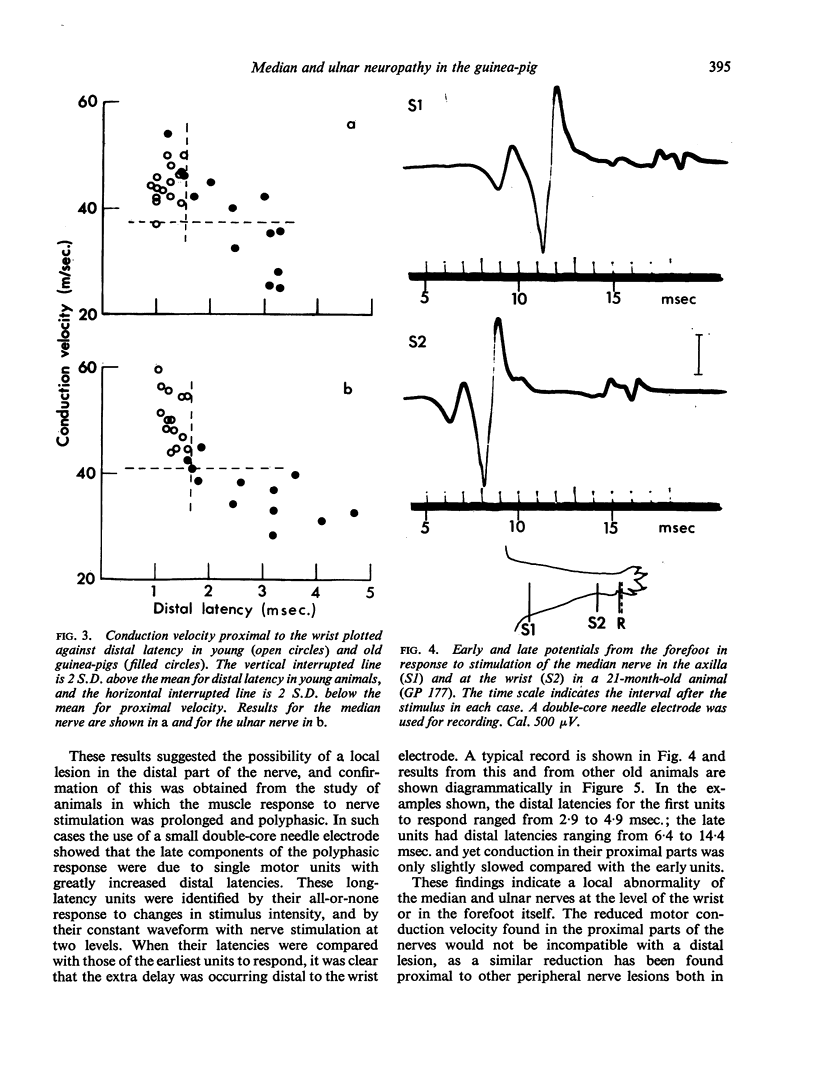
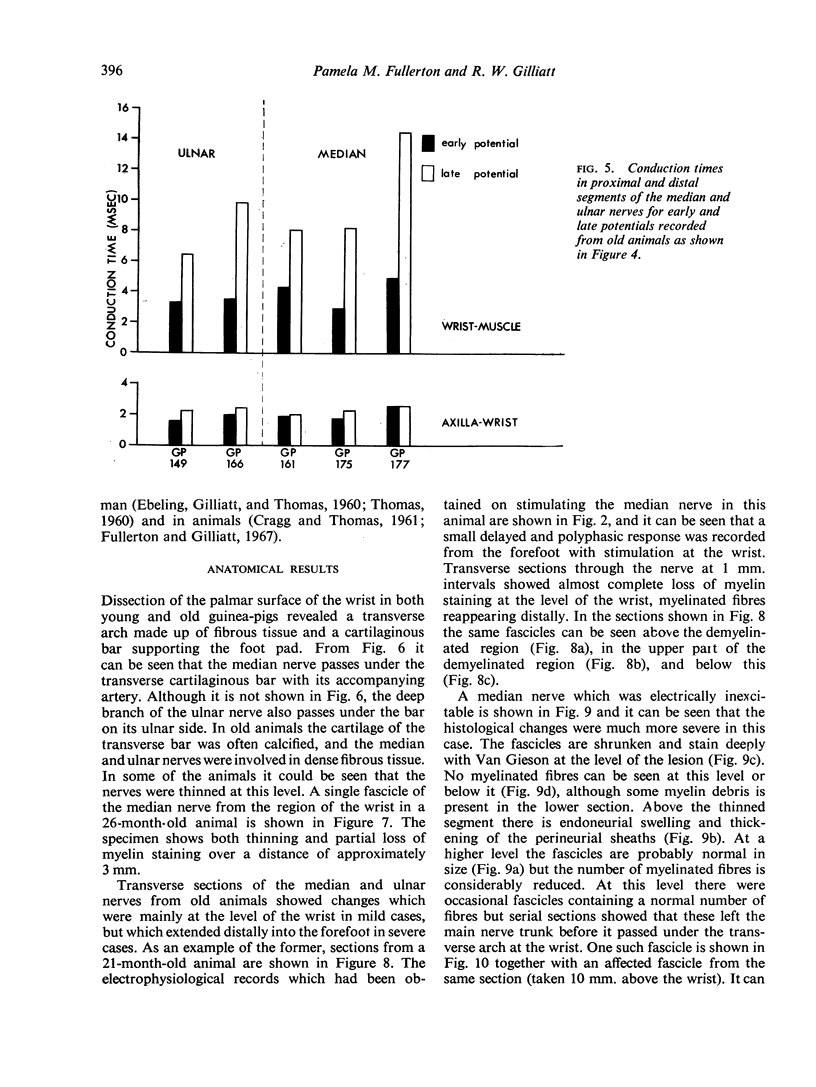
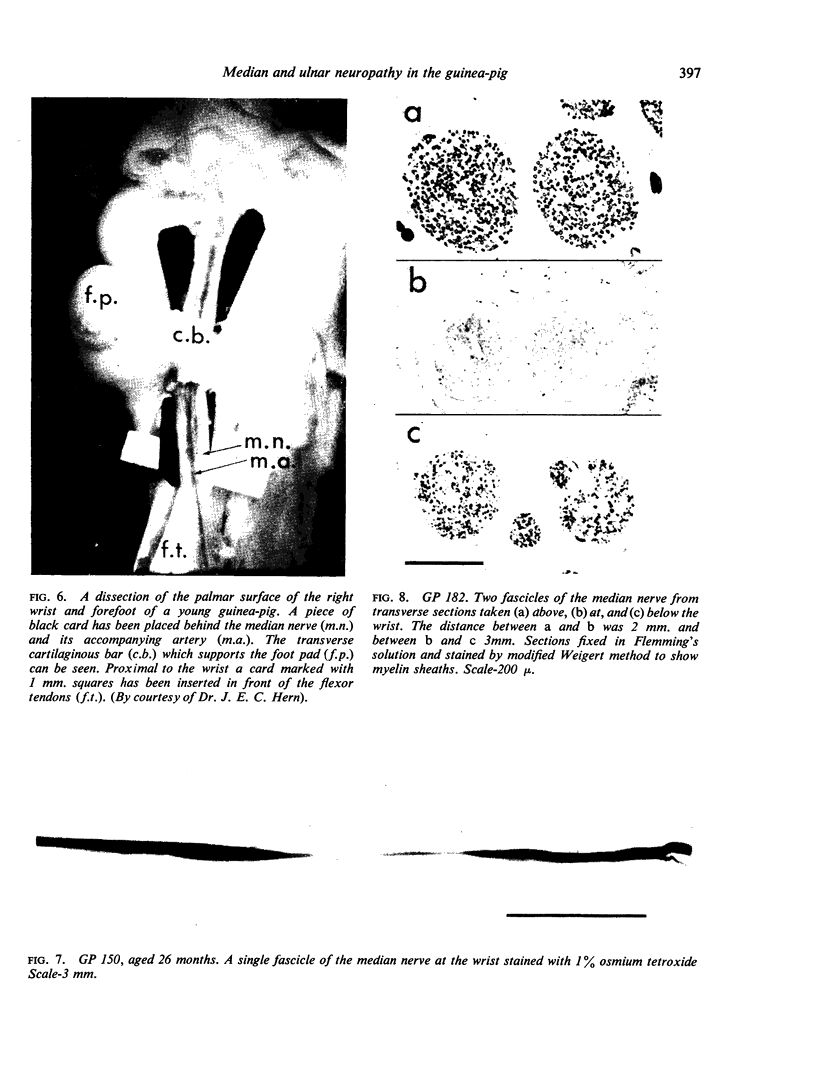
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AITKEN J. T., THOMAS P. K. Retrograde changes in fibre size following nerve section. J Anat. 1962 Jan;96:121–129. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COVELL W. P., ROGERS J. B. Pathologic changes in the inner ears of senile guinea pigs. Laryngoscope. 1957 Feb;67(2):118–129. doi: 10.1288/00005537-195702000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRAGG B. G., THOMAS P. K. Changes in conduction velocity and fibre size proximal to peripheral nerve lesions. J Physiol. 1961 Jul;157:315–327. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006724. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EBELING P., GILLIATT R. W., THOMAS P. K. A clinical and electrical study of ulnar nerve lesions in the hand. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1960 Feb;23:1–9. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.23.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fullerton P. M. Chronic peripheral neuropathy produced by lead poisoning in guinea-pigs. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1966 Apr;25(2):214–236. doi: 10.1097/00005072-196604000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutmann E., Sanders F. K. Recovery of fibre numbers and diameters in the regeneration of peripheral nerves. J Physiol. 1943 Mar 25;101(4):489–518. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1943.sp004002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIRALY J. K., KRNJEVIC K. Some retrograde changes in function of nerves after peripheral section. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1959 Jul;44:244–257. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1959.sp001397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann H. J., Pretschner D. P. Experimentelle Untersuchungen zum Engpasssyndrom peripherer Nerven. Dtsch Z Nervenheilkd. 1966 May 6;188(4):308–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAYER R. F., DENNY-BROWN D. CONDUCTION VELOCITY IN PERIPHERAL NERVE DURING EXPERIMENTAL DEMYELINATION IN THE CAT. Neurology. 1964 Aug;14:714–726. doi: 10.1212/wnl.14.8_part_1.714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCDONALD W. I. THE EFFECTS OF EXPERIMENTAL DEMYELINATION ON CONDUCTION IN PERIPHERAL NERVE: A HISTOLOGICAL AND ELECTROPHYSIOLOGICAL STUDY. II. ELECTROPHYSIOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS. Brain. 1963 Sep;86:501–524. doi: 10.1093/brain/86.3.501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMAS P. K., FULLERTON P. M. NERVE FIBRE SIZE IN THE CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1963 Dec;26:520–527. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.26.6.520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMAS P. K. Growth changes in the myelin sheath of peripheral nerve fibres in fishes. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1955 Mar 15;143(912):380–391. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1955.0018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]